评估 Agent
AI Agent 是 GenAI 应用中的一种新兴模式,它们可以利用工具、做出决策并执行多步工作流。然而,评估这些复杂 Agent 的性能充满挑战。MLflow 提供了一个强大的工具集,可以通过 traces 和 scorers 精准地系统化评估 Agent 的行为。
工作流
构建你的 Agent
为你的特定用例创建具有工具、指令和能力的 AI Agent。
创建评估数据集
设计包含输入和预期的测试用例,包括输出和 Agent 的行为(如工具使用)。
定义 Agent 特定的 Scorers
创建使用 traces 评估 Agent 多步行为的 scorers。
运行评估
在 MLflow UI 中执行评估,并分析最终输出和 Agent 的中间行为。
示例:评估一个工具调用 Agent
先决条件
首先,通过运行以下命令安装所需包
pip install --upgrade mlflow>=3.3 openai
MLflow 将评估结果存储在跟踪服务器中。通过以下任一方法将您的本地环境连接到跟踪服务器。
- 本地 (pip)
- 本地 (docker)
- 远程 MLflow 服务器
- Databricks
为了最快的设置,您可以安装 mlflow Python 包并在本地运行 MLflow
mlflow ui --backend-store-uri sqlite:///mlflow.db --port 5000
这将启动本地计算机上的服务器,端口为 5000。通过设置跟踪 URI 将您的 notebook/IDE 连接到服务器。您也可以访问 MLflow UI,地址为 https://:5000。
import mlflow
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("https://:5000")
您也可以在 https://:5000 访问 MLflow UI。
MLflow 提供了一个 Docker Compose 文件,用于启动一个本地 MLflow 服务器,其中包含一个 postgres 数据库和一个 minio 服务器。
git clone https://github.com/mlflow/mlflow.git
cd docker-compose
cp .env.dev.example .env
docker compose up -d
这将启动本地计算机上的服务器,端口为 5000。通过设置跟踪 URI 将您的 notebook/IDE 连接到服务器。您也可以访问 MLflow UI,地址为 https://:5000。
import mlflow
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("https://:5000")
有关更多详细信息,请参阅 说明,例如覆盖默认环境变量。
如果您有远程 MLflow 跟踪服务器,请配置连接
import os
import mlflow
# Set your MLflow tracking URI
os.environ["MLFLOW_TRACKING_URI"] = "http://your-mlflow-server:5000"
# Or directly in code
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("http://your-mlflow-server:5000")
如果您有 Databricks 帐户,请配置连接
import mlflow
mlflow.login()
这将提示您输入配置详细信息(Databricks 主机 URL 和 PAT)。
如果您不确定如何设置 MLflow 跟踪服务器,可以从基于云的 MLflow 开始,该服务由 Databricks 提供支持:免费注册 →
步骤 1:构建 Agent
创建一个可以利用工具回答问题的数学 Agent。我们使用 OpenAI Agents,用几行代码构建工具调用 Agent。
from agents import Agent, Runner, function_tool
@function_tool
def add(a: float, b: float) -> float:
"""Adds two numbers."""
return a + b
@function_tool
def multiply(a: float, b: float) -> float:
"""Multiply two numbers."""
return a * b
@function_tool
def modular(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Modular arithmetic"""
return a % b
agent = Agent(
name="Math Agent",
instructions=(
"You will be given a math question. Calculate the answer using the given calculator tools. "
"Return the final number only as an integer."
),
tools=[add, multiply, modular],
)
确保你可以在本地运行 Agent。
from agents import Runner
result = await Runner.run(agent, "What is 15% of 240?")
print(result.final_output)
# 36
最后,将其封装在一个 MLflow 可以调用的函数中。请注意,MLflow 在线程池中运行每个预测,因此使用同步函数不会减慢评估速度。
from openai import OpenAI
# If you are using Jupyter Notebook, you need to apply nest_asyncio.
# import nest_asyncio
# nest_asyncio.apply()
def predict_fn(question: str) -> str:
return Runner.run_sync(agent, question).final_output
步骤 2:创建评估数据集
将测试用例设计为字典列表,每个字典包含 inputs、expectations 和可选的 tags 字段。我们希望评估输出的正确性,以及 Agent 使用的工具调用。
eval_dataset = [
{
"inputs": {"task": "What is 15% of 240?"},
"expectations": {"answer": 36, "tool_calls": ["multiply"]},
"tags": {"topic": "math"},
},
{
"inputs": {
"task": "I have 8 cookies and 3 friends. How many more cookies should I buy to share equally?"
},
"expectations": {"answer": 1, "tool_calls": ["modular", "add"]},
"tags": {"topic": "math"},
},
{
"inputs": {
"task": "I bought 2 shares of stock at $100 each. It's now worth $150. How much profit did I make?"
