MLflow LLM 评估(旧版)
MLflow 3 引入了一个新的 LLM/GenAI 评估套件。这个新套件仅在 Databricks 上的托管 MLflow 中可用,但即将推出到 OSS MLflow。如果您有兴趣通过免费的 Databricks 试用版进行尝试,请单击此处了解更多信息。
随着 ChatGPT 的兴起,LLM 在问答、翻译和文本摘要等各个领域都展现了其文本生成能力。评估 LLM 的性能与评估传统 ML 模型略有不同,因为通常没有单一的正确答案可以进行比较。MLflow 提供了一个 API mlflow.evaluate() 来帮助评估您的 LLM。
MLflow 的 LLM 评估功能包含 3 个主要组件
- 待评估的模型:它可以是 MLflow
pyfunc模型、指向已注册 MLflow 模型的 URI,或者代表您模型的任何 Python 可调用对象,例如 HuggingFace 文本摘要管道。 - 指标:需要计算的指标,LLM 评估将使用 LLM 指标。
- 评估数据:模型将在此数据上进行评估,它可以是 pandas Dataframe、Python 列表、numpy 数组或
mlflow.data.dataset.Dataset()实例。
快速入门
下面是一个简单的示例,概述了 MLflow LLM 评估的工作原理。该示例通过包装“openai/gpt-4”和自定义提示来构建一个简单的问答模型。您可以将其粘贴到您的 IPython 或本地编辑器中并执行,并在提示时安装缺少的依赖项。运行代码需要 OpenAI API 密钥,如果您没有 OpenAI 密钥,可以按照OpenAI 指南进行设置。
export OPENAI_API_KEY='your-api-key-here'
import mlflow
import openai
import os
import pandas as pd
from getpass import getpass
eval_data = pd.DataFrame(
{
"inputs": [
"What is MLflow?",
"What is Spark?",
],
"ground_truth": [
"MLflow is an open-source platform for managing the end-to-end machine learning (ML) "
"lifecycle. It was developed by Databricks, a company that specializes in big data and "
"machine learning solutions. MLflow is designed to address the challenges that data "
"scientists and machine learning engineers face when developing, training, and deploying "
"machine learning models.",
"Apache Spark is an open-source, distributed computing system designed for big data "
"processing and analytics. It was developed in response to limitations of the Hadoop "
"MapReduce computing model, offering improvements in speed and ease of use. Spark "
"provides libraries for various tasks such as data ingestion, processing, and analysis "
"through its components like Spark SQL for structured data, Spark Streaming for "
"real-time data processing, and MLlib for machine learning tasks",
],
}
)
with mlflow.start_run() as run:
system_prompt = "Answer the following question in two sentences"
# Wrap "gpt-4" as an MLflow model.
logged_model_info = mlflow.openai.log_model(
model="gpt-4",
task=openai.chat.completions,
name="model",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": "{question}"},
],
)
# Use predefined question-answering metrics to evaluate our model.
results = mlflow.evaluate(
logged_model_info.model_uri,
eval_data,
targets="ground_truth",
model_type="question-answering",
)
print(f"See aggregated evaluation results below: \n{results.metrics}")
# Evaluation result for each data record is available in `results.tables`.
eval_table = results.tables["eval_results_table"]
print(f"See evaluation table below: \n{eval_table}")
LLM 评估指标
MLflow 中有两种类型的 LLM 评估指标
-
基于启发式方法的指标:这些指标基于特定函数为每个数据记录(Pandas/Spark 数据帧中的行)计算分数,例如:Rouge (
mlflow.metrics.rougeL())、Flesch Kincaid (mlflow.metrics.flesch_kincaid_grade_level()) 或 Bilingual Evaluation Understudy (BLEU) (mlflow.metrics.bleu())。这些指标类似于传统的连续值指标。有关内置启发式指标列表以及如何定义具有自定义函数定义的指标,请参阅基于启发式方法的指标部分。 -
