MLflow DSPy Flavor
dspy flavor 正在积极开发中,并被标记为实验性。公共 API 可能会发生更改,并且随着 flavor 的发展,可能会添加新功能。
简介
DSPy 是一个用于算法优化 LM 提示和权重的框架。它旨在通过用模块化组件替换手动编写的提示字符串来改进提示工程过程。这些模块简洁、定义明确,并保持高质量和强大的表达能力,使提示创建更有效率和可扩展性。通过参数化这些模块并将提示视为优化问题,DSPy 可以更好地适应不同的语言模型,可能优于专家手工制作的提示。这种模块化还使得探索复杂管道更加容易,从而可以根据特定任务或细微的指标对性能进行微调。
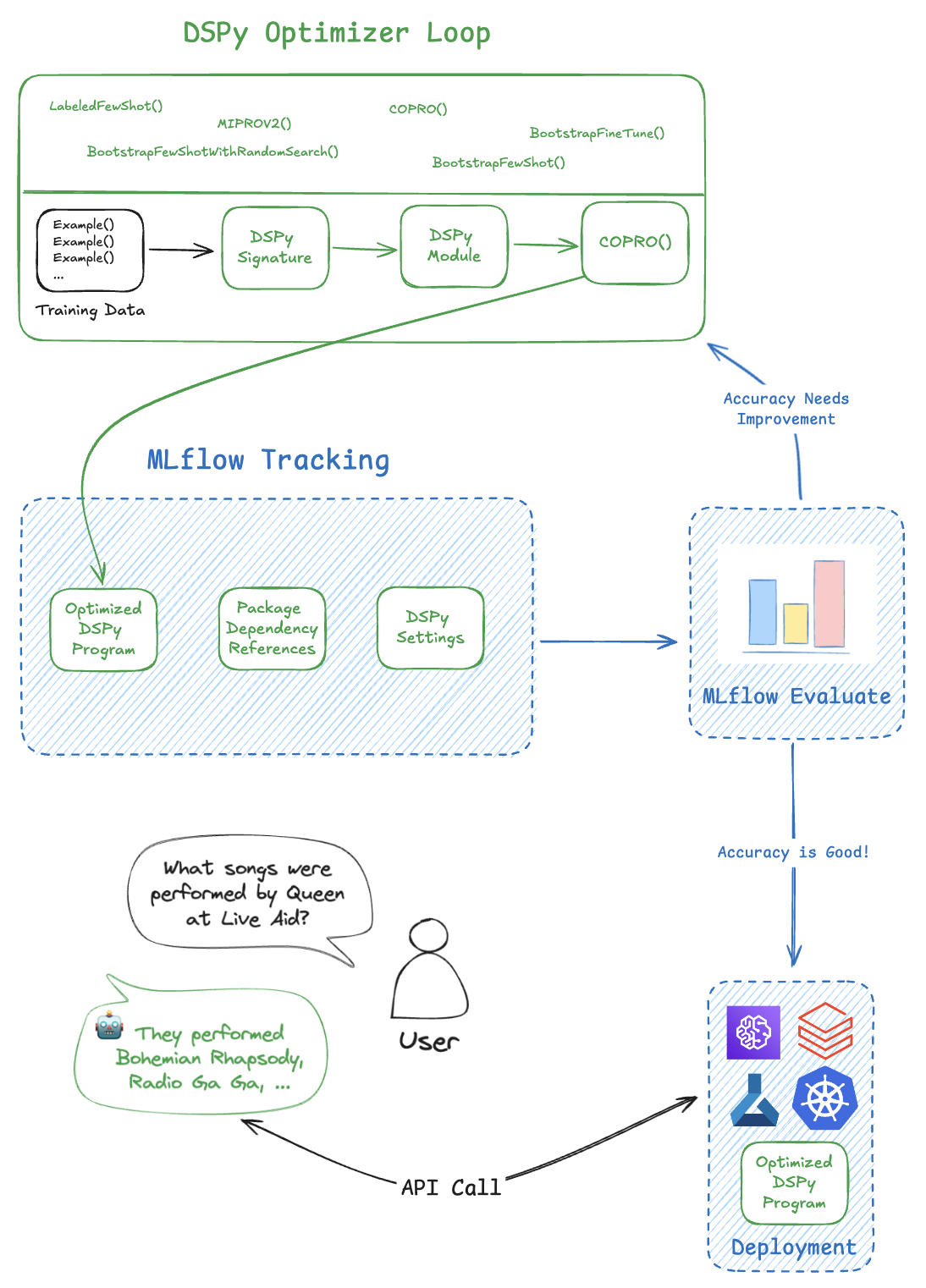
为什么要将 DSPy 与 MLflow 一起使用?
