跟踪 Anthropic
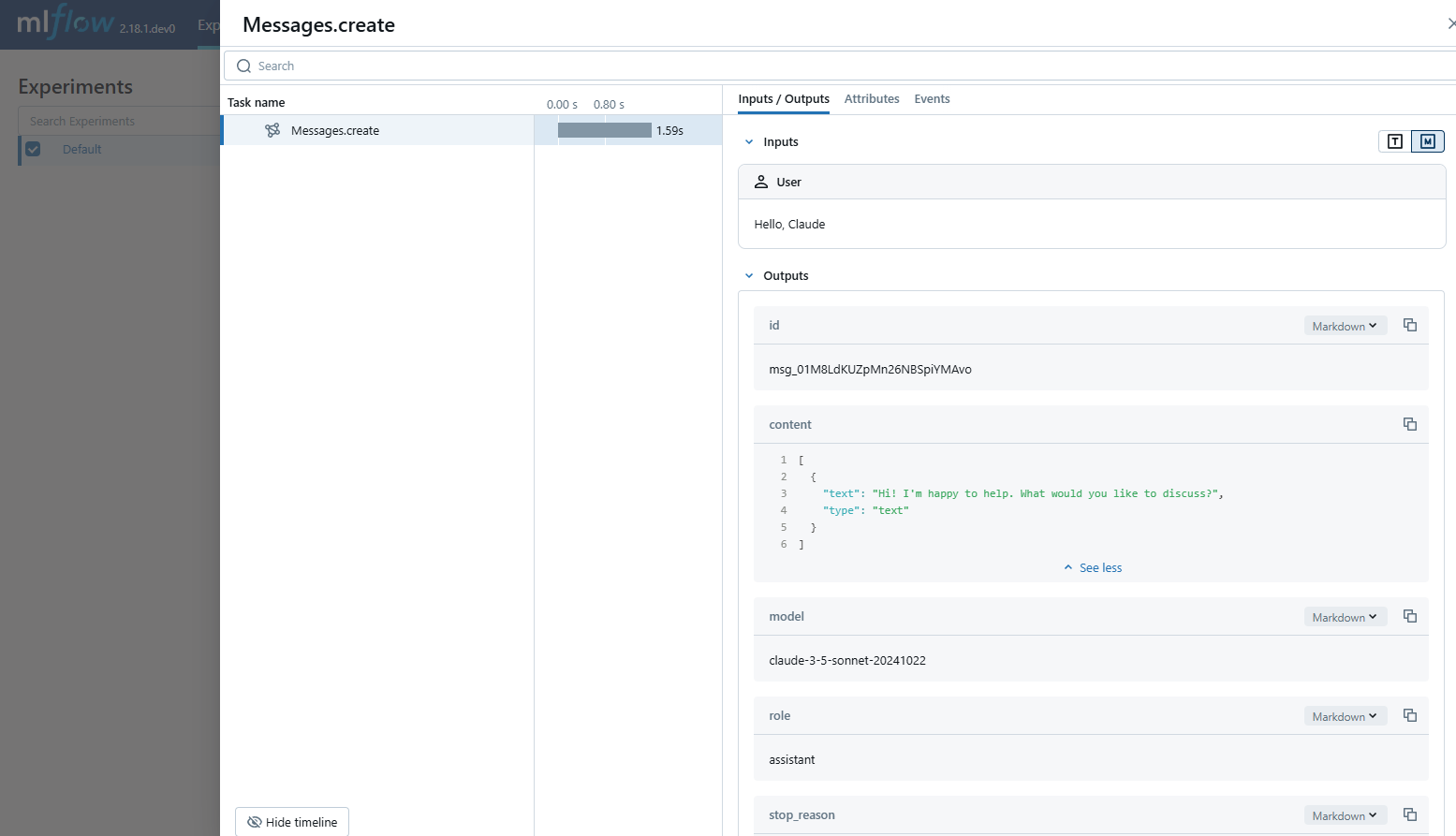
MLflow Tracing 为 Anthropic LLM 提供了自动跟踪功能。通过调用 mlflow.anthropic.autolog() 函数启用 Anthropic 的自动跟踪,MLflow 将在调用 Anthropic Python SDK 时捕获嵌套跟踪并将其记录到当前的 MLflow 实验中。在 Typescript 中,您可以改用 tracedAnthropic 函数来包装 Anthropic 客户端。
- Python
- JS / TS
import mlflow
mlflow.anthropic.autolog()
import Anthropic from "@anthropic-ai/sdk";
import { tracedAnthropic } from "mlflow-anthropic";
const client = tracedAnthropic(new Anthropic());
MLflow trace 会自动捕获 Anthropic 调用相关的以下信息
- 提示和完成响应
- 延迟
- 模型名称
- 如果指定,还包括额外的元数据,如
temperature、max_tokens。 - 如果响应中返回函数调用
- Token 使用信息
- 如果抛出任何异常
支持的 API
MLflow 支持以下 Anthropic API 的自动追踪
Python
| 聊天补全 | 函数调用 | 流式传输 | 异步 | 图像 | Batch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✅ | ✅ | - | ✅ (*1) | - | - |
(*1) Async 支持已在 MLflow 2.21.0 中添加。
TypeScript / JavaScript
| 聊天补全 | 函数调用 | 流式传输 | 异步 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ✅ | ✅ (*2) | - | ✅ |
(*2) 响应中的函数调用将被捕获,并可以在 MLflow UI 中进行渲染。TypeScript SDK 原生支持异步。
如需支持更多 API,请在 GitHub 上提交 功能请求。
基本示例
- Python
- JS / TS
import anthropic
import mlflow
# Enable auto-tracing for Anthropic
mlflow.anthropic.autolog()
# Optional: Set a tracking URI and an experiment
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("https://:5000")
mlflow.set_experiment("Anthropic")
# Configure your API key.
client = anthropic.Anthropic(api_key=os.environ["ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"])
