mlflow.pytorch
The mlflow.pytorch module provides an API for logging and loading PyTorch models. This module exports PyTorch models with the following flavors
- PyTorch (native) format
This is the main flavor that can be loaded back into PyTorch.
mlflow.pyfuncProduced for use by generic pyfunc-based deployment tools and batch inference.
- class mlflow.pytorch.MlflowModelCheckpointCallback(monitor='val_loss', mode='min', save_best_only=True, save_weights_only=False, save_freq='epoch')[source]
Bases:
pytorch_lightning.callbacks.callback.Callback,mlflow.utils.checkpoint_utils.MlflowModelCheckpointCallbackBaseCallback for auto-logging pytorch-lightning model checkpoints to MLflow. This callback implementation only supports pytorch-lightning >= 1.6.0.
- 参数
monitor – In automatic model checkpointing, the metric name to monitor if you set model_checkpoint_save_best_only to True.
save_best_only – If True, automatic model checkpointing only saves when the model is considered the “best” model according to the quantity monitored and previous checkpoint model is overwritten.
mode – one of {“min”, “max”}. In automatic model checkpointing, if save_best_only=True, the decision to overwrite the current save file is made based on either the maximization or the minimization of the monitored quantity.
save_weights_only – In automatic model checkpointing, if True, then only the model’s weights will be saved. Otherwise, the optimizer states, lr-scheduler states, etc are added in the checkpoint too.
save_freq – “epoch” or integer. When using “epoch”, the callback saves the model after each epoch. When using integer, the callback saves the model at end of this many batches. Note that if the saving isn’t aligned to epochs, the monitored metric may potentially be less reliable (it could reflect as little as 1 batch, since the metrics get reset every epoch). Defaults to “epoch”.
import mlflow from mlflow.pytorch import MlflowModelCheckpointCallback from pytorch_lightning import Trainer mlflow.pytorch.autolog(checkpoint=True) model = MyLightningModuleNet() # A custom-pytorch lightning model train_loader = create_train_dataset_loader() mlflow_checkpoint_callback = MlflowModelCheckpointCallback() trainer = Trainer(callbacks=[mlflow_checkpoint_callback]) with mlflow.start_run() as run: trainer.fit(model, train_loader)
- on_fit_start(trainer: pytorch_lightning.trainer.trainer.Trainer, pl_module: pytorch_lightning.core.module.LightningModule) None[source]
Called when fit begins.
- on_train_batch_end(trainer: pytorch_lightning.trainer.trainer.Trainer, pl_module: pytorch_lightning.core.module.LightningModule, outputs, batch, batch_idx) None[source]
Called when the train batch ends.
注意
The value
outputs["loss"]here will be the normalized value w.r.taccumulate_grad_batchesof the loss returned fromtraining_step.
- on_train_epoch_end(trainer: pytorch_lightning.trainer.trainer.Trainer, pl_module: pytorch_lightning.core.module.LightningModule) None[source]
Called when the train epoch ends.
To access all batch outputs at the end of the epoch, you can cache step outputs as an attribute of the
pytorch_lightning.core.LightningModuleand access them in this hookclass MyLightningModule(L.LightningModule): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.training_step_outputs = [] def training_step(self): loss = ... self.training_step_outputs.append(loss) return loss class MyCallback(L.Callback): def on_train_epoch_end(self, trainer, pl_module): # do something with all training_step outputs, for example: epoch_mean = torch.stack(pl_module.training_step_outputs).mean() pl_module.log("training_epoch_mean", epoch_mean) # free up the memory pl_module.training_step_outputs.clear()
- save_checkpoint(filepath: str)[source]
- mlflow.pytorch.autolog(log_every_n_epoch=1, log_every_n_step=None, log_models=True, log_datasets=True, disable=False, exclusive=False, disable_for_unsupported_versions=False, silent=False, registered_model_name=None, extra_tags=None, checkpoint=True, checkpoint_monitor='val_loss', checkpoint_mode='min', checkpoint_save_best_only=True, checkpoint_save_weights_only=False, checkpoint_save_freq='epoch', log_model_signatures=True)[source]
注意
Autologging is known to be compatible with the following package versions:
2.1.2<=torch<=2.9.1. Autologging may not succeed when used with package versions outside of this range.Enables (or disables) and configures autologging from PyTorch Lightning to MLflow.