DSPy 库与 MLflow 的原生集成有助于用户管理 DSPy 的开发生命周期。以下是将 DSPy 与 MLflow 结合使用的一些主要优势:
- MLflow Tracking 允许您跟踪 DSPy 程序的训练和执行。通过 MLflow API,您可以记录各种工件并组织训练运行,从而提高对模型性能的可见性。
- MLflow Model 将您编译的 DSPy 程序与依赖项版本、输入输出接口和其他重要元数据打包在一起。这使您可以轻松部署编译后的 DSPy 程序,因为您知道在 ML 生命周期的不同阶段环境是一致的。
- MLflow Evaluate 在 MLflow 中提供原生功能来评估 GenAI 应用程序。此功能有助于有效评估 DSPy 编译程序的推理结果,确保稳健的性能分析并促进快速迭代。
- MLflow Tracing 是一个强大的可观测性工具,用于监视和调试 DSPy 模型内部发生的情况,帮助您快速识别潜在的瓶颈或问题。凭借其强大的自动日志记录功能,您无需编写任何额外的代码,只需运行一个命令即可对 DSPy 应用程序进行检测。
开始使用
在本入门教程中,您将学习 DSPy 最基本的组件,以及如何利用与 MLflow 的集成来存储、检索和使用 DSPy 程序。
概念
Module
Modules 是处理特定文本转换的组件,例如回答问题或进行摘要。它们取代了传统的手写提示,并且可以从示例中学习,使其更具适应性。
Signature
a signature is a natural language description of a module's input and output behavior. For example, "question -> answer" specifies that the module should take a question as input and return an answer.
Optimizer
An optimizer improves LM pipelines by adjusting modules to meet a performance metric, either by generating better prompts or fine-tuning models.
Program
A program is a a set of modules connected into a pipeline to perform complex tasks. DSPy programs are flexible, allowing you to optimize and adapt them using the compiler.
Automatic Tracing
MLflow Tracing tracing is a powerful feature that allows you to monitor and debug your DSPy programs. With MLflow, you can enable auto tracing just by calling the mlflow.dspy.autolog() function in your code.
import mlflow
mlflow.dspy.autolog()
Once enabled, MLflow will generate traces whenever your DSPy program is executed and record them in your MLflow Experiment.
Learn more about MLflow DSPy tracing capabilities here.
Tracking DSPy Program in MLflow Experiment
Creating a DSPy Program
The Module object is the centerpiece of the DSPy and MLflow integration. With DSPy, you can create complex agentic logic via a module or set of modules.
pip install mlflow dspy -U
import dspy
# Define our language model
lm = dspy.LM(model="openai/gpt-4o-mini", max_tokens=250)
dspy.settings.configure(lm=lm)
# Define a Chain of Thought module
class CoT(dspy.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.prog = dspy.ChainOfThought("question -> answer")
def forward(self, question):
return self.prog(question=question)
dspy_model = CoT()
Typically you'd want to leverage a compiled DSPy module. MLflow will natively supports logging both compiled and uncompiled DSPy modules. Above we show an uncompiled version for simplicity, but in production you'd want to leverage an optimizer and log the outputted object instead.