LLM 作为法官(LLM-as-a-Judge)的指标:LLM 作为法官是一种新型指标,它使用 LLM 对模型输出的质量进行评分。它克服了基于启发式方法的指标的局限性,这些指标常常忽略上下文和语义准确性等细微差别。LLM 作为法官的指标为复杂的语言任务提供了更接近人类的评估,同时比人工评估更具可扩展性和成本效益。MLflow 提供了各种内置的 LLM 作为法官的指标,并支持使用自定义提示、评分标准和示例来创建自定义指标。有关更多详细信息,请参阅LLM 作为法官的指标部分。
基于启发式方法的指标
内置启发式指标
有关内置启发式指标的完整列表,请参阅此页面。
预定义模型类型的默认指标
MLflow LLM 评估包含预选任务(例如,“问答”)的默认指标集合。根据您正在评估的 LLM 用例,这些预定义集合可以大大简化评估过程。要使用预选任务的默认指标,请在 mlflow.evaluate() 中指定 model_type 参数,如下面的示例所示
results = mlflow.evaluate(
model,
eval_data,
targets="ground_truth",
model_type="question-answering",
)
以下列出了支持的 LLM 模型类型和相关指标
-
问答:
model_type="question-answering"- 精确匹配
- 毒性 [1]
- ari_grade_level [2]
- flesch_kincaid_grade_level [2]
-
文本摘要:
model_type="text-summarization"- ROUGE [3]
- 毒性 [1]
- ari_grade_level [2]
- flesch_kincaid_grade_level [2]
-
文本模型:
model_type="text"- 毒性 [1]
- ari_grade_level [2]
- flesch_kincaid_grade_level [2]
-
检索器:
model_type="retriever"- precision_at_k [4]
- recall_at_k [4]
- ndcg_at_k [4]
[1] 需要 evaluate、torch 和 transformers 包
[2] 需要 textstat 包
[3] 需要 evaluate、nltk 和 rouge-score <https://pypi.ac.cn/project/rouge-score>_ 包
[4] 所有检索器指标都有一个默认的 retriever_k 值 3,可以通过在 evaluator_config 参数中指定 retriever_k 来覆盖。
使用自定义指标列表
使用给定模型类型关联的预定义指标并不是在 MLflow 中生成 LLM 评估评分指标的唯一方法。您可以在 mlflow.evaluate 的 extra_metrics 参数中指定一个自定义指标列表
-
要向预定义模型类型的默认指标列表添加额外指标,请保留
model_type并将您的指标添加到extra_metrics。results = mlflow.evaluate(
model,
eval_data,
targets="ground_truth",
model_type="question-answering",
extra_metrics=[mlflow.metrics.latency()],
)上面的代码将使用“问答”模型的所有指标以及
mlflow.metrics.latency()来评估您的模型。 -
要禁用默认指标计算并仅计算您选择的指标,请删除
model_type参数并定义所需的指标。results = mlflow.evaluate(
model,
eval_data,
targets="ground_truth",
extra_metrics=[mlflow.metrics.toxicity(), mlflow.metrics.latency()],
)
支持的评估指标的完整参考可以在此处找到。
创建自定义基于启发式方法的 LLM 评估指标
这与创建自定义传统指标非常相似,不同之处在于返回 mlflow.metrics.MetricValue() 实例。基本上,您需要
- 实现一个
eval_fn来定义您的评分逻辑。此函数必须接受 2 个参数:predictions和target。eval_fn必须返回一个mlflow.metrics.MetricValue()实例。 - 将
eval_fn和其他参数传递给mlflow.metrics.make_metricAPI 来创建指标。
以下代码创建一个名为 "over_10_chars" 的虚拟每行指标;如果模型输出大于 10 个字符,则得分为“是”,否则为“否”。
def eval_fn(predictions, targets):
scores = ["yes" if len(pred) > 10 else "no" for pred in predictions]
return MetricValue(
scores=scores,
aggregate_results=standard_aggregations(scores),
)
# Create an EvaluationMetric object.
passing_code_metric = make_metric(
eval_fn=eval_fn, greater_is_better=False, name="over_10_chars"
)
要创建依赖于其他指标的自定义指标,请将其他指标的名称作为参数包含在 predictions 和 targets 之后。这可以是内置指标的名称,也可以是另一个自定义指标的名称。确保您没有不小心造成指标之间的循环依赖,否则评估将会失败。
以下代码创建一个名为 "toxic_or_over_10_chars" 的虚拟每行指标:如果模型输出大于 10 个字符或毒性分数大于 0.5,则得分为“是”,否则为“否”。
def eval_fn(predictions, targets, toxicity, over_10_chars):
scores = [
"yes" if toxicity.scores[i] > 0.5 or over_10_chars.scores[i] else "no"
for i in len(toxicity.scores)
]
return MetricValue(scores=scores)
