基于自定义代码的评分器
自定义评分器提供了最大的灵活性,可以精确定义 GenAI 应用程序的质量衡量标准。它们允许您根据具体业务用例来定义评估指标,无论是基于简单的启发式方法、高级逻辑还是编程评估。
示例用法
要定义自定义评分器,您可以定义一个接收 输入参数 的函数,并为该函数添加 @scorer 装饰器。
from mlflow.genai import scorer
@scorer
def exact_match(outputs: dict, expectations: dict) -> bool:
return outputs == expectations["expected_response"]
要返回除基本值以外的更丰富信息,您可以返回一个 Feedback 对象。
from mlflow.entities import Feedback
@scorer
def is_short(outputs: dict) -> Feedback:
score = len(outputs.split()) <= 5
rationale = (
"The response is short enough."
if score
else f"The response is not short enough because it has ({len(outputs.split())} words)."
)
return Feedback(value=score, rationale=rationale)
然后,您可以直接将这些函数传递给 mlflow.genai.evaluate 函数,就像其他预定义或基于 LLM 的评分器一样。
import mlflow
eval_dataset = [
{
"inputs": {"question": "How many countries are there in the world?"},
"outputs": "195",
"expectations": {"expected_response": "195"},
},
{
"inputs": {"question": "What is the capital of France?"},
"outputs": "The capital of France is Paris.",
"expectations": {"expected_response": "Paris"},
},
]
mlflow.genai.evaluate(
data=eval_dataset,
scorers=[exact_match, is_short],
)
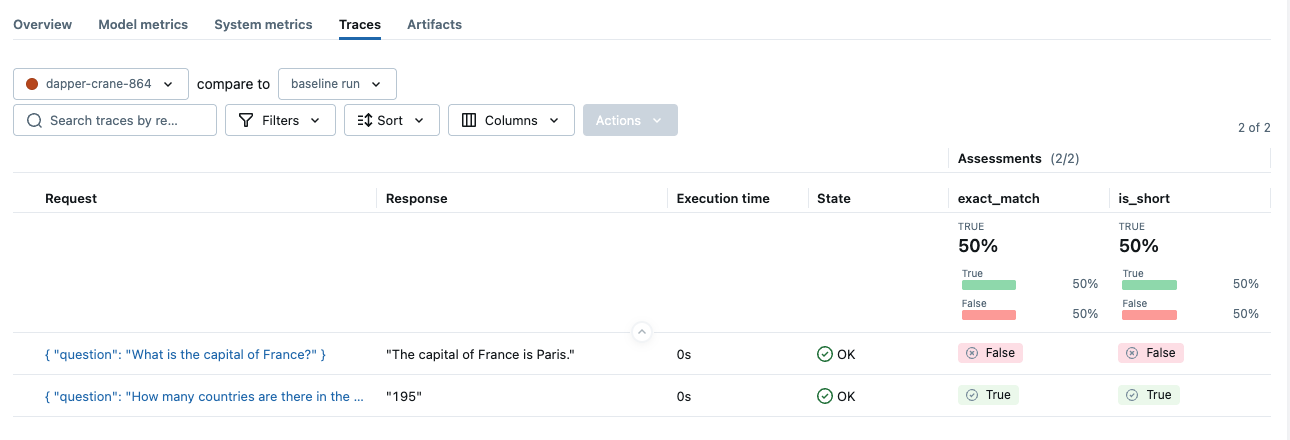
输入格式
作为输入,自定义评分器可以访问:
inputs字典,源自输入数据集或 MLflow 对您跟踪的后处理结果。outputs值,源自输入数据集或跟踪。如果提供了predict_fn,则outputs值将是predict_fn的返回值。expectations字典,源自输入数据集中的expectations字段,或与跟踪相关联。- 完整的 MLflow 跟踪,包括 spans、属性和输出。
@scorer
def my_scorer(
*,
inputs: dict[str, Any],
outputs: Any,
expectations: dict[str, Any],
trace: Trace,
) -> float | bool | str | Feedback | list[Feedback]:
# Your evaluation logic here
...
所有参数都是 **可选** 的;只需声明您的评分器需要的参数。
# ✔️ All of these signatures are valid for scorers
def my_scorer(inputs, outputs, expectations, trace) -> bool:
def my_scorer(inputs, outputs) -> str:
def my_scorer(outputs, expectations) -> Feedback:
def my_scorer(trace) -> list[Feedback]:
# 🔴 Additional parameters are not allowed
def my_scorer(inputs, outputs, expectations, trace, additional_param) -> float
在运行 mlflow.genai.evaluate() 时,inputs、outputs 和 expectations 参数可以在 data 参数中指定,或从跟踪中解析。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 评分器工作原理。
返回类型
评分器可以根据您的评估需求返回不同的类型:
简单值
返回基本值,用于简单的通过/失败或数值评估。
- 通过/失败字符串:
"yes"或"no"在 UI 中会显示为通过或失败在 UI 中 - 布尔值:
True或False,用于二元评估。 - 数值:整数或浮点数,用于分数、计数或度量。
丰富反馈
返回 Feedback 对象,用于详细评估,并附带其他元数据,如解释、来源信息和错误摘要。
from mlflow.entities import Feedback, AssessmentSource
@scorer
def content_quality(outputs):