Autologging is performed when you call the fit method of pytorch_lightning.Trainer().
Explore the complete PyTorch MNIST for an expansive example with implementation of additional lightening steps.
Note: Full autologging is only supported for PyTorch Lightning models, i.e., models that subclass pytorch_lightning.LightningModule. Autologging support for vanilla PyTorch (ie models that only subclass torch.nn.Module) only autologs calls to torch.utils.tensorboard.SummaryWriter’s
add_scalarandadd_hparamsmethods to mlflow. In this case, there’s also no notion of an “epoch”.- 参数
log_every_n_epoch – If specified, logs metrics once every n epochs. By default, metrics are logged after every epoch.
log_every_n_step – If specified, logs batch metrics once every n training step. By default, metrics are not logged for steps. Note that setting this to 1 can cause performance issues and is not recommended. Metrics are logged against Lightning’s global step number, and when multiple optimizers are used it is assumed that all optimizers are stepped in each training step.
log_models – If
True, trained models are logged as MLflow model artifacts. IfFalse, trained models are not logged.log_datasets – 如果为
True,则数据集信息将被记录到 MLflow Tracking。如果为False,则不记录数据集信息。disable – If
True, disables the PyTorch Lightning autologging integration. IfFalse, enables the PyTorch Lightning autologging integration.exclusive – 如果为
True,则自动记录的内容不会记录到用户创建的流畅运行中。如果为False,则自动记录的内容将记录到活动的流畅运行中,该运行可能是用户创建的。disable_for_unsupported_versions – If
True, disable autologging for versions of pytorch and pytorch-lightning that have not been tested against this version of the MLflow client or are incompatible.silent – If
True, suppress all event logs and warnings from MLflow during PyTorch Lightning autologging. IfFalse, show all events and warnings during PyTorch Lightning autologging.registered_model_name – If given, each time a model is trained, it is registered as a new model version of the registered model with this name. The registered model is created if it does not already exist.
extra_tags – 要为自动日志记录创建的每个托管运行设置的额外标签的字典。
checkpoint – Enable automatic model checkpointing, this feature only supports pytorch-lightning >= 1.6.0.
checkpoint_monitor – In automatic model checkpointing, the metric name to monitor if you set model_checkpoint_save_best_only to True.
checkpoint_mode – one of {“min”, “max”}. In automatic model checkpointing, if save_best_only=True, the decision to overwrite the current save file is made based on either the maximization or the minimization of the monitored quantity.
checkpoint_save_best_only – If True, automatic model checkpointing only saves when the model is considered the “best” model according to the quantity monitored and previous checkpoint model is overwritten.
checkpoint_save_weights_only – In automatic model checkpointing, if True, then only the model’s weights will be saved. Otherwise, the optimizer states, lr-scheduler states, etc are added in the checkpoint too.
checkpoint_save_freq – “epoch” or integer. When using “epoch”, the callback saves the model after each epoch. When using integer, the callback saves the model at end of this many batches. Note that if the saving isn’t aligned to epochs, the monitored metric may potentially be less reliable (it could reflect as little as 1 batch, since the metrics get reset every epoch). Defaults to “epoch”.
log_model_signatures – Whether to log model signature when log_model is True.
