Judge Alignment: Teaching AI to Match Human Preferences
将通用评判者转变为领域专家
Judge alignment 是一个优化 LLM 评判者以匹配人类评估标准的过程。通过系统地学习人类反馈,评判者可以从通用评估者演变为理解您独特质量标准的领域专家。
为何对齐很重要
即使是最复杂的 LLM 也需要校准才能匹配您的特定评估标准。什么是“好的”客户服务因行业而异。医疗准确性要求与一般健康建议不同。对齐通过示例来弥合这一差距,教授评判者您的特定质量标准。
从专家反馈中学习
评判者通过从领域专家的评估中学习来改进,捕捉通用提示会遗漏的细微质量标准。
大规模一致的标准
一旦对齐,评判者将在数百万次评估中一致地应用您的确切质量标准。
持续改进
随着您的标准演变,评判者可以根据新反馈重新对齐,从而随着时间的推移保持相关性。
减少评估错误
与通用评估提示相比,对齐后的评判者误报/漏报减少了 30-50%。
Judge Alignment 如何工作
对齐生命周期
快速入门:对齐您的第一个评判者
为了使对齐工作,每个 trace 都必须同时具有评判者评估和人类反馈,**且评估名称相同**。对齐过程通过将评判者评估与同一 trace 上的人类反馈进行比较来学习。
评估名称必须与评判者名称完全匹配——如果您的评判者名为“product_quality”,那么评判者的评估和人类反馈都必须使用名称“product_quality”。
顺序无关紧要——人类可以在评判者评估之前或之后提供反馈。
步骤 1:设置和生成 Trace
首先,创建您的评判者并生成具有初始评估的 trace
from mlflow.genai.judges import make_judge
from mlflow.genai.judges.optimizers import SIMBAAlignmentOptimizer
from mlflow.entities import AssessmentSource, AssessmentSourceType
from typing import Literal
import mlflow
# Create experiment and initial judge
experiment_id = mlflow.create_experiment("product-quality-alignment")
mlflow.set_experiment(experiment_id=experiment_id)
initial_judge = make_judge(
name="product_quality",
instructions=(
"Evaluate if the product description in {{ outputs }} "
"is accurate and helpful for the query in {{ inputs }}. "
"Rate as: excellent, good, fair, or poor"
),
feedback_value_type=Literal["excellent", "good", "fair", "poor"],
model="anthropic:/claude-opus-4-1-20250805",
)
# Generate traces from your application (minimum 10 required)
traces = []
for i in range(15): # Generate 15 traces (more than minimum of 10)
with mlflow.start_span(f"product_description_{i}") as span:
# Your application logic
query = f"Product query {i}"
description = f"Product description for query {i}"
span.set_inputs({"query": query})
span.set_outputs({"description": description})
traces.append(span.trace_id)
# Run the judge on these traces to get initial assessments
for trace_id in traces:
trace = mlflow.get_trace(trace_id)
# Extract inputs and outputs from the trace for field-based evaluation
inputs = trace.data.spans[0].inputs # Get inputs from trace
outputs = trace.data.spans[0].outputs # Get outputs from trace
# Judge evaluates using field-based approach (inputs/outputs)
judge_result = initial_judge(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs)
# Judge's assessment is automatically logged when called
步骤 2:收集人类反馈
在运行您的评判者对 trace 进行评估后,您需要收集人类反馈。您可以选择
- 使用 MLflow UI(推荐):通过直观的界面审查 trace 并添加反馈
- 以编程方式记录:如果您已有地面真相标签
有关收集反馈的详细说明,请参阅下方 收集用于对齐的反馈。
步骤 3:对齐和注册
收集反馈后,对齐您的评判者并注册它
- 默认优化器(推荐)
- 显式优化器
# Retrieve traces with both judge and human assessments
traces_for_alignment = mlflow.search_traces(
experiment_ids=[experiment_id], max_results=15, return_type="list"
)
# Align the judge using human corrections (minimum 10 traces recommended)
if len(traces_for_alignment) >= 10:
optimizer = SIMBAAlignmentOptimizer(model="anthropic:/claude-opus-4-1-20250805")
# Run alignment - shows minimal progress by default:
# INFO: Starting SIMBA optimization with 15 examples (set logging to DEBUG for detailed output)
# INFO: SIMBA optimization completed
aligned_judge = initial_judge.align(optimizer, traces_for_alignment)
# Register the aligned judge
aligned_judge.register(experiment_id=experiment_id)
print("Judge aligned successfully with human feedback")
else:
print(f"Need at least 10 traces for alignment, have {len(traces_for_alignment)}")