return Feedback(
value=0.85, # Can be numeric, boolean, or string
rationale="Clear and accurate, minor grammar issues",
# Optional: source of the assessment. Several source types are supported,
# such as "HUMAN", "CODE", "LLM_JUDGE".
source=AssessmentSource(source_type="CODE", source_id="grammar_checker_v1"),
# Optional: additional metadata about the assessment.
metadata={
"annotator": "me@example.com",
},
)
可以返回多个 Feedback 对象,形式为列表。每个 Feedback 对象将在评估结果中显示为一个单独的指标。
@scorer
def comprehensive_check(inputs, outputs):
return [
Feedback(name="relevance", value=True, rationale="Directly addresses query"),
Feedback(name="tone", value="professional", rationale="Appropriate for audience"),
Feedback(name="length", value=150, rationale="Word count within limits")
]
解析跟踪进行评分
接受 trace 参数的评分器 **不能与 pandas DataFrame 一起使用**。它们需要您应用程序的实际执行跟踪。
如果您需要评估静态数据(例如,包含预生成响应的 CSV 文件),请使用仅与 inputs、outputs 和 expectations 参数配合使用的基于字段的评分器。
评分器可以访问完整的 MLflow 跟踪,包括 spans、属性和输出,从而使您能够精确评估代理的行为,而不仅仅是最终输出。 Trace.search_spans API 是从跟踪中检索此类中间信息的强大方法。
打开下面的选项卡,查看自定义评分器的示例,这些评分器通过解析跟踪来评估代理的详细行为。
- 检索文档召回率
- 工具调用轨迹
- 子代理路由
示例 1:评估检索文档召回率
from mlflow.entities import SpanType, Trace
from mlflow.genai import scorer
@scorer
def retrieved_document_recall(trace: Trace, expectations: dict) -> Feedback:
# Search for retriever spans in the trace
retriever_spans = trace.search_spans(span_type=SpanType.RETRIEVER)
# If there are no retriever spans
if not retriever_spans:
return Feedback(
value=0,
rationale="No retriever span found in the trace.",
)
# Gather all retrieved document URLs from the retriever spans
all_document_urls = []
for span in retriever_spans:
all_document_urls.extend([document["doc_uri"] for document in span.outputs])
# Compute the recall
true_positives = len(
set(all_document_urls) & set(expectations["relevant_document_urls"])
)
expected_positives = len(expectations["relevant_document_urls"])
recall = true_positives / expected_positives
return Feedback(
value=recall,
rationale=f"Retrieved {true_positives} relevant documents out of {expected_positives} expected.",
)
示例 2:评估工具调用轨迹
from mlflow.entities import SpanType, Trace
from mlflow.genai import scorer
@scorer
def tool_call_trajectory(trace: Trace, expectations: dict) -> Feedback:
# Search for tool call spans in the trace
tool_call_spans = trace.search_spans(span_type=SpanType.TOOL)
# Compare the tool trajectory with expectations
actual_trajectory = [span.name for span in tool_call_spans]
expected_trajectory = expectations["tool_call_trajectory"]
if actual_trajectory == expected_trajectory:
return Feedback(value=1, rationale="The tool call trajectory is correct.")
else:
return Feedback(
value=0,
rationale=(
"The tool call trajectory is incorrect.\n"
f"Expected: {expected_trajectory}.\n"
f"Actual: {actual_trajectory}."
),
)
示例 3:评估子代理路由
from mlflow.entities import SpanType, Trace
from mlflow.genai import scorer
@scorer
def is_routing_correct(trace: Trace, expectations: dict) -> Feedback:
# Search for sub-agent spans in the trace
sub_agent_spans = trace.search_spans(span_type=SpanType.AGENT)
invoked_agents = [span.name for span in sub_agent_spans]
expected_agents = expectations["expected_agents"]
if invoked_agents == expected_agents:
return Feedback(value=True, rationale="The sub-agents routing is correct.")
else:
return Feedback(
value=False,
rationale=(
"The sub-agents routing is incorrect.\n"
f"Expected: {expected_agents}.\n"
f"Actual: {invoked_agents}."
