基于代理的评分器(又名代理即评判者)
代理即评判者代表了 LLM 评估范式的一个转变。这些评判者不仅仅是评估输入和输出,它们充当了 **自主代理**,配备了工具来深入探查你的应用程序的执行情况。
工作原理
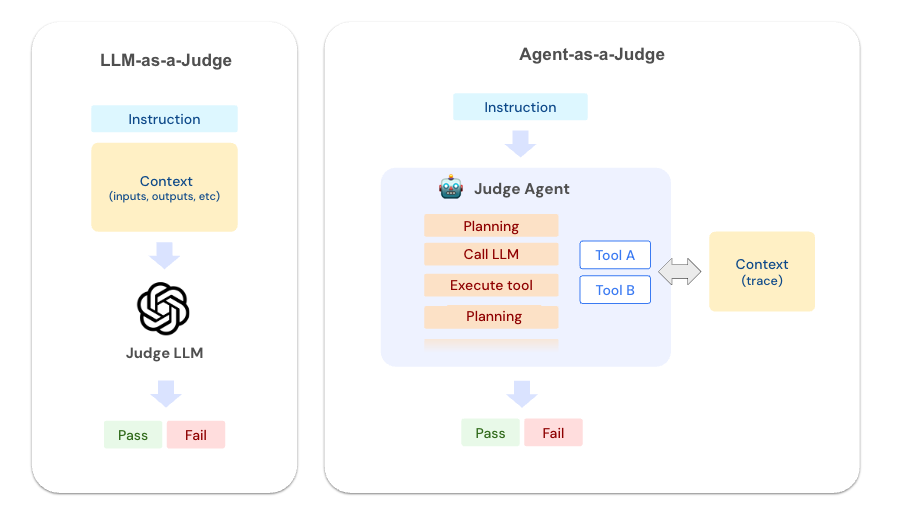
代理即评判者使用以下工具来探查记录到 MLflow 后端的可追溯数据。这些工具使评判者能够像经验丰富的调试器一样,系统地探索你应用程序的执行。
| 工具 | 描述 |
|---|---|
GetTraceInfo | 检索关于可追溯数据的顶层信息,包括时间、状态和元数据。 |
ListSpans | 列出可追溯数据中的所有跨度及其层次结构、时间信息和基本属性。 |
GetSpan | 获取特定跨度的详细信息,包括输入、输出和自定义属性。 |
SearchTraceRegex | 使用正则表达式在所有跨度数据中搜索模式。 |
为什么不直接将可追溯数据传递给 LLM?
虽然这对于简单的情况有效,但真实应用程序的可追溯数据通常很大且复杂。将整个可追溯数据传递给 LLM 会很快超出上下文窗口限制并降低评判者的准确性。代理方法使用工具来探索可追溯数据的结构并获取必要的详细信息,而不会耗尽上下文窗口。
与 LLM 即评判者的比较
理解何时使用每种方法取决于你所处的开发生命周期阶段
| 方面 | 代理即评判者 | LLM 即裁判 (LLM-as-a-Judge) |
|---|---|---|
| 设置简易性 | 简单 - 只需描述要调查的内容 | 需要仔细的提示工程和细化 |
| 它们评估什么 | 完整的执行跟踪和轨迹 | 特定的输入和输出字段 |
| 性能 | 较慢(详细探索可追溯数据) | 执行速度快 |
| 成本 | 较高(更多的上下文和工具使用) | 较低(较少的上下文) |
何时使用代理即评判者?
代理即评判者适合 **启动** 评估飞轮。
- 开始使用新应用程序
- 修改和完善你的代理
- 识别失败模式
- 理解意外行为
何时使用 LLM 即评判者?
LLM 即评判者在评估特定标准方面更有效,因此适合 **持续评估** 和 **生产使用**。
- 生产监控
- 回归测试
- 部署前的最终验证
- 满足特定的质量期望
快速入门
要创建代理即评判者,只需调用 make_judge API 并传递一个包含 **{{ trace }}** 模板变量的指令
python
import mlflow
from mlflow.genai.judges import make_judge
from typing import Literal
import time
performance_judge = make_judge(
name="performance_analyzer",
instructions=(
"Analyze the {{ trace }} for performance issues.\n\n"
"Check for:\n"
"- Operations taking longer than 2 seconds\n"
"- Redundant API calls or database queries\n"
"- Inefficient data processing patterns\n"
"- Proper use of caching mechanisms\n\n"
"Rate as: 'optimal', 'acceptable', or 'needs_improvement'"
),
feedback_value_type=Literal["optimal", "acceptable", "needs_improvement"],
model="openai:/gpt-5",
# model="anthropic:/claude-opus-4-1-20250805",
)
注意
{{ trace }} 模板变量的使用很重要。如果模板不包含 {{ trace }},MLflow 会假定评分器是普通的 LLM 即评判者,并且不使用 MCP 工具。
然后,从你的应用程序生成一个可追溯数据,并将其传递给评分器
python
@mlflow.trace
def slow_data_processor(query: str):
"""Example application with performance bottlenecks."""