from mlflow.genai.judges.optimizers import SIMBAAlignmentOptimizer
# Retrieve traces with both judge and human assessments
traces_for_alignment = mlflow.search_traces(
experiment_ids=[experiment_id], max_results=15, return_type="list"
)
# Align the judge using human corrections (minimum 10 traces recommended)
if len(traces_for_alignment) >= 10:
# Explicitly specify SIMBA with custom model configuration
optimizer = SIMBAAlignmentOptimizer(model="anthropic:/claude-opus-4-1-20250805")
aligned_judge = initial_judge.align(traces_for_alignment, optimizer)
# Register the aligned judge
aligned_judge.register(experiment_id=experiment_id)
print("Judge aligned successfully with human feedback")
else:
print(f"Need at least 10 traces for alignment, have {len(traces_for_alignment)}")
SIMBA 对齐优化器
MLflow 提供使用DSPy 对 SIMBA(Simplified Multi-Bootstrap Aggregation)的实现**默认对齐优化器**。当您调用 align() 而不指定优化器时,SIMBA 优化器会自动使用。
# Default: Uses SIMBA optimizer automatically
aligned_judge = initial_judge.align(traces_with_feedback)
# Explicit: Same as above but with custom model specification
from mlflow.genai.judges.optimizers import SIMBAAlignmentOptimizer
optimizer = SIMBAAlignmentOptimizer(
model="anthropic:/claude-opus-4-1-20250805" # Model used for optimization
)
aligned_judge = initial_judge.align(traces_with_feedback, optimizer)
# Requirements for alignment:
# - Minimum 10 traces with BOTH judge assessments and human feedback
# - Both assessments must use the same name (matching the judge name)
# - Order doesn't matter - humans can assess before or after judge
# - Mix of agreements and disagreements between judge and human recommended
当在不带优化器参数的情况下使用 align() 时,MLflow 会自动使用 SIMBA 优化器。这简化了对齐过程,同时仍允许在需要时进行自定义。
控制优化输出
默认情况下,对齐显示最少的进度信息,以保持日志整洁。如果您需要调试优化过程或查看详细的迭代进度,请启用 DEBUG 日志记录。
import logging
# Enable detailed optimization output
logging.getLogger("mlflow.genai.judges.optimizers.simba").setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# Now alignment will show:
# - Detailed iteration-by-iteration progress
# - Score improvements at each step
# - Strategy selection details
# - Full DSPy optimization output
aligned_judge = initial_judge.align(optimizer, traces_with_feedback)
# Reset to default (minimal output) after debugging
logging.getLogger("mlflow.genai.judges.optimizers.simba").setLevel(logging.INFO)
启用 DEBUG 日志记录,当
- 优化似乎卡住或耗时过长
- 您想了解优化器如何改进指令
- 调试对齐失败或意外结果
- 了解 SIMBA 优化器如何工作
对于生产环境,请将其保留为 INFO(默认),以避免冗长的输出。
收集用于对齐的反馈
对齐的质量取决于反馈的质量和数量。选择最适合您情况的方法
反馈收集方法
- MLflow UI(推荐)
- 编程(地面真相)
何时使用:您没有现有的地面真相标签,需要收集人类反馈。
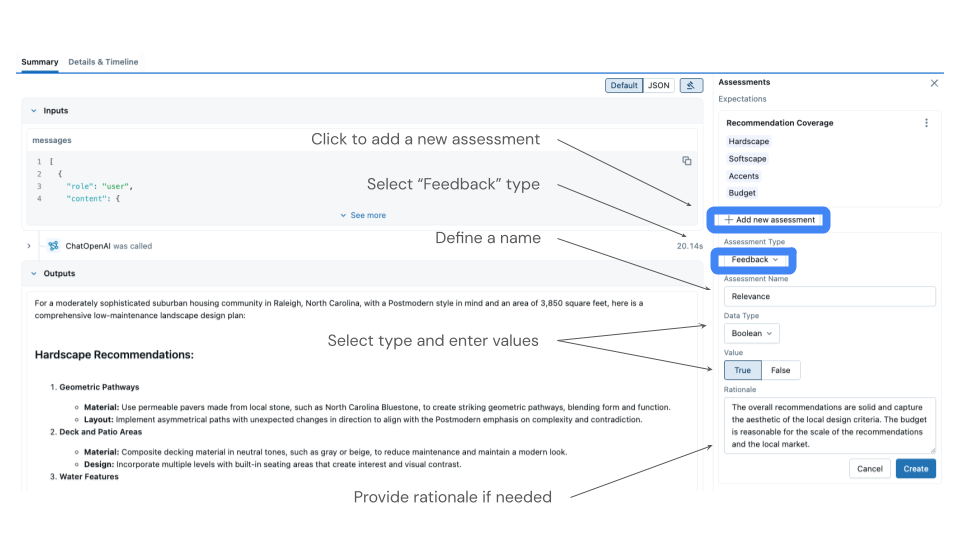
MLflow UI 提供了一个直观的界面,用于审查 trace 并添加反馈。
- 导航到实验中的“Trace”选项卡
- 单击单个 trace 来审查输入、输出和任何现有的评判者评估。
- 通过单击“添加反馈”按钮**添加反馈**
- 选择与您的评判者名称匹配的评估名称(例如,“product_quality”)
- 根据您的评估标准提供评分
有效反馈收集技巧
- 如果您**不是领域专家**:将 trace 分发给团队成员或领域专家进行审查。
- 如果您**是领域专家**:创建一套评分标准或指南文档以确保一致性。
- 对于**多个审阅者**:组织反馈会议,让审阅者可以一起处理批次。
- 为了**保持一致性**:在开始之前清晰地记录您的评估标准。
UI 会自动以正确的格式为对齐记录反馈。
何时使用:您已有数据的地面真相标签。
如果您已有标记数据,您可以以编程方式将其记录为反馈。
import mlflow
from mlflow.entities import AssessmentSource, AssessmentSourceType
# Your existing ground truth dataset
ground_truth_data = [
{"trace_id": "trace1", "label": "excellent", "query": "What is MLflow?"},
{"trace_id": "trace2", "label": "poor", "query": "How to use tracking?"},
{"trace_id": "trace3", "label": "good", "query": "How to log models?"},
]