# Use the create method to create new message.
message = client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022",
max_tokens=1024,
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, Claude"},
],
)
import Anthropic from "@anthropic-ai/sdk";
import { tracedAnthropic } from "mlflow-anthropic";
// Wrap the Anthropic client with the tracedAnthropic function
const client = tracedAnthropic(new Anthropic());
// Invoke the client as usual
const message = await client.messages.create({
model: "claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219",
max_tokens: 1024,
messages: [
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, Claude"},
],
});
异步
MLflow Tracing 自 MLflow 2.21.0 起支持 Anthropic SDK 的异步 API。其用法与同步 API 相同。
- Python
- JS / TS
import anthropic
# Enable trace logging
mlflow.anthropic.autolog()
client = anthropic.AsyncAnthropic()
response = await client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022",
max_tokens=1024,
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, Claude"},
],
)
Anthropic Typescript / Javascript SDK 原生支持异步。请参阅上面的基本示例。
高级示例:工具调用代理
MLflow Tracing 会自动捕获来自 Anthropic 模型的工具调用响应。响应中的函数指令将在跟踪 UI 中突出显示。此外,您还可以使用 @mlflow.trace 装饰器注解工具函数,为工具执行创建 span。
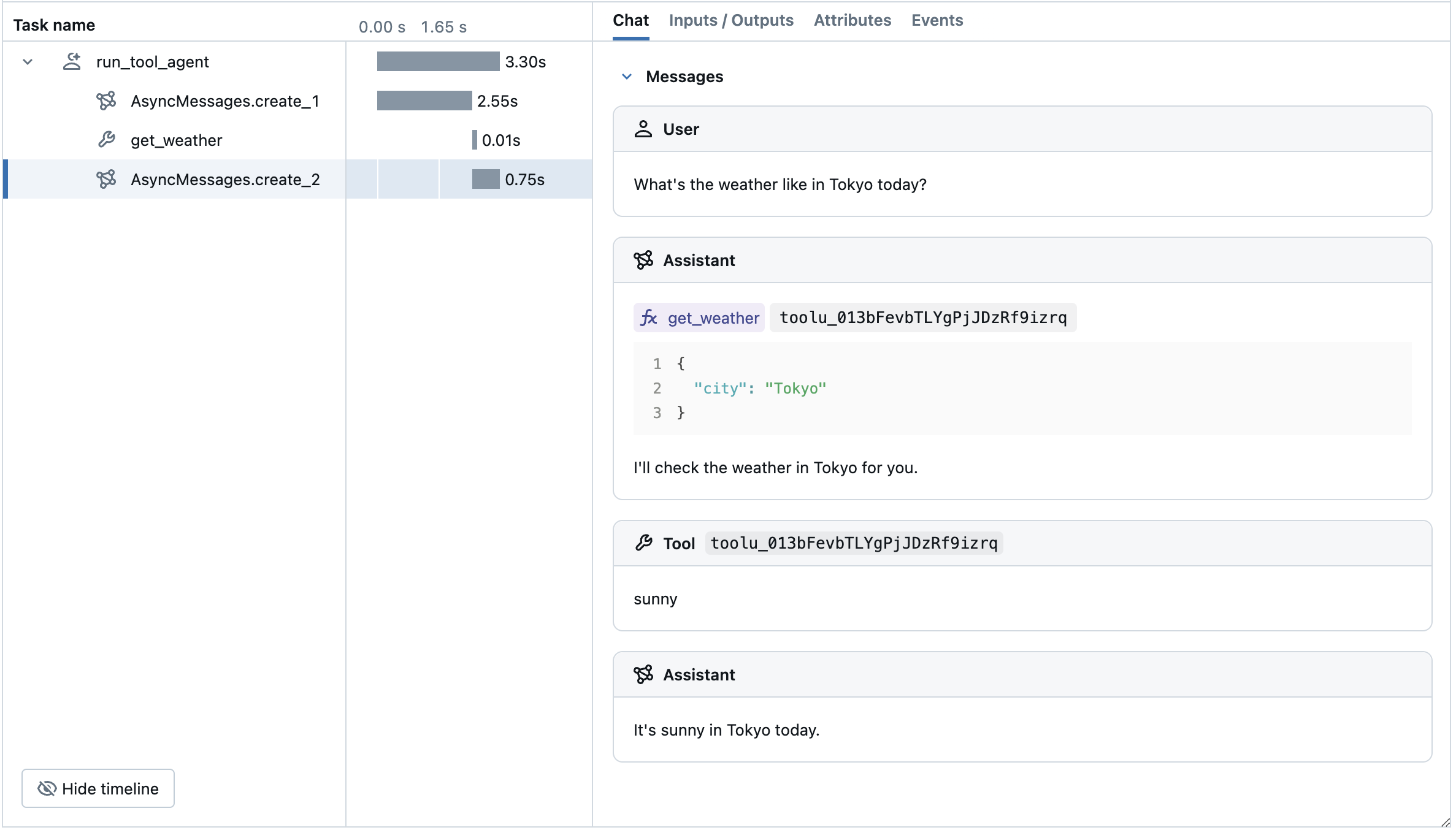
以下示例使用 Anthropic 工具调用和 MLflow Tracing for Anthropic 实现了一个简单的函数调用代理。该示例进一步使用了异步 Anthropic SDK,以便代理能够处理并发调用而不发生阻塞。
import json
import anthropic
import mlflow
import asyncio
from mlflow.entities import SpanType
client = anthropic.AsyncAnthropic()
model_name = "claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022"
# Define the tool function. Decorate it with `@mlflow.trace` to create a span for its execution.
@mlflow.trace(span_type=SpanType.TOOL)
async def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
if city == "Tokyo":
return "sunny"
elif city == "Paris":
return "rainy"
return "unknown"
tools = [
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Returns the weather condition of a given city.",
"input_schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {"city": {"type": "string"}},
"required": ["city"],
},
}
]
_tool_functions = {"get_weather": get_weather}
# Define a simple tool calling agent
@mlflow.trace(span_type=SpanType.AGENT)
async def run_tool_agent(question: str):
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": question}]
# Invoke the model with the given question and available tools
ai_msg = await client.messages.create(
model=model_name,
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
max_tokens=2048,
)
messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": ai_msg.content})
# If the model requests tool call(s), invoke the function with the specified arguments
tool_calls = [c for c in ai_msg.content if c.type == "tool_use"]
for tool_call in tool_calls:
if tool_func := _tool_functions.get(tool_call.name):
tool_result = await tool_func(**tool_call.input)
else:
raise RuntimeError("An invalid tool is returned from the assistant!")