# Create an EvaluationMetric object.
toxic_and_over_10_chars_metric = make_metric(
eval_fn=eval_fn, greater_is_better=False, name="toxic_or_over_10_chars"
)
LLM 作为法官(LLM-as-a-Judge)的指标
LLM 作为法官是一种新型指标,它使用 LLM 对模型输出的质量进行评分,为复杂的语言任务提供更接近人类的评估,同时比人工评估更具可扩展性和成本效益。
MLflow 支持几种内置的 LLM 作为法官的指标,同时也允许您使用自定义配置和提示来创建自己的 LLM 作为法官的指标。
内置 LLM 作为法官的指标
要在 MLflow 中使用内置的 LLM 作为法官的指标,请将指标定义列表传递给 mlflow.evaluate() 函数的 extra_metrics 参数。
下面的示例除了延迟指标(启发式)之外,还使用了内置的答案正确性指标进行评估。
from mlflow.metrics import latency
from mlflow.metrics.genai import answer_correctness
results = mlflow.evaluate(
eval_data,
targets="ground_truth",
extra_metrics=[
answer_correctness(),
latency(),
],
)
以下是内置 LLM 作为法官的指标列表。单击链接可查看每个指标的完整文档
mlflow.metrics.genai.answer_similarity():评估模型生成的输出与正确答案数据中的信息有多相似。mlflow.metrics.genai.answer_correctness():根据正确答案数据中的信息,评估模型生成的输出在事实上的正确性。mlflow.metrics.genai.answer_relevance():评估模型生成的输出与输入的相关性(忽略上下文)。mlflow.metrics.genai.relevance():评估模型生成的输出与输入和上下文的相关性。mlflow.metrics.genai.faithfulness():评估模型生成的输出在给定上下文中的忠实度。
选择法官模型
默认情况下,MLflow 将使用 OpenAI 的 GPT-4 模型作为评分指标的法官模型。您可以通过在指标定义内的 model 参数中传递一个覆盖值来更改法官模型。
1. SaaS LLM 提供商
要使用 OpenAI 或 Anthropic 等 SaaS LLM 提供商,请在指标定义中设置 model 参数,格式为 <provider>:/<model-name>。目前,MLflow 支持 ["openai", "anthropic", "bedrock", "mistral", "togetherai"] 作为任何法官模型的可行 LLM 提供商。
- OpenAI / Azure OpenAI
- Anthropic
- Bedrock
- Mistral
- TogetherAI
可以通过 openai:/<model-name> URI 访问 OpenAI 模型。
import mlflow
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "<your-openai-api-key>"
answer_correctness = mlflow.metrics.genai.answer_correctness(model="openai:/gpt-4o")
# Test the metric definition
answer_correctness(
inputs="What is MLflow?",
predictions="MLflow is an innovative full self-driving airship.",
targets="MLflow is an open-source platform for managing the end-to-end ML lifecycle.",
)
可以通过相同的 openai:/<model-name> URI 访问 Azure OpenAI 端点,方法是设置环境变量,例如 OPENAI_API_BASE、OPENAI_API_TYPE 等。
os.environ["OPENAI_API_TYPE"] = "azure"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_BASE"] = "https:/my-azure-openai-endpoint.azure.com/"
os.environ["OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT_NAME"] = "gpt-4o-mini"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_VERSION"] = "2024-08-01-preview"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "<your-api-key-for-azure-openai-endpoint>"
可以通过 anthropic:/<model-name> URI 访问 Anthropic 模型。请注意,需要通过向指标定义传递 parameters 参数来覆盖 默认法官参数 <#overriding-default-judge-parameters>,因为默认参数违反了 Anthropic 端点的要求(temperature 和 top_p 不能同时指定)。
import mlflow
import os
os.environ["ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"] = "<your-anthropic-api-key>"
answer_correctness = mlflow.metrics.genai.answer_correctness(
model="anthropic:/claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022",
# Override default judge parameters to meet Claude endpoint requirements.
parameters={"temperature": 0, "max_tokens": 256},
)
# Test the metric definition
answer_correctness(
inputs="What is MLflow?",
predictions="MLflow is an innovative full self-driving airship.",
targets="MLflow is an open-source platform for managing the end-to-end ML lifecycle.",
)
可以通过 bedrock:/<model-name> URI 访问 Bedrock 模型。请确保您已通过环境变量设置了身份验证信息。您可以同时使用基于角色的身份验证或基于 API 密钥的身份验证来访问 Bedrock 模型。
import mlflow
import os
os.environ["AWS_REGION"] = "<your-aws-region>"
# Option 1. Role-based authentication
os.environ["AWS_ROLE_ARN"] = "<your-aws-role-arn>"
# Option 2. API key-based authentication
os.environ["AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"] = "<your-aws-access-key-id>"
os.environ["AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY"] = "<your-aws-secret-access-key>"