# Log ground truth as feedback for alignment
for item in ground_truth_data:
mlflow.log_feedback(
trace_id=item["trace_id"],
name="product_quality", # Must match your judge name
value=item["label"],
source=AssessmentSource(
source_type=AssessmentSourceType.HUMAN, source_id="ground_truth_dataset"
),
)
print(f"Logged {len(ground_truth_data)} ground truth labels for alignment")
当您已有预标记数据时,此方法很有效,这些数据来自
• 以前的手动标记工作 • 专家注释 • 生产反馈系统 • 具有已知正确答案的测试数据集
多位审阅者
纳入多位专家的反馈,以捕捉不同的观点并减少个人偏见。
平衡的示例
包含正面和负面示例。每种类型至少占 30%,以帮助评判者学习边界。
充足的数量
收集至少 10 个反馈示例(SIMBA 的最小值),但 50-100 个示例通常会产生更好的结果。
一致的标准
确保审阅者使用一致的标准。提供指南或评分表以标准化评估。
自定义对齐优化器
MLflow 的对齐系统设计为**插件架构**,允许您创建自定义优化器以实现不同的对齐策略。这种可扩展性使您能够实现特定于领域的优化方法,同时利用 MLflow 的评判者基础设施。
创建自定义优化器
要创建自定义对齐优化器,请扩展 AlignmentOptimizer 抽象基类。
from mlflow.genai.judges.base import AlignmentOptimizer, Judge
from mlflow.entities.trace import Trace
class MyCustomOptimizer(AlignmentOptimizer):
"""Custom optimizer implementation for judge alignment."""
def __init__(self, model: str = None, **kwargs):
"""Initialize your optimizer with custom parameters."""
self.model = model
# Add any custom initialization logic
def align(self, judge: Judge, traces: list[Trace]) -> Judge:
"""
Implement your alignment algorithm.
Args:
judge: The judge to be optimized
traces: List of traces containing human feedback
Returns:
A new Judge instance with improved alignment
"""
# Your custom alignment logic here
# 1. Extract feedback from traces
# 2. Analyze disagreements between judge and human
# 3. Generate improved instructions
# 4. Return new judge with better alignment
# Example: Return judge with modified instructions
from mlflow.genai.judges import make_judge
improved_instructions = self._optimize_instructions(judge.instructions, traces)
return make_judge(
name=judge.name,
instructions=improved_instructions,
feedback_value_type=str,
model=judge.model,
)
def _optimize_instructions(self, instructions: str, traces: list[Trace]) -> str:
"""Your custom optimization logic."""
# Implement your optimization strategy
pass
使用自定义优化器
实现后,像使用内置优化器一样使用您的自定义优化器。
# Create your custom optimizer
custom_optimizer = MyCustomOptimizer(model="your-model")
# Use it for alignment
aligned_judge = initial_judge.align(traces_with_feedback, custom_optimizer)
可用优化器
MLflow 目前提供
- SIMBAAlignmentOptimizer(默认):使用 DSPy 的 Simplified Multi-Bootstrap Aggregation 进行稳健的对齐。
- 自定义优化器:扩展
AlignmentOptimizer以实现您自己的策略。
插件架构确保可以在不修改核心评判者系统的情况下添加新的优化策略,从而促进不同对齐方法的扩展性和实验。
测试对齐效果
验证对齐是否改进了您的评判者。
def test_alignment_improvement(
original_judge, aligned_judge, test_traces: list
) -> dict:
"""Compare judge performance before and after alignment."""
original_correct = 0
aligned_correct = 0
for trace in test_traces:
# Get human ground truth from trace assessments
feedbacks = trace.search_assessments(type="feedback")
human_feedback = next(
(f for f in feedbacks if f.source.source_type == "HUMAN"), None
)
if not human_feedback:
continue
# Get judge evaluations
original_eval = original_judge(trace=trace)
aligned_eval = aligned_judge(trace=trace)
# Check agreement with human
if original_eval.value == human_feedback.value:
original_correct += 1
if aligned_eval.value == human_feedback.value:
aligned_correct += 1
total = len(test_traces)
return {
"original_accuracy": original_correct / total,
"aligned_accuracy": aligned_correct / total,
"improvement": (aligned_correct - original_correct) / total,
}