messages.append(
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "tool_result",
"tool_use_id": tool_call.id,
"content": tool_result,
}
],
}
)
# Send the tool results to the model and get a new response
response = await client.messages.create(
model=model_name,
messages=messages,
max_tokens=2048,
)
return response.content[-1].text
# Run the tool calling agent
cities = ["Tokyo", "Paris", "Sydney"]
questions = [f"What's the weather like in {city} today?" for city in cities]
answers = await asyncio.gather(*(run_tool_agent(q) for q in questions))
for city, answer in zip(cities, answers):
print(f"{city}: {answer}")
Token 用量
MLflow >= 3.2.0 支持 Anthropic 的 token 使用情况跟踪。每次 LLM 调用的 token 使用情况将记录在 mlflow.chat.tokenUsage 属性中。跟踪期间的总 token 使用情况可在 trace info 对象的 token_usage 字段中找到。
- Python
- JS / TS
import json
import mlflow
mlflow.anthropic.autolog()
client = anthropic.Anthropic()
message = client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022",
max_tokens=1024,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Hello"}],
)
# Get the trace object just created
last_trace_id = mlflow.get_last_active_trace_id()
trace = mlflow.get_trace(trace_id=last_trace_id)
# Print the token usage
total_usage = trace.info.token_usage
print("== Total token usage: ==")
print(f" Input tokens: {total_usage['input_tokens']}")
print(f" Output tokens: {total_usage['output_tokens']}")
print(f" Total tokens: {total_usage['total_tokens']}")
# Print the token usage for each LLM call
print("\n== Detailed usage for each LLM call: ==")
for span in trace.data.spans:
if usage := span.get_attribute("mlflow.chat.tokenUsage"):
print(f"{span.name}:")
print(f" Input tokens: {usage['input_tokens']}")
print(f" Output tokens: {usage['output_tokens']}")
print(f" Total tokens: {usage['total_tokens']}")
import * as mlflow from "mlflow-tracing";
// After your Anthropic call completes, flush and fetch the trace
await mlflow.flushTraces();
const lastTraceId = mlflow.getLastActiveTraceId();
if (lastTraceId) {
const client = new mlflow.MlflowClient({ trackingUri: "https://:5000" });
const trace = await client.getTrace(lastTraceId);
// Total token usage on the trace
console.log("== Total token usage: ==");
console.log(trace.info.tokenUsage); // { input_tokens, output_tokens, total_tokens }
// Per-span usage (if provided by the provider)
console.log("\n== Detailed usage for each LLM call: ==");
for (const span of trace.data.spans) {
const usage = span.attributes?.["mlflow.chat.tokenUsage"];
if (usage) {
console.log(`${span.name}:`, usage);
}
}
}
== Total token usage: ==
Input tokens: 8
Output tokens: 12
Total tokens: 20
== Detailed usage for each LLM call: ==
Messages.create:
Input tokens: 8
Output tokens: 12
Total tokens: 20
支持的 API:
以下 Anthropic API 支持 token 使用情况跟踪
| 聊天补全 | 函数调用 | 流式传输 | 异步 | 图像 | Batch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✅ | ✅ | - | ✅ (*1) | - | - |
(*1) Async 支持已在 MLflow 2.21.0 中添加。
禁用自动跟踪
可以通过调用 mlflow.anthropic.autolog(disable=True) 或 mlflow.autolog(disable=True) 来全局禁用 Anthropic 的自动跟踪。