# You can also use session token for temporary credentials.
# os.environ["AWS_SESSION_TOKEN"] = "<your-aws-session-token>"
answer_correctness = mlflow.metrics.genai.answer_correctness(
model="bedrock:/anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022-v2:0",
parameters={
"temperature": 0,
"max_tokens": 256,
"anthropic_version": "bedrock-2023-05-31",
},
)
# Test the metric definition
answer_correctness(
inputs="What is MLflow?",
predictions="MLflow is an innovative full self-driving airship.",
targets="MLflow is an open-source platform for managing the end-to-end ML lifecycle.",
)
可以通过 mistral:/<model-name> URI 访问 Mistral 模型。
import mlflow
import os
os.environ["MISTRAL_API_KEY"] = "<your-mistral-api-key>"
answer_correctness = mlflow.metrics.genai.answer_correctness(
model="mistral:/mistral-small-latest",
)
# Test the metric definition
answer_correctness(
inputs="What is MLflow?",
predictions="MLflow is an innovative full self-driving airship.",
targets="MLflow is an open-source platform for managing the end-to-end ML lifecycle.",
)
可以通过 togetherai:/<model-name> URI 访问 TogetherAI 模型。
import mlflow
import os
os.environ["TOGETHERAI_API_KEY"] = "<your-togetherai-api-key>"
answer_correctness = mlflow.metrics.genai.answer_correctness(
model="togetherai:/togetherai-small-latest",
)
# Test the metric definition
answer_correctness(
inputs="What is MLflow?",
predictions="MLflow is an innovative full self-driving airship.",
targets="MLflow is an open-source platform for managing the end-to-end ML lifecycle.",
)
您使用第三方 LLM 服务(例如 OpenAI)进行评估可能会受到 LLM 服务使用条款的约束和管辖。
2. 自托管代理端点
如果您通过代理端点(例如,出于安全合规性)访问 SaaS LLM 提供商,可以在指标定义中设置 proxy_url 参数。此外,使用 extra_headers 参数来传递用于身份验证的端点的额外标头。
answer_similarity = mlflow.metrics.genai.answer_similarity(
model="openai:/gpt-4o",
proxy_url="https://my-proxy-endpoint/chat",
extra_headers={"Group-ID": "my-group-id"},
)
3. MLflow AI 网关端点
MLflow AI 网关是一个自托管解决方案,允许您通过统一的界面查询各种 LLM 提供商。要使用 MLflow AI 网关托管的端点
- 按照这些步骤使用您的 LLM 设置启动 MLflow AI 网关服务器。
- 使用 :py:func:
~mlflow.deployments.set_deployments_target()将 MLflow 部署客户端设置为目标服务器地址。 - 在指标定义中将
endpoints:/<endpoint-name>设置为model参数。
from mlflow.deployments import set_deployments_target
# When the MLflow AI Gateway server is running at https://:5000
set_deployments_target("https://:5000")
my_answer_similarity = mlflow.metrics.genai.answer_similarity(
model="endpoints:/my-endpoint"
)
4. Databricks 模型服务
如果您有一个托管在 Databricks 上的模型,可以通过将 endpoints:/<endpoint-name> 设置为指标定义中的 model 参数来将其用作法官模型。以下代码使用了通过基础模型 API 可用的 Llama 3.1 405B 模型。
from mlflow.deployments import set_deployments_target
set_deployments_target("databricks")
llama3_answer_similarity = mlflow.metrics.genai.answer_similarity(
model="endpoints:/databricks-llama-3-1-405b-instruct"
)
覆盖默认法官参数
默认情况下,MLflow 使用以下参数查询法官 LLM 模型
temperature: 0.0
max_tokens: 200
top_p: 1.0
但是,这可能不适用于所有 LLM 提供商。例如,在 Amazon Bedrock 上访问 Anthropic 的 Claude 模型需要在请求载荷中指定 anthropic_version 参数。您可以通过向指标定义传递 parameters 参数来覆盖这些默认参数。
my_answer_similarity = mlflow.metrics.genai.answer_similarity(
model="bedrock:/anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022-v2:0",
parameters={
"temperature": 0,
"max_tokens": 256,
"anthropic_version": "bedrock-2023-05-31",
},
)
请注意,您在 parameters 参数中传递的参数字典将替换默认参数,而不是与之合并。例如,在上面的代码示例中,top_p不会发送到模型。
创建自定义 LLM 作为法官的指标
您还可以使用 mlflow.metrics.genai.make_genai_metric() API 创建自己的 LLM 作为法官的评估指标,该 API 需要以下信息
name:您的自定义指标的名称。definition:描述指标的作用。grading_prompt:描述评分标准。examples(可选):一些带有分数的输入/输出示例;用作 LLM 法官的参考。
有关配置的完整列表,请参阅API 文档。
在底层,definition、grading_prompt、examples 以及评估数据和模型输出将组合成一个长提示并发送给 LLM。如果您熟悉提示工程的概念,SaaS LLM 评估指标基本上是在尝试组合一个包含指令、数据和模型输出的“正确”提示,以便 LLM(例如 GPT4)可以输出我们想要的信息。
现在,让我们创建一个名为“专业性”的自定义 GenAI 指标,该指标衡量我们的模型输出的专业程度。
让我们首先创建一些带有分数的示例,这些将是 LLM 法官使用的参考样本。要创建这样的示例,我们将使用 mlflow.metrics.genai.EvaluationExample() 类,该类有 4 个字段
input:输入文本。output:输出文本。score:在输入上下文中输出的分数。justification:为什么我们为数据提供score。
professionalism_example_score_2 = mlflow.metrics.genai.EvaluationExample(
input="What is MLflow?",
output=(
"MLflow is like your friendly neighborhood toolkit for managing your machine learning projects. It helps "
"you track experiments, package your code and models, and collaborate with your team, making the whole ML "
"workflow smoother. It's like your Swiss Army knife for machine learning!"