with mlflow.start_span("fetch_data") as span:
time.sleep(2.5)
span.set_inputs({"query": query})
span.set_outputs({"data": ["item1", "item2", "item3"]})
with mlflow.start_span("process_data") as span:
for i in range(3):
with mlflow.start_span(f"redundant_api_call_{i}"):
time.sleep(0.5)
span.set_outputs({"processed": "results"})
return "Processing complete"
result = slow_data_processor("SELECT * FROM users")
trace_id = mlflow.get_last_active_trace_id()
trace = mlflow.get_trace(trace_id)
feedback = performance_judge(trace=trace)
print(f"Performance Rating: {feedback.value}")
print(f"Analysis: {feedback.rationale}")
text
Performance Rating: needs_improvement
Analysis: Found critical performance issues:
1. The 'fetch_data' span took 2.5 seconds, exceeding the 2-second threshold
2. Detected 3 redundant API calls (redundant_api_call_0, redundant_api_call_1,
redundant_api_call_2) that appear to be duplicate operations
3. Total execution time of 4 seconds could be optimized by parallelizing
the redundant operations or implementing caching
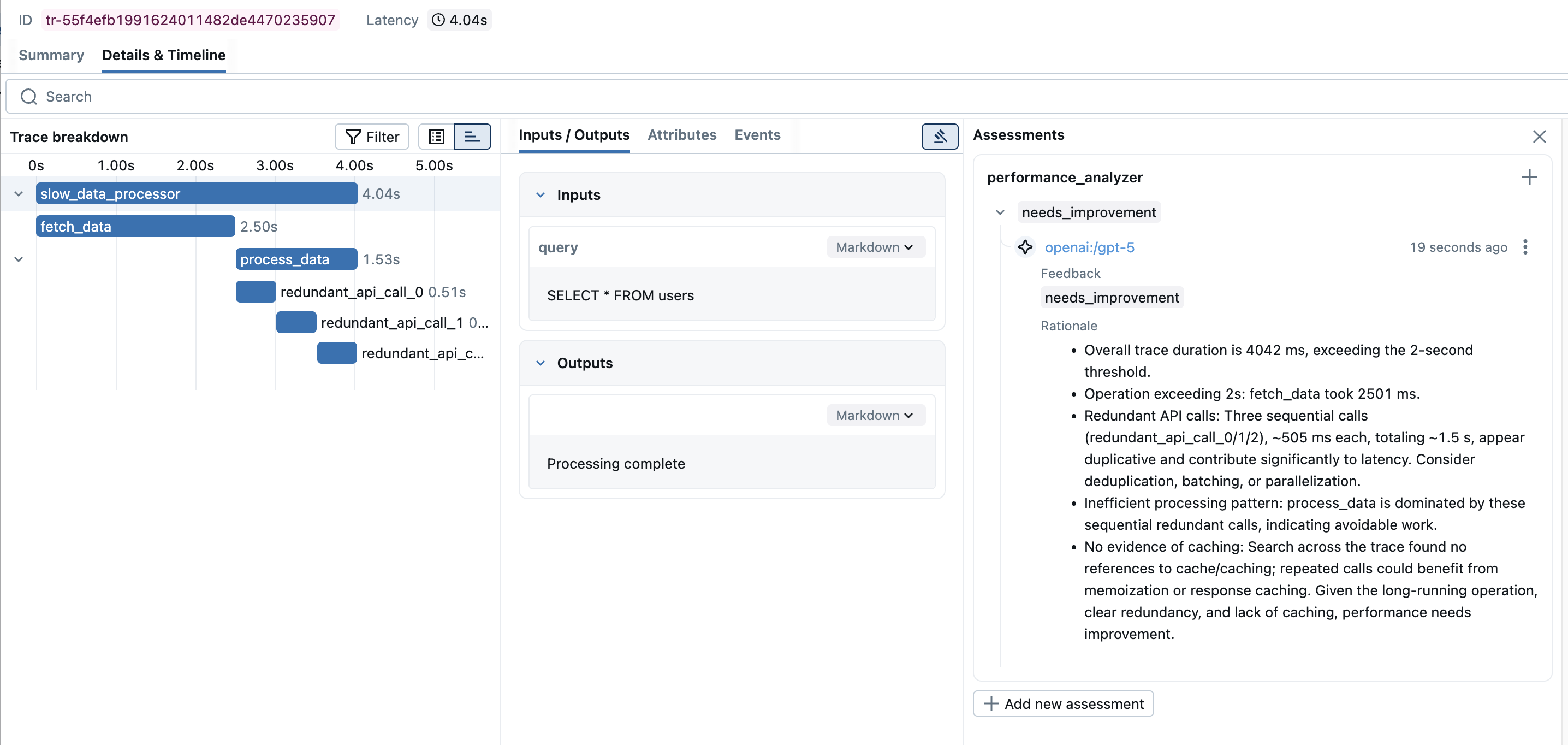
对批量可追溯数据运行评判者
要将评分器应用于批量可追溯数据,请使用 mlflow.genai.evaluate API。
python
import mlflow
# Retrieve traces from MLflow
traces = mlflow.search_traces(filter_string="timestamp > 1727174400000")
# Run evaluation with Agent-as-a-Judge
results = mlflow.genai.evaluate(
data=traces,
scorers=[performance_judge],
)
高级示例
- 工具使用分析
- 循环检测
- 推理分析
- RAG 代理评估
- 错误处理评估
python
tool_optimization_judge = make_judge(
name="tool_optimizer",
instructions=(
"Analyze tool usage patterns in {{ trace }}.\n\n"
"Check for:\n"
"1. Unnecessary tool calls (could be answered without tools)\n"
"2. Wrong tool selection (better tool available)\n"
"3. Inefficient sequencing (could parallelize or reorder)\n"
"4. Missing tool usage (should have used a tool)\n\n"
"Provide specific optimization suggestions.\n"
"Rate efficiency as: 'optimal', 'good', 'suboptimal', or 'poor'"
),
feedback_value_type=Literal["optimal", "good", "suboptimal", "poor"],
model="anthropic:/claude-opus-4-1-20250805",
)
python
loop_detector_judge = make_judge(
name="loop_detector",
instructions=(
"Detect problematic loops in {{ trace }}.\n\n"
"Identify:\n"
"1. Infinite loop risks\n"
"2. Unnecessary iterations\n"
"3. Circular reasoning patterns\n"
"4. Recursive calls without proper termination\n\n"
"Report specific span patterns that indicate issues.\n"
"Classify as: 'clean', 'warning', or 'critical'"
),
feedback_value_type=Literal["clean", "warning", "critical"],
model="anthropic:/claude-opus-4-1-20250805",
)
python
reasoning_judge = make_judge(
name="reasoning_validator",
instructions=(