import os import lightning as L import torch from torch.nn import functional as F from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Subset from torchmetrics import Accuracy from torchvision import transforms from torchvision.datasets import MNIST import mlflow.pytorch from mlflow import MlflowClient class MNISTModel(L.LightningModule): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.l1 = torch.nn.Linear(28 * 28, 10) self.accuracy = Accuracy("multiclass", num_classes=10) def forward(self, x): return torch.relu(self.l1(x.view(x.size(0), -1))) def training_step(self, batch, batch_nb): x, y = batch logits = self(x) loss = F.cross_entropy(logits, y) pred = logits.argmax(dim=1) acc = self.accuracy(pred, y) # PyTorch `self.log` will be automatically captured by MLflow. self.log("train_loss", loss, on_epoch=True) self.log("acc", acc, on_epoch=True) return loss def configure_optimizers(self): return torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=0.02) def print_auto_logged_info(r): tags = {k: v for k, v in r.data.tags.items() if not k.startswith("mlflow.")} artifacts = [f.path for f in MlflowClient().list_artifacts(r.info.run_id, "model")] print(f"run_id: {r.info.run_id}") print(f"artifacts: {artifacts}") print(f"params: {r.data.params}") print(f"metrics: {r.data.metrics}") print(f"tags: {tags}") # Initialize our model. mnist_model = MNISTModel() # Load MNIST dataset. train_ds = MNIST( os.getcwd(), train=True, download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor() ) # Only take a subset of the data for faster training. indices = torch.arange(32) train_ds = Subset(train_ds, indices) train_loader = DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=8) # Initialize a trainer. trainer = L.Trainer(max_epochs=3) # Auto log all MLflow entities mlflow.pytorch.autolog() # Train the model. with mlflow.start_run() as run: trainer.fit(mnist_model, train_loader) # Fetch the auto logged parameters and metrics. print_auto_logged_info(mlflow.get_run(run_id=run.info.run_id))
- mlflow.pytorch.get_default_conda_env()[source]
- 返回
The default Conda environment as a dictionary for MLflow Models produced by calls to
save_model()andlog_model().
import mlflow # Log PyTorch model with mlflow.start_run() as run: mlflow.pytorch.log_model(model, name="model", signature=signature) # Fetch the associated conda environment env = mlflow.pytorch.get_default_conda_env() print(f"conda env: {env}")
- mlflow.pytorch.get_default_pip_requirements()[source]
- 返回
A list of default pip requirements for MLflow Models produced by this flavor. Calls to
save_model()andlog_model()produce a pip environment that, at minimum, contains these requirements.
- mlflow.pytorch.load_checkpoint(model_class, run_id=None, epoch=None, global_step=None, kwargs=None)[source]
If you enable “checkpoint” in autologging, during pytorch-lightning model training execution, checkpointed models are logged as MLflow artifacts. Using this API, you can load the checkpointed model.
If you want to load the latest checkpoint, set both epoch and global_step to None. If “checkpoint_save_freq” is set to “epoch” in autologging, you can set epoch param to the epoch of the checkpoint to load specific epoch checkpoint. If “checkpoint_save_freq” is set to an integer in autologging, you can set global_step param to the global step of the checkpoint to load specific global step checkpoint. epoch param and global_step can’t be set together.
- 参数
model_class – The class of the training model, the class should inherit ‘pytorch_lightning.LightningModule’.
run_id – The id of the run which model is logged to. If not provided, current active run is used.
epoch – The epoch of the checkpoint to be loaded, if you set “checkpoint_save_freq” to “epoch”.
global_step – The global step of the checkpoint to be loaded, if you set “checkpoint_save_freq” to an integer.
kwargs – Any extra kwargs needed to init the model.
- 返回
The instance of a pytorch-lightning model restored from the specified checkpoint.
import mlflow mlflow.pytorch.autolog(checkpoint=True) model = MyLightningModuleNet() # A custom-pytorch lightning model train_loader = create_train_dataset_loader() trainer = Trainer() with mlflow.start_run() as run: trainer.fit(model, train_loader) run_id = run.info.run_id # load latest checkpoint model latest_checkpoint_model = mlflow.pytorch.load_checkpoint(MyLightningModuleNet, run_id) # load history checkpoint model logged in second epoch checkpoint_model = mlflow.pytorch.load_checkpoint(MyLightningModuleNet, run_id, epoch=2)
- mlflow.pytorch.load_model(model_uri, dst_path=None, **kwargs)[source]
Load a PyTorch model from a local file or a run.
- 参数
model_uri –
The location, in URI format, of the MLflow model, for example
/Users/me/path/to/local/modelrelative/path/to/local/models3://my_bucket/path/to/modelruns:/<mlflow_run_id>/run-relative/path/to/modelmodels:/<model_name>/<model_version>models:/<model_name>/<stage>
For more information about supported URI schemes, see Referencing Artifacts.
dst_path – The local filesystem path to which to download the model artifact. This directory must already exist. If unspecified, a local output path will be created.
kwargs – kwargs to pass to
torch.loadmethod.