),
score=2,
justification=(
"The response is written in a casual tone. It uses contractions, filler words such as 'like', and "
"exclamation points, which make it sound less professional. "
),
)
professionalism_example_score_4 = mlflow.metrics.genai.EvaluationExample(
input="What is MLflow?",
output=(
"MLflow is an open-source platform for managing the end-to-end machine learning (ML) lifecycle. It was "
"developed by Databricks, a company that specializes in big data and machine learning solutions. MLflow is "
"designed to address the challenges that data scientists and machine learning engineers face when "
"developing, training, and deploying machine learning models.",
),
score=4,
justification=("The response is written in a formal language and a neutral tone. "),
)
现在让我们定义 professionalism 指标,您将看到每个字段是如何设置的。
professionalism = mlflow.metrics.genai.make_genai_metric(
name="professionalism",
definition=(
"Professionalism refers to the use of a formal, respectful, and appropriate style of communication that is "
"tailored to the context and audience. It often involves avoiding overly casual language, slang, or "
"colloquialisms, and instead using clear, concise, and respectful language."
),
grading_prompt=(
"Professionalism: If the answer is written using a professional tone, below are the details for different scores: "
"- Score 0: Language is extremely casual, informal, and may include slang or colloquialisms. Not suitable for "
"professional contexts."
"- Score 1: Language is casual but generally respectful and avoids strong informality or slang. Acceptable in "
"some informal professional settings."
"- Score 2: Language is overall formal but still have casual words/phrases. Borderline for professional contexts."
"- Score 3: Language is balanced and avoids extreme informality or formality. Suitable for most professional contexts. "
"- Score 4: Language is noticeably formal, respectful, and avoids casual elements. Appropriate for formal "
"business or academic settings. "
),
examples=[professionalism_example_score_2, professionalism_example_score_4],
model="openai:/gpt-4o-mini",
parameters={"temperature": 0.0},
aggregations=["mean", "variance"],
greater_is_better=True,
)
准备您的目标模型
为了使用 mlflow.evaluate() 评估您的模型,您的模型必须是以下类型之一
-
一个
mlflow.pyfunc.PyFuncModel()实例或指向已记录的mlflow.pyfunc.PyFuncModel模型的 URI。通常我们称之为 MLflow 模型。 -
一个接受字符串输入并输出单个字符串的 Python 函数。您的可调用对象必须匹配
mlflow.pyfunc.PyFuncModel.predict()的签名(不带params参数),简而言之,它应该
- 只有
data作为参数,它可以是pandas.Dataframe、numpy.ndarray、Python 列表、字典或 scipy 矩阵。 - 返回
pandas.DataFrame、pandas.Series、numpy.ndarray或列表之一。
- 只有
-
指向本地 MLflow AI 网关、Databricks 基础模型 API 和 Databricks 模型服务中的外部模型 的 MLflow Deployments 端点 URI。
-
将
model=None,并将模型输出放在data中。仅当数据是 Pandas 数据帧时适用。
使用 MLflow 模型进行评估
有关如何将模型转换为 mlflow.pyfunc.PyFuncModel 实例的详细说明,请阅读此文档。但简而言之,要将您的模型作为 MLflow 模型进行评估,我们建议遵循以下步骤
-
通过
log_model将您的模型记录到 MLflow 服务器。每个格式(opeanai、pytorch等)都有自己的log_modelAPI,例如mlflow.openai.log_model()with mlflow.start_run():
system_prompt = "Answer the following question in two sentences"