"Evaluate the reasoning chain in {{ trace }}.\n\n"
"Analysis criteria:\n"
"1. Logical Progression: Does each step follow logically from the previous?\n"
"2. Assumption Validity: Are assumptions reasonable and stated?\n"
"3. Evidence Usage: Is evidence properly cited and used?\n"
"4. Conclusion Soundness: Does the conclusion follow from the premises?\n\n"
"Identify specific reasoning flaws with span IDs.\n"
"Score 1-100 for reasoning quality."
),
feedback_value_type=int,
model="anthropic:/claude-opus-4-1-20250805",
)
python
rag_judge = make_judge(
name="rag_evaluator",
instructions=(
"Evaluate the RAG agent's behavior in {{ trace }}.\n\n"
"Check for:\n"
"1. Were the right documents retrieved?\n"
"2. Is the response grounded in the retrieved context?\n"
"3. Are sources properly cited?\n\n"
"Rate as: 'good', 'acceptable', or 'poor'"
),
feedback_value_type=Literal["good", "acceptable", "poor"],
model="anthropic:/claude-opus-4-1-20250805",
)
# Use with your RAG pipeline
@mlflow.trace
def rag_pipeline(query):
docs = retrieve_documents(query)
response = generate_with_context(query, docs)
return response
result = rag_pipeline("What is MLflow?")
trace = mlflow.get_last_active_trace()
evaluation = rag_judge(trace=trace)
python
error_handling_judge = make_judge(
name="error_handler_checker",
instructions=(
"Analyze error handling in the {{ trace }}.\n\n"
"Look for:\n"
"1. Spans with error status or exceptions\n"
"2. Retry attempts and their patterns\n"
"3. Fallback mechanisms\n"
"4. Error propagation and recovery\n\n"
"Identify specific error scenarios and how they were handled.\n"
"Rate as: 'robust', 'adequate', or 'fragile'"
),
feedback_value_type=Literal["robust", "adequate", "fragile"],
model="anthropic:/claude-opus-4-1-20250805",
)
调试代理评判者
要查看代理即评判者在分析你的可追溯数据时实际进行的 MCP 工具调用,请启用调试日志记录
python
import logging
# Enable debug logging to see agent tool calls
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)
logger = logging.getLogger("mlflow.genai.judges")
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# Now when you run the judge, you'll see detailed tool usage
feedback = performance_judge(trace=trace)
启用调试日志记录后,你将看到类似以下的输出
text
DEBUG:mlflow.genai.judges:Calling tool: GetTraceInfo
DEBUG:mlflow.genai.judges:Tool response: {"trace_id": "abc123", "duration_ms": 4000, ...}
DEBUG:mlflow.genai.judges:Calling tool: ListSpans
DEBUG:mlflow.genai.judges:Tool response: [{"span_id": "def456", "name": "fetch_data", ...}]
DEBUG:mlflow.genai.judges:Calling tool: GetSpan with span_id=def456
DEBUG:mlflow.genai.judges:Tool response: {"duration_ms": 2500, "inputs": {"query": "SELECT * FROM users"}, ...}