- 返回
A PyTorch model.
import torch import mlflow.pytorch model = nn.Linear(1, 1) # Log the model with mlflow.start_run() as run: mlflow.pytorch.log_model(model, name="model") # Inference after loading the logged model model_uri = f"runs:/{run.info.run_id}/model" loaded_model = mlflow.pytorch.load_model(model_uri) for x in [4.0, 6.0, 30.0]: X = torch.Tensor([[x]]) y_pred = loaded_model(X) print(f"predict X: {x}, y_pred: {y_pred.data.item():.2f}")
- mlflow.pytorch.log_model(pytorch_model, artifact_path: str | None = None, conda_env=None, code_paths=None, pickle_module=None, registered_model_name=None, signature: mlflow.models.signature.ModelSignature = None, input_example: Union[pandas.core.frame.DataFrame, numpy.ndarray, dict, list, csr_matrix, csc_matrix, str, bytes, tuple] = None, await_registration_for=300, extra_files=None, pip_requirements=None, extra_pip_requirements=None, metadata=None, name: str | None = None, params: dict[str, typing.Any] | None = None, tags: dict[str, typing.Any] | None = None, model_type: str | None = None, step: int = 0, model_id: str | None = None, **kwargs)[source]
Log a PyTorch model as an MLflow artifact for the current run.
警告
Log the model with a signature to avoid inference errors. If the model is logged without a signature, the MLflow Model Server relies on the default inferred data type from NumPy. However, PyTorch often expects different defaults, particularly when parsing floats. You must include the signature to ensure that the model is logged with the correct data type so that the MLflow model server can correctly provide valid input.
- 参数
pytorch_model –
PyTorch model to be saved. Can be either an eager model (subclass of
torch.nn.Module) or scripted model prepared viatorch.jit.scriptortorch.jit.trace.The model accept a single
torch.FloatTensoras input and produce a single output tensor.If saving an eager model, any code dependencies of the model’s class, including the class definition itself, should be included in one of the following locations
The package(s) listed in the model’s Conda environment, specified by the
conda_envparameter.One or more of the files specified by the
code_pathsparameter.
artifact_path – Deprecated. Use name instead.
conda_env –
Either a dictionary representation of a Conda environment or the path to a conda environment yaml file. If provided, this describes the environment this model should be run in. At a minimum, it should specify the dependencies contained in get_default_conda_env(). If
None, a conda environment with pip requirements inferred bymlflow.models.infer_pip_requirements()is added to the model. If the requirement inference fails, it falls back to using get_default_pip_requirements. pip requirements fromconda_envare written to a piprequirements.txtfile and the full conda environment is written toconda.yaml. The following is an example dictionary representation of a conda environment{ "name": "mlflow-env", "channels": ["conda-forge"], "dependencies": [ "python=3.8.15", { "pip": [ "torch==x.y.z" ], }, ], }
code_paths –