# Wrap "gpt-4o-mini" as an MLflow model.
logged_model_info = mlflow.openai.log_model(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
task=openai.chat.completions,
name="model",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": "{question}"},
],
) -
在
mlflow.evaluate()中使用已记录模型的 URI 作为模型实例results = mlflow.evaluate(
logged_model_info.model_uri,
eval_data,
targets="ground_truth",
model_type="question-answering",
)
使用自定义函数进行评估
从 MLflow 2.8.0 开始,mlflow.evaluate() 支持评估 Python 函数,而无需将模型记录到 MLflow。当您不想记录模型而只想评估它时,这很有用。以下示例使用 mlflow.evaluate() 来评估一个函数。您还需要设置 OpenAI 身份验证才能运行以下代码。
import mlflow
import openai
import pandas as pd
from typing import List
eval_data = pd.DataFrame(
{
"inputs": [
"What is MLflow?",
"What is Spark?",
],
"ground_truth": [
"MLflow is an open-source platform for managing the end-to-end machine learning (ML) lifecycle. It was developed by Databricks, a company that specializes in big data and machine learning solutions. MLflow is designed to address the challenges that data scientists and machine learning engineers face when developing, training, and deploying machine learning models.",
"Apache Spark is an open-source, distributed computing system designed for big data processing and analytics. It was developed in response to limitations of the Hadoop MapReduce computing model, offering improvements in speed and ease of use. Spark provides libraries for various tasks such as data ingestion, processing, and analysis through its components like Spark SQL for structured data, Spark Streaming for real-time data processing, and MLlib for machine learning tasks",
],
}
)
def openai_qa(inputs: pd.DataFrame) -> List[str]:
predictions = []
system_prompt = "Please answer the following question in formal language."
for _, row in inputs.iterrows():
completion = openai.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": row["inputs"]},
],
)
predictions.append(completion.choices[0].message.content)
return predictions
with mlflow.start_run():
results = mlflow.evaluate(
model=openai_qa,
data=eval_data,
targets="ground_truth",
model_type="question-answering",
)
print(results.metrics)
输出
{
"flesch_kincaid_grade_level/v1/mean": 14.75,
"flesch_kincaid_grade_level/v1/variance": 0.5625,
"flesch_kincaid_grade_level/v1/p90": 15.35,
"ari_grade_level/v1/mean": 18.15,
"ari_grade_level/v1/variance": 0.5625,
"ari_grade_level/v1/p90": 18.75,
"exact_match/v1": 0.0,
}
使用 MLflow Deployment 端点进行评估
对于 MLflow >= 2.11.0,mlflow.evaluate() 支持通过直接将 MLflow Deployment 端点 URI 传递给 model 参数来评估模型端点。这在您想评估由本地 MLflow AI 网关、Databricks 基础模型 API 和 Databricks 模型服务中的外部模型 托管的已部署模型,而无需实现自定义预测逻辑将其包装为 MLflow 模型或 Python 函数时特别有用。
在将端点 URI 与 mlflow.evaluate() 一起使用之前,请不要忘记使用 mlflow.deployments.set_deployments_target() 设置目标部署客户端,如下面的示例所示。否则,您将看到类似 MlflowException: No deployments target has been set... 的错误消息。
当您想使用未由 MLflow AI 网关或 Databricks 托管的端点时,您可以遵循使用自定义函数进行评估指南创建自定义 Python 函数,并将其用作 model 参数。
支持的输入数据格式
当使用 MLflow Deployment Endpoint 的 URI 作为模型时,输入数据可以是以下任一格式
| 数据格式 | 示例 | 附加说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 一个带有字符串列的 pandas DataFrame。 | | 对于此输入格式,MLflow 将构造适当的请求载荷到模型端点类型。例如,如果您的模型是聊天端点(llm/v1/chat),MLflow 将使用聊天消息格式(例如 {"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "What is MLflow?"}]})包装您的输入字符串。如果您想自定义请求载荷(例如,包括系统提示),请使用下一个格式。 |
| 一个带有字典列的 pandas DataFrame。 | | 在此格式下,字典应具有模型端点的正确请求格式。有关不同模型端点类型的请求格式的更多信息,请参阅MLflow Deployments 文档。 |
| 输入字符串列表。 | | mlflow.evaluate() 也接受列表输入。 |
| 请求载荷(字典)列表。 | | 与 Pandas DataFrame 输入类似,字典应具有模型端点的正确请求格式。 |
传递推理参数
您可以通过设置 mlflow.evaluate() 中的 inference_params 参数来将其他推理参数(例如 max_tokens、temperature、n)传递给模型端点。inference_params 参数是一个包含要传递给模型端点的参数的字典。指定的参数将用于评估数据集中的所有输入记录。
当您的输入是代表请求载荷的字典格式时,它还可以包含 max_tokens 等参数。如果 inference_params 和输入数据中存在重叠参数,则 inference_params 中的值将优先。
示例
由本地 MLflow AI 网关托管的聊天端点
import mlflow
from mlflow.deployments import set_deployments_target
import pandas as pd
# Point the client to the local MLflow AI Gateway
set_deployments_target("https://:5000")