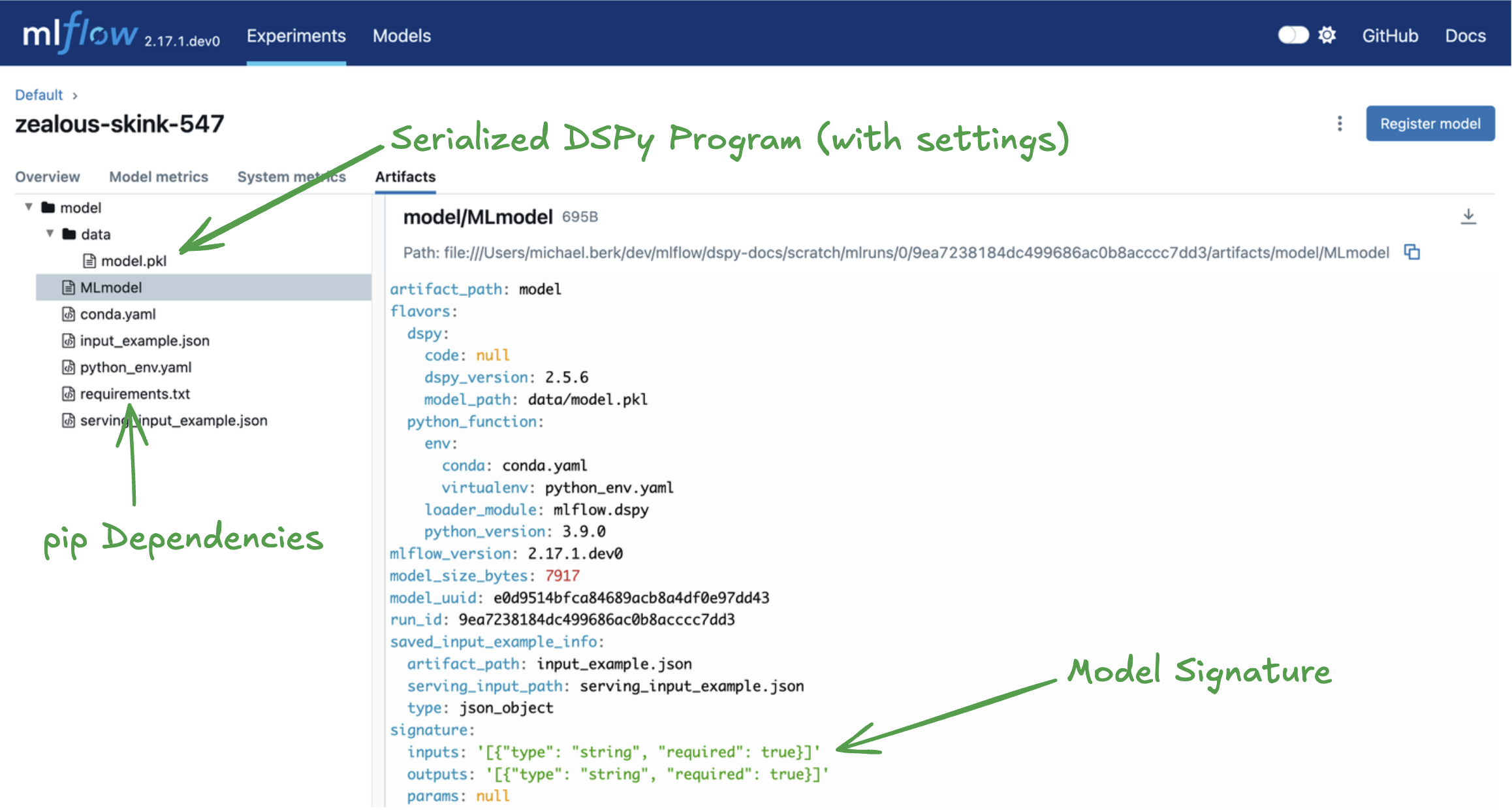
Logging the Program to MLflow
You can log the dspy.Module object to an MLflow run using the mlflow.dspy.log_model() function.