},
"expectations": {"answer": 100, "tool_calls": ["add", "multiply"]},
"tags": {"topic": "math"},
},
]
步骤 3:定义 Agent 特定的 Scorers
创建评估 Agent 特定行为的 scorers。
MLflow 的 scorer 可以接受 Agent 执行产生的 **Trace**。Trace 是精确评估 Agent 行为的强大方法,而不仅仅是最终输出。例如,在这里我们使用 Trace.search_spans 方法来提取工具调用的顺序,并将其与预期的工具调用进行比较。
有关更多详细信息,请参阅 评估 Traces 指南。
from mlflow.entities import Feedback, SpanType, Trace
from mlflow.genai import scorer
@scorer
def exact_match(outputs, expectations) -> bool:
return int(outputs) == expectations["answer"]
@scorer
def uses_correct_tools(trace: Trace, expectations: dict) -> Feedback:
"""Evaluate if agent used tools appropriately"""
expected_tools = expectations["tool_calls"]
# Parse the trace to get the actual tool calls
tool_spans = trace.search_spans(span_type=SpanType.TOOL)
tool_names = [span.name for span in tool_spans]
score = "yes" if tool_names == expected_tools else "no"
rationale = (
"The agent used the correct tools."
if tool_names == expected_tools
else f"The agent used the incorrect tools: {tool_names}"
)
# Return a Feedback object with the score and rationale
return Feedback(value=score, rationale=rationale)
步骤 4:运行评估
现在我们准备运行评估了!
results = mlflow.genai.evaluate(