),
)
错误处理
当评分器遇到错误时,MLflow 提供两种方法:
允许异常传播(推荐)
最简单的方法是让异常自然抛出。MLflow 会自动捕获异常并创建一个包含错误详细信息的 Feedback 对象。
import json
import mlflow
from mlflow.entities import Feedback
from mlflow.genai.scorers import scorer
@scorer
def is_valid_response(outputs: str) -> Feedback:
# Let json.JSONDecodeError propagate if response isn't valid JSON
data = json.loads(outputs)
# Let KeyError propagate if required fields are missing
summary = data["summary"]
confidence = data["confidence"]
return Feedback(value=True, rationale=f"Valid JSON with confidence: {confidence}")
# Run the scorer on invalid data that triggers exceptions
invalid_data = [
{
# Valid JSON
"outputs": '{"summary": "this is a summary", "confidence": 0.95}'
},
{
# Invalid JSON
"outputs": "invalid json",
},
{
# Missing required fields
"outputs": '{"summary": "this is a summary"}'
},
]
mlflow.genai.evaluate(
data=invalid_data,
scorers=[is_valid_response],
)
当发生异常时,MLflow 会创建一个 Feedback 对象,其中包含:
value: Noneerror: 异常详细信息,例如异常对象、错误消息和堆栈跟踪。
错误信息将在评估结果中显示。打开相应的行即可查看错误详细信息。
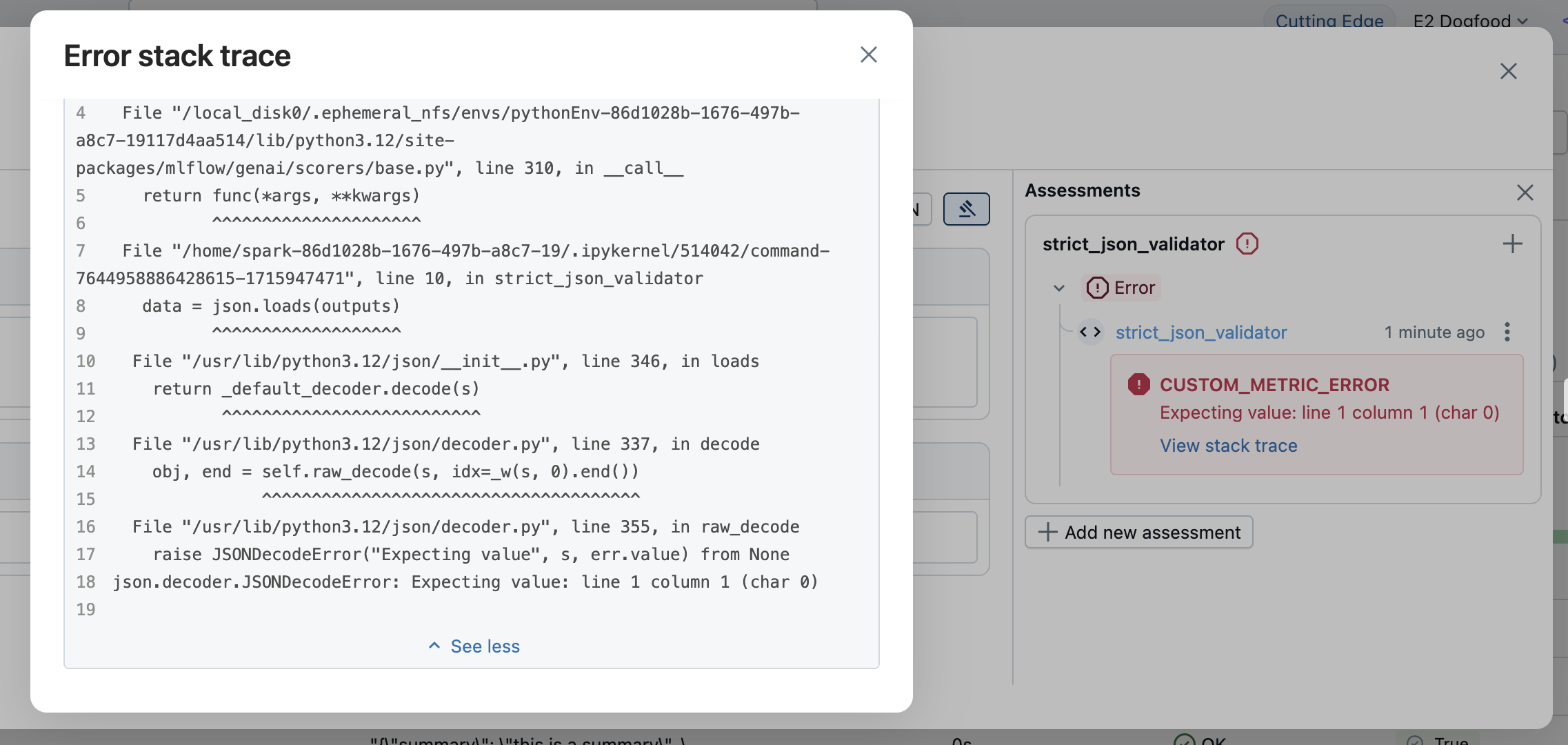
显式处理异常
为了进行自定义错误处理或提供特定的错误消息,请捕获异常并返回一个值为 None 且包含错误详细信息的 Feedback 对象。
import json
from mlflow.entities import AssessmentError, Feedback
@scorer
def is_valid_response(outputs):
try:
data = json.loads(outputs)
required_fields = ["summary", "confidence", "sources"]
missing = [f for f in required_fields if f not in data]
if missing:
# Specify the AssessmentError object explicitly
return Feedback(
error=AssessmentError(
error_code="MISSING_REQUIRED_FIELDS",
error_message=f"Missing required fields: {missing}",
),
)
return Feedback(value=True, rationale="Valid JSON with all required fields")
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
# Can pass exception object directly to the error parameter as well
return Feedback(error=e)