We will also specify a model signature. An MLflow model signature defines the expected schema for model inputs and outputs, ensuring consistency and correctness during model inference.
import mlflow
# Start an MLflow run
with mlflow.start_run():
# Log the model
model_info = mlflow.dspy.log_model(
dspy_model,
name="model",
input_example="what is 2 + 2?",
)
Loading the Module for inference
The saved module can be loaded back for inference using the mlflow.pyfunc.load_model() function. This function gives an MLflow Python Model backed by the DSPy module.
import mlflow
# Load the model as an MLflow PythonModel
model = mlflow.pyfunc.load_model(model_info.model_uri)
# Predict with the object
response = model.predict("What kind of bear is best?")
print(response)
{
"reasoning": """The question "What kind of bear is best?" is often associated with a
humorous reference from the television show "The Office," where the character Jim
Halpert jokingly states, "Bears, beets, Battlestar Galactica." However, if we consider
the question seriously, it depends on the context. Different species of bears have
different characteristics and adaptations that make them "best" in various ways.
For example, the American black bear is known for its adaptability, while the polar bear is
the largest land carnivore and is well adapted to its Arctic environment. Ultimately, the
answer can vary based on personal preference or specific criteria such as strength,
intelligence, or adaptability.""",
"answer": """There isn\'t a definitive answer, as it depends on the context. However, many
people humorously refer to the American black bear or the polar bear when discussing
"the best" kind of bear.""",
}
The MLflow PythonModel for DSPy supports streaming. To enable streaming, ensure the following conditions are met
- Install
dspyversion greater than 2.6.23. - Log your model with a signature.
- Ensure all outputs of your model are strings.
stream_response = model.predict_stream("What kind of bear is best?")
for output in stream_response:
print(output)
{"predict_name": "prog.predict", "signature_field_name": "reasoning", "chunk": "The"}
{
"predict_name": "prog.predict",
"signature_field_name": "reasoning",
"chunk": " question",
}
{"predict_name": "prog.predict", "signature_field_name": "reasoning", "chunk": " of"}
{"predict_name": "prog.predict", "signature_field_name": "reasoning", "chunk": " what"}
{"predict_name": "prog.predict", "signature_field_name": "reasoning", "chunk": " kind"}
{"predict_name": "prog.predict", "signature_field_name": "reasoning", "chunk": " of"}
{"predict_name": "prog.predict", "signature_field_name": "reasoning", "chunk": " bear"}
{"predict_name": "prog.predict", "signature_field_name": "reasoning", "chunk": " is"}
{"predict_name": "prog.predict", "signature_field_name": "reasoning", "chunk": " best"}
{"predict_name": "prog.predict", "signature_field_name": "reasoning", "chunk": " is"}
...
To load the DSPy program itself back instead of the PyFunc-wrapped model, use the mlflow.dspy.load_model() function.
model = mlflow.dspy.load_model(model_uri)
Optimizer Autologging
The MLflow DSPy flavor supports autologging for DSPy optimizers. See the Optimizer Autologging page for details.
常见问题
How can I save a compiled vs. uncompiled model?
DSPy compiles models by updating various LLM parameters, such as prompts, hyperparameters, and model weights, to optimize training. While MLflow allows logging both compiled and uncompiled models, it's generally preferable to use a compiled model, as it is expected to perform better in practice.
What can be serialized by MLflow?
When using mlflow.dspy.log_model() or mlflow.dspy.save_model() in MLflow, the DSPy program is serialized and saved to the tracking server as a .pkl file. This enables easy deployment. Under the hood, MLflow uses cloudpickle to serialize the DSPy object, but some DSPy artifacts are note serializable. Relevant examples are listed below.
- API tokens. These should be managed separately and passed securely via environment variables.
- The DSPy trace object, which is primarily used during training, not inference.
How do I manage secrets?
When serializing using the MLflow DSPy flavor, tokens are dropped from the settings objects. It is the user's responsibility to securely pass the required secrets to the deployment environment.
How is the DSPy settings object saved?
To ensure program reproducibility, the service context is converted to a Python dictionary and pickled with the model artifact. Service context is a concept that has been popularized in GenAI frameworks. Put simply, it stores a configuration that is global to your project. For DSPy specifically, we can set information such as the language model, reranker, adapter, etc.
DSPy stores this service context in a Settings singleton class. Sensitive API access keys that are set within the Settings object are not persisted when logging your model. When deploying your DSPy model, you must ensure that the deployment environment has these keys set so that your DSPy model can make remote calls to services that require access keys.