data=eval_dataset, predict_fn=predict_fn, scorers=[exact_match, uses_correct_tools]
)
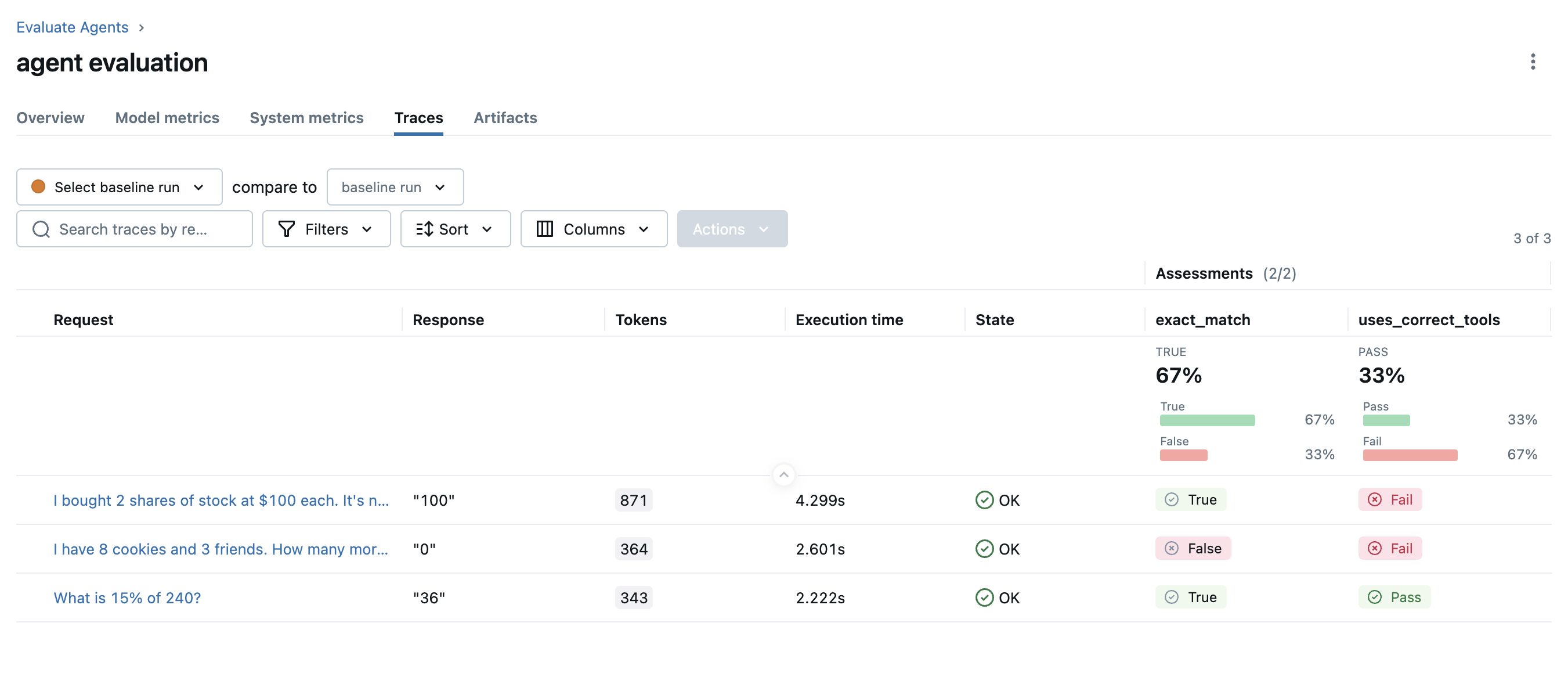
评估完成后,在浏览器中打开 MLflow UI,然后导航到实验页面。你应该会看到 MLflow 创建了一个新的 Run 并记录了评估结果。
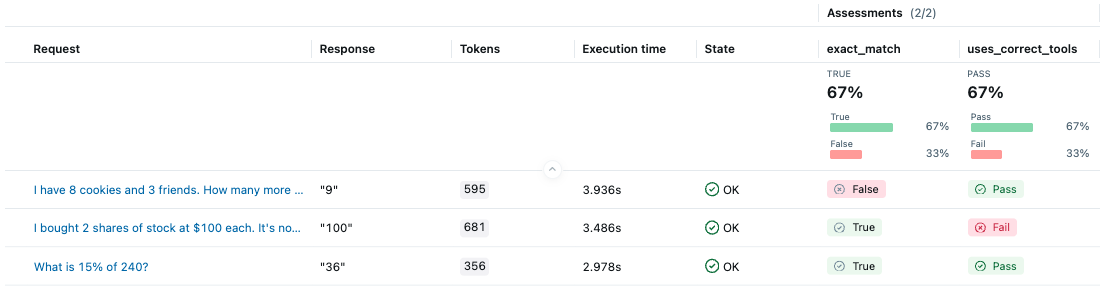
看来 Agent 在第二个测试用例中没有按正确的顺序调用工具。让我们点击该行来**打开 trace 并检查后台发生了什么**。
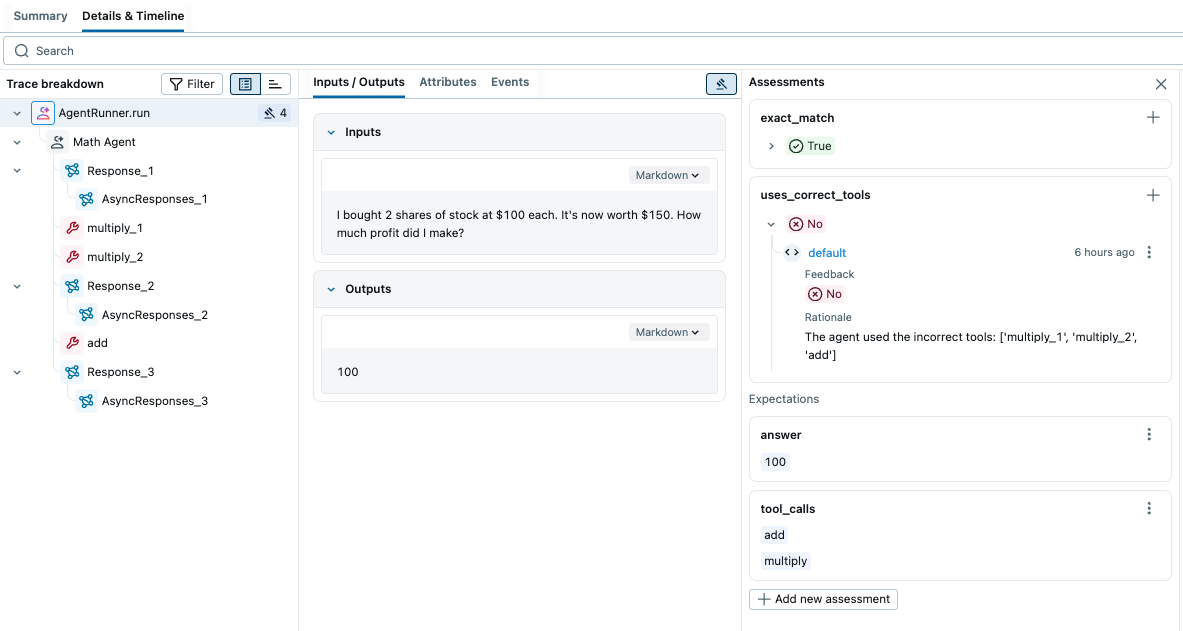
通过查看 trace,我们可以发现 Agent 分三步计算答案:(1)计算 100 * 2,(2)计算 150 * 2,(3)将这两个结果相减。然而,更有效的方法是:(1)将 100 从 150 中减去,(2)将结果乘以 2。在下一个版本中,我们可以更新系统指令,以便更有效地使用工具。
配置并行化
运行一个复杂的 Agent 可能需要很长时间。MLflow 默认使用后台线程池来加速评估过程。你可以通过设置 MLFLOW_GENAI_EVAL_MAX_WORKERS 环境变量来配置要使用的 worker 数量。
export MLFLOW_GENAI_EVAL_MAX_WORKERS=10
评估 MLflow 模型
在 MLflow 2.x 中,你可以将模型 URI 直接传递给旧版 mlflow.evaluate() API(已弃用)的 model 参数。MLflow **3.x** 中的新 GenAI 评估 API 仍然支持评估 MLflow 模型,但工作流略有不同。
import mlflow
# Load the model **outside** the prediction function.
model = mlflow.pyfunc.load_model("models:/math_agent/1")
# Wrap the model in a function that MLflow can call.
def predict_fn(question: str) -> str:
return model.predict(question)
# Run the evaluation as usual.
mlflow.genai.evaluate(
data=eval_dataset, predict_fn=predict_fn, scorers=[exact_match, uses_correct_tools]
)