DSPy 快速入门
DSPy 通过用结构化的“文本转换图”取代手动 Prompt 工程,从而简化了构建语言模型(LM)管道的过程。这些图使用灵活的、可学习的模块,自动化并优化 LM 任务,例如推理、检索和回答复杂问题。
工作原理是什么?
从高层次上看,DSPy 会优化 Prompt,选择最佳语言模型,甚至可以使用训练数据对模型进行微调。
该过程遵循以下三个步骤,这在大多数 DSPy 优化器中都很常见
- 候选生成:DSPy 在程序中查找所有
Predict模块,并生成指令和演示(例如,用于 Prompt 的示例)的变体。此步骤为下一阶段创建了一组可能的候选对象。 - 参数优化:DSPy 然后使用随机搜索、TPE 或 Optuna 等方法来选择最佳候选对象。在此阶段也可以进行模型微调。
本演示
下面我们将创建一个简单的程序来演示 DSPy 的强大功能。我们将利用 OpenAI 构建一个文本分类器。在本教程结束时,我们将...
- 定义一个 dspy.Signature 和一个 dspy.Module 来执行文本分类。
- 利用 dspy.teleprompt.BootstrapFewShotWithRandomSearch 来编译我们的模块,使其更好地对文本进行分类。
- 使用 MLflow Tracing 分析内部步骤。
- 使用 MLflow 记录已编译模型。
- 加载已记录的模型并执行推理。
%pip install -U openai dspy>=2.5.17 mlflow>=2.18.0
zsh:1: 2.5.1 not found Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
设置
设置 LLM
安装相关依赖项后,让我们利用 Databricks 基础模型服务终端作为我们选择的 LLM。这里,我们将利用 OpenAI 的 gpt-4o-mini 模型。
# Set OpenAI API Key to the environment variable. You can also pass the token to dspy.LM()
import getpass
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("Enter your OpenAI Key:")
import dspy
# Define your model. We will use OpenAI for simplicity
model_name = "gpt-4o-mini"
# Leverage default authentication inside the Databricks context (notebooks, workflows, etc.)
# Note that an OPENAI_API_KEY environment must be present. You can also pass the token to dspy.LM()
lm = dspy.LM(
model=f"openai/{model_name}",
max_tokens=500,
temperature=0.1,
)
dspy.settings.configure(lm=lm)
创建 MLflow Experiment
创建一个新的 MLflow Experiment 来在一个地方跟踪您的 DSPy 模型、指标、参数和跟踪信息。尽管您的工作空间中已经创建了一个“default”实验,但强烈建议为不同的任务创建单独的实验以组织实验工件。
💡 如果您在 Databricks Notebook 上运行本教程,请跳过此步骤。当您创建任何笔记本时,会自动设置一个 MLflow experiment。
import mlflow
mlflow.set_experiment("DSPy Quickstart")
开启 MLflow 自动跟踪
MLflow Tracing 是一个强大的可观测性工具,用于监控和调试您的 DSPy 模块内部发生的情况,帮助您快速识别潜在的瓶颈或问题。要启用 DSPy 跟踪,您只需调用 mlflow.dspy.autolog 即可!
mlflow.dspy.autolog()
设置数据
接下来,我们将从 Huggingface 下载 Reuters 21578 数据集。我们还编写了一个实用程序,以确保我们的训练/测试集具有相同的标签。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from dspy.datasets.dataset import Dataset
def read_data_and_subset_to_categories() -> tuple[pd.DataFrame]:
"""
Read the reuters-21578 dataset. Docs can be found in the url below:
https://hugging-face.cn/datasets/yangwang825/reuters-21578
"""
# Read train/test split
file_path = "hf://datasets/yangwang825/reuters-21578/{}.json"
train = pd.read_json(file_path.format("train"))
test = pd.read_json(file_path.format("test"))
# Clean the labels
label_map = {
0: "acq",
1: "crude",
2: "earn",
3: "grain",
4: "interest",
5: "money-fx",
6: "ship",
7: "trade",
}
train["label"] = train["label"].map(label_map)
test["label"] = test["label"].map(label_map)
return train, test
class CSVDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(
self, n_train_per_label: int = 20, n_test_per_label: int = 10, *args, **kwargs
) -> None:
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.n_train_per_label = n_train_per_label
self.n_test_per_label = n_test_per_label
self._create_train_test_split_and_ensure_labels()
def _create_train_test_split_and_ensure_labels(self) -> None:
"""Perform a train/test split that ensure labels in `dev` are also in `train`."""