eval_data = pd.DataFrame(
{
# Input data must be a string column and named "inputs".
"inputs": [
"What is MLflow?",
"What is Spark?",
],
# Additional ground truth data for evaluating the answer
"ground_truth": [
"MLflow is an open-source platform ....",
"Apache Spark is an open-source, ...",
],
}
)
with mlflow.start_run() as run:
results = mlflow.evaluate(
model="endpoints:/my-chat-endpoint",
data=eval_data,
targets="ground_truth",
inference_params={"max_tokens": 100, "temperature": 0.0},
model_type="question-answering",
)
托管在 Databricks 基础模型 API上的完成端点
import mlflow
from mlflow.deployments import set_deployments_target
import pandas as pd
# Point the client to Databricks Foundation Models API
set_deployments_target("databricks")
eval_data = pd.DataFrame(
{
# Input data must be a string column and named "inputs".
"inputs": [
"Write 3 reasons why you should use MLflow?",
"Can you explain the difference between classification and regression?",
],
}
)
with mlflow.start_run() as run:
results = mlflow.evaluate(
model="endpoints:/databricks-mpt-7b-instruct",
data=eval_data,
inference_params={"max_tokens": 100, "temperature": 0.0},
model_type="text",
)
评估 Databricks 模型服务中的外部模型 的方法相同,您只需指定指向服务终端点的不同 URI,例如 "endpoints:/your-chat-endpoint"。
使用静态数据集进行评估
对于 MLflow >= 2.8.0,mlflow.evaluate() 支持在不指定模型的情况下评估静态数据集。当您将模型输出保存到 Pandas DataFrame 的列或 MLflow PandasDataset 中,并且想评估静态数据集而不重新运行模型时,这很有用。
如果您使用的是 Pandas DataFrame,则必须使用 mlflow.evaluate() 中的顶级 predictions 参数指定包含模型输出的列名。
import mlflow
import pandas as pd
eval_data = pd.DataFrame(
{
"inputs": [
"What is MLflow?",
"What is Spark?",
],
"ground_truth": [
"MLflow is an open-source platform for managing the end-to-end machine learning (ML) lifecycle. "
"It was developed by Databricks, a company that specializes in big data and machine learning solutions. "
"MLflow is designed to address the challenges that data scientists and machine learning engineers "
"face when developing, training, and deploying machine learning models.",
"Apache Spark is an open-source, distributed computing system designed for big data processing and "