A list of local filesystem paths to Python file dependencies (or directories containing file dependencies). These files are prepended to the system path when the model is loaded. Files declared as dependencies for a given model should have relative imports declared from a common root path if multiple files are defined with import dependencies between them to avoid import errors when loading the model.
For a detailed explanation of
code_pathsfunctionality, recommended usage patterns and limitations, see the code_paths usage guide.pickle_module – The module that PyTorch should use to serialize (“pickle”) the specified
pytorch_model. This is passed as thepickle_moduleparameter totorch.save(). By default, this module is also used to deserialize (“unpickle”) the PyTorch model at load time.registered_model_name – If given, create a model version under
registered_model_name, also create a registered model if one with the given name does not exist.signature –
一个
ModelSignature类的实例,描述模型的输入和输出。如果未指定signature但提供了input_example,则会根据提供的输入示例和模型自动推断签名。要禁用在提供输入示例时自动推断签名,请将signature设置为False。要手动推断模型签名,请在具有有效模型输入的 数据集(例如,省略目标列的训练数据集)和有效模型输出(例如,在训练数据集上进行的模型预测)上调用infer_signature(),例如from mlflow.models import infer_signature train = df.drop_column("target_label") predictions = ... # compute model predictions signature = infer_signature(train, predictions)
input_example – 一个或多个有效的模型输入实例。输入示例用作要馈送给模型的数据的提示。它将被转换为 Pandas DataFrame,然后使用 Pandas 的面向拆分(split-oriented)格式序列化为 json,或者转换为 numpy 数组,其中示例将通过转换为列表来序列化为 json。字节将进行 base64 编码。当
signature参数为None时,输入示例用于推断模型签名。await_registration_for – 等待模型版本完成创建并处于
READY状态的秒数。默认情况下,函数等待五分钟。指定 0 或 None 可跳过等待。extra_files –
包含相应额外文件的路径的列表,如果为
None,则不会将额外文件添加到模型中。远程 URI 将解析为绝对文件系统路径。例如,考虑以下extra_files列表extra_files = ["s3://my-bucket/path/to/my_file1", "s3://my-bucket/path/to/my_file2"]
在这种情况下,
"my_file1 & my_file2"额外文件将从 S3 下载。pip_requirements – 可以是 pip requirement 字符串的可迭代对象(例如
["torch", "-r requirements.txt", "-c constraints.txt"])或本地文件系统上的 pip requirements 文件的字符串路径(例如"requirements.txt")。如果提供,这将描述模型应运行的环境。如果为None,则mlflow.models.infer_pip_requirements()会从当前软件环境中推断默认的 requirements 列表。如果 requirements 推断失败,则会回退到使用 get_default_pip_requirements。requirements 和 constraints 都会被自动解析并分别写入requirements.txt和constraints.txt文件,并作为模型的一部分存储。requirements 也会被写入模型 conda 环境(conda.yaml)文件的pip部分。extra_pip_requirements –
可以是 pip requirement 字符串的可迭代对象(例如
["pandas", "-r requirements.txt", "-c constraints.txt"])或本地文件系统上的 pip requirements 文件的字符串路径(例如"requirements.txt")。如果提供,这将描述附加到根据用户当前软件环境自动生成的默认 pip requirements 集的额外 pip requirements。requirements 和 constraints 都会被自动解析并分别写入requirements.txt和constraints.txt文件,并作为模型的一部分存储。requirements 也会被写入模型 conda 环境(conda.yaml)文件的pip部分。警告
以下参数不能同时指定
conda_envpip_requirementsextra_pip_requirements
此示例演示了如何使用
pip_requirements和extra_pip_requirements指定 pip requirements。metadata – 传递给模型并存储在 MLmodel 文件中的自定义元数据字典。
name – 模型名称。
params – 要与模型一起记录的参数字典。
tags – 要与模型一起记录的标签字典。
model_type – 模型的类型。
step – 记录模型输出和指标的步骤
model_id – 模型的 ID。
kwargs – 要传递给
torch.save方法的 kwargs。
- 返回
一个
ModelInfo实例,其中包含已记录模型的元数据。
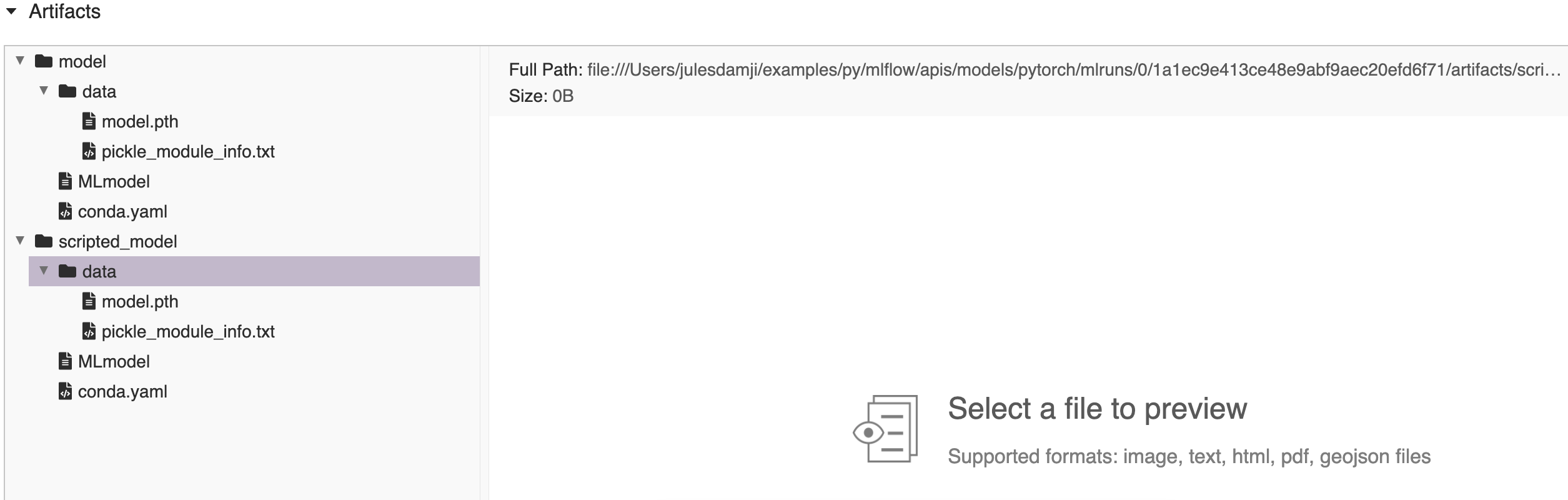