"analytics. It was developed in response to limitations of the Hadoop MapReduce computing model, "
"offering improvements in speed and ease of use. Spark provides libraries for various tasks such as "
"data ingestion, processing, and analysis through its components like Spark SQL for structured data, "
"Spark Streaming for real-time data processing, and MLlib for machine learning tasks",
],
"predictions": [
"MLflow is an open-source platform that provides handy tools to manage Machine Learning workflow "
"lifecycle in a simple way",
"Spark is a popular open-source distributed computing system designed for big data processing and analytics.",
],
}
)
with mlflow.start_run() as run:
results = mlflow.evaluate(
data=eval_data,
targets="ground_truth",
predictions="predictions",
extra_metrics=[mlflow.metrics.genai.answer_similarity()],
evaluators="default",
)
print(f"See aggregated evaluation results below: \n{results.metrics}")
eval_table = results.tables["eval_results_table"]
print(f"See evaluation table below: \n{eval_table}")
查看评估结果
通过代码查看评估结果
mlflow.evaluate() 以 mlflow.models.EvaluationResult() 实例的形式返回评估结果。要查看选定指标的分数,您可以检查
-
metrics:存储聚合结果,例如在整个评估数据集上的平均值/方差。让我们再次回顾上面的代码示例,重点关注打印聚合结果。with mlflow.start_run() as run:
results = mlflow.evaluate(
data=eval_data,
targets="ground_truth",
predictions="predictions",
extra_metrics=[mlflow.metrics.genai.answer_similarity()],
evaluators="default",
)
print(f"See aggregated evaluation results below: \n{results.metrics}") -
tables["eval_results_table"]:存储每行评估结果。with mlflow.start_run() as run:
results = mlflow.evaluate(
data=eval_data,
targets="ground_truth",
predictions="predictions",
extra_metrics=[mlflow.metrics.genai.answer_similarity()],
evaluators="default",
)
print(
f"See per-data evaluation results below: \n{results.tables['eval_results_table']}"
)
通过 MLflow UI 查看评估结果
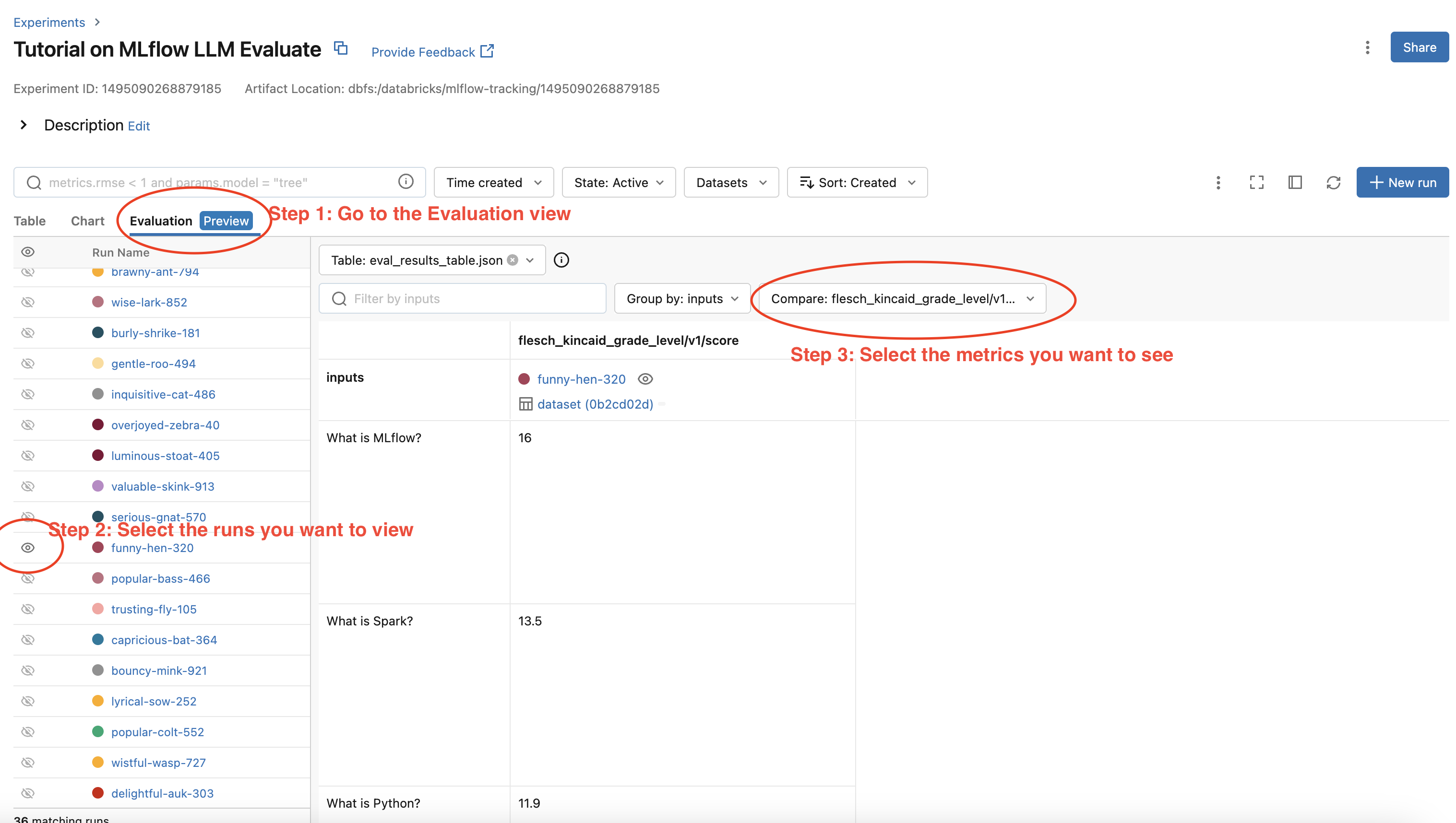
您的评估结果会自动记录到 MLflow 服务器,因此您可以直接从 MLflow UI 查看评估结果。要查看 MLflow UI 上的评估结果,请按照以下步骤操作
- 转到 MLflow 实验的实验视图。
- 选择“评估”选项卡。
- 选择要检查评估结果的运行。
- 从右侧的下拉菜单中选择指标。
为清晰起见,请参阅下面的截图