import numpy as np import torch import mlflow from mlflow import MlflowClient from mlflow.models import infer_signature # Define model, loss, and optimizer model = nn.Linear(1, 1) criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss() optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.001) # Create training data with relationship y = 2X X = torch.arange(1.0, 26.0).reshape(-1, 1) y = X * 2 # Training loop epochs = 250 for epoch in range(epochs): # Forward pass: Compute predicted y by passing X to the model y_pred = model(X) # Compute the loss loss = criterion(y_pred, y) # Zero gradients, perform a backward pass, and update the weights. optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() optimizer.step() # Create model signature signature = infer_signature(X.numpy(), model(X).detach().numpy()) # Log the model with mlflow.start_run() as run: mlflow.pytorch.log_model(model, name="model") # convert to scripted model and log the model scripted_pytorch_model = torch.jit.script(model) mlflow.pytorch.log_model(scripted_pytorch_model, name="scripted_model") # Fetch the logged model artifacts print(f"run_id: {run.info.run_id}") for artifact_path in ["model/data", "scripted_model/data"]: artifacts = [ f.path for f in MlflowClient().list_artifacts(run.info.run_id, artifact_path) ] print(f"artifacts: {artifacts}")
run_id: 1a1ec9e413ce48e9abf9aec20efd6f71 artifacts: ['model/data/model.pth', 'model/data/pickle_module_info.txt'] artifacts: ['scripted_model/data/model.pth', 'scripted_model/data/pickle_module_info.txt']
- mlflow.pytorch.save_model(pytorch_model, path, conda_env=None, mlflow_model=None, code_paths=None, pickle_module=None, signature: mlflow.models.signature.ModelSignature = None, input_example: Union[pandas.core.frame.DataFrame, numpy.ndarray, dict, list, csr_matrix, csc_matrix, str, bytes, tuple] = None, extra_files=None, pip_requirements=None, extra_pip_requirements=None, metadata=None, **kwargs)[source]
将 PyTorch 模型保存到本地文件系统上的一个路径。
- 参数
pytorch_model –
要保存的 PyTorch 模型。可以是 eager 模型(
torch.nn.Module的子类)或通过torch.jit.script或torch.jit.trace准备的已脚本化模型。要保存 eager 模型,模型类的任何代码依赖项,包括类定义本身,都应包含在以下位置之一:
The package(s) listed in the model’s Conda environment, specified by the
conda_envparameter.One or more of the files specified by the
code_pathsparameter.
path – 要保存模型的本地路径。
conda_env –
Either a dictionary representation of a Conda environment or the path to a conda environment yaml file. If provided, this describes the environment this model should be run in. At a minimum, it should specify the dependencies contained in get_default_conda_env(). If
None, a conda environment with pip requirements inferred bymlflow.models.infer_pip_requirements()is added to the model. If the requirement inference fails, it falls back to using get_default_pip_requirements. pip requirements fromconda_envare written to a piprequirements.txtfile and the full conda environment is written toconda.yaml. The following is an example dictionary representation of a conda environment{ "name": "mlflow-env", "channels": ["conda-forge"], "dependencies": [ "python=3.8.15", { "pip": [ "torch==x.y.z" ], }, ], }
mlflow_model – 要添加此 flavor 的
mlflow.models.Model。code_paths –
A list of local filesystem paths to Python file dependencies (or directories containing file dependencies). These files are prepended to the system path when the model is loaded. Files declared as dependencies for a given model should have relative imports declared from a common root path if multiple files are defined with import dependencies between them to avoid import errors when loading the model.
For a detailed explanation of
code_pathsfunctionality, recommended usage patterns and limitations, see the code_paths usage guide.pickle_module – PyTorch 应使用哪个模块来序列化(“pickle”)指定的
pytorch_model。此参数将作为pickle_module参数传递给torch.save()。默认情况下,此模块还在加载时用于反序列化(“unpickle”)模型。signature –
一个
ModelSignature类的实例,描述模型的输入和输出。如果未指定signature但提供了input_example,则会根据提供的输入示例和模型自动推断签名。要禁用在提供输入示例时自动推断签名,请将signature设置为False。要手动推断模型签名,请在具有有效模型输入的 数据集(例如,省略目标列的训练数据集)和有效模型输出(例如,在训练数据集上进行的模型预测)上调用infer_signature(),例如from mlflow.models import infer_signature train = df.drop_column("target_label") predictions = ... # compute model predictions signature = infer_signature(train, predictions)
input_example – 一个或多个有效的模型输入实例。输入示例用作要馈送给模型的数据的提示。它将被转换为 Pandas DataFrame,然后使用 Pandas 的面向拆分(split-oriented)格式序列化为 json,或者转换为 numpy 数组,其中示例将通过转换为列表来序列化为 json。字节将进行 base64 编码。当
signature参数为None时,输入示例用于推断模型签名。extra_files –
包含相应额外文件的路径的列表。远程 URI 将解析为绝对文件系统路径。例如,考虑以下
extra_files列表 -extra_files = [“s3://my-bucket/path/to/my_file1”, “s3://my-bucket/path/to/my_file2”]
在这种情况下,
"my_file1 & my_file2"额外文件将从 S3 下载。如果为
None,则不会将额外文件添加到模型中。pip_requirements – 可以是 pip requirement 字符串的可迭代对象(例如
["torch", "-r requirements.txt", "-c constraints.txt"])或本地文件系统上的 pip requirements 文件的字符串路径(例如"requirements.txt")。如果提供,这将描述模型应运行的环境。如果为None,则mlflow.models.infer_pip_requirements()会从当前软件环境中推断默认的 requirements 列表。如果 requirements 推断失败,则会回退到使用 get_default_pip_requirements。requirements 和 constraints 都会被自动解析并分别写入requirements.txt和constraints.txt文件,并作为模型的一部分存储。requirements 也会被写入模型 conda 环境(conda.yaml)文件的pip部分。extra_pip_requirements –
可以是 pip requirement 字符串的可迭代对象(例如
["pandas", "-r requirements.txt", "-c constraints.txt"])或本地文件系统上的 pip requirements 文件的字符串路径(例如"requirements.txt")。如果提供,这将描述附加到根据用户当前软件环境自动生成的默认 pip requirements 集的额外 pip requirements。requirements 和 constraints 都会被自动解析并分别写入requirements.txt和constraints.txt文件,并作为模型的一部分存储。requirements 也会被写入模型 conda 环境(conda.yaml)文件的pip部分。警告
以下参数不能同时指定
conda_envpip_requirementsextra_pip_requirements
此示例演示了如何使用
pip_requirements和extra_pip_requirements指定 pip requirements。metadata – 传递给模型并存储在 MLmodel 文件中的自定义元数据字典。
kwargs – 要传递给
torch.save方法的 kwargs。
import os import mlflow import torch model = nn.Linear(1, 1) # Save PyTorch models to current working directory with mlflow.start_run() as run: mlflow.pytorch.save_model(model, "model") # Convert to a scripted model and save it scripted_pytorch_model = torch.jit.script(model) mlflow.pytorch.save_model(scripted_pytorch_model, "scripted_model") # Load each saved model for inference for model_path in ["model", "scripted_model"]: model_uri = f"{os.getcwd()}/{model_path}" loaded_model = mlflow.pytorch.load_model(model_uri) print(f"Loaded {model_path}:") for x in [6.0, 8.0, 12.0, 30.0]: X = torch.Tensor([[x]]) y_pred = loaded_model(X) print(f"predict X: {x}, y_pred: {y_pred.data.item():.2f}") print("--")