# Read the data
train_df, test_df = read_data_and_subset_to_categories()
# Sample for each label
train_samples_df = pd.concat(
[group.sample(n=self.n_train_per_label) for _, group in train_df.groupby("label")]
)
test_samples_df = pd.concat(
[group.sample(n=self.n_test_per_label) for _, group in test_df.groupby("label")]
)
# Set DSPy class variables
self._train = train_samples_df.to_dict(orient="records")
self._dev = test_samples_df.to_dict(orient="records")
# Limit to a small dataset to showcase the value of bootstrapping
dataset = CSVDataset(n_train_per_label=3, n_test_per_label=1)
# Create train and test sets containing DSPy
# Note that we must specify the expected input value name
train_dataset = [example.with_inputs("text") for example in dataset.train]
test_dataset = [example.with_inputs("text") for example in dataset.dev]
unique_train_labels = {example.label for example in dataset.train}
print(len(train_dataset), len(test_dataset))
print(f"Train labels: {unique_train_labels}")
print(train_dataset[0])
24 8
Train labels: {'interest', 'acq', 'grain', 'earn', 'money-fx', 'ship', 'crude', 'trade'}
Example({'label': 'interest', 'text': 'u s urges banks to weigh philippine debt plan the u s is urging reluctant commercial banks to seriously consider accepting a novel philippine proposal for paying its interest bill and believes the innovation is fully consistent with its third world debt strategy a reagan administration official said the official s comments also suggest that debtors pleas for interest rate concessions should be treated much more seriously by the commercial banks in cases where developing nations are carrying out genuine economic reforms in addition he signaled that the banks might want to reconsider the idea of a megabank where third world debt would be pooled and suggested the administration would support such a plan even though it was not formally proposing it at the same time however the official expressed reservations that such a scheme would ever get off the ground the philippine proposal together with argentine suggestions that exit bonds be issued to end the troublesome role of small banks in the debt strategy would help to underpin the flagging role of private banks within the plan the official said in an interview with reuters all of these things would fit within the definition of our initiative as we have asked it and we think any novel and unique approach such as those should be considered said the official who asked not to be named in october washington outlined a debt crisis strategy under which commercial banks and multilateral institutions such as the world bank and the international monetary fund imf were urged to step up lending to major debtors nations in return america called on the debtor countries to enact economic reforms promoting inflation free economic growth the multilaterals have been performing well the debtors have been performing well said the official but he admitted that the largest third world debtor brazil was clearly an exception the official who played a key role in developing the u s debt strategy and is an administration economic policymaker also said these new ideas would help commercial banks improve their role in resolving the third world debt crisis we called at the very beginning for the bank syndications to find procedures or processes whereby they could operate more effectively the official said among those ideas the official said were suggestions that commercial banks create a megabank which could swap third world debt paper for so called exit bonds for banks like regional american or european institutions such bonds in theory would rid these banks of the need to lend money to their former debtors every time a new money package was assembled and has been suggested by argentina in its current negotiations for a new loan of billion dlrs he emphasised that the megabank was not an administration plan but something some people have suggested other u s officials said japanese commercial banks are examining the creation of a consortium bank to assume third world debt this plan actively under consideration would differ slightly from the one the official described but the official expressed deep misgivings that such a plan would work in the united states if the banks thought that that was a suitable way to go fine i don t think they ever will he pointed out that banks would swap their third world loans for capital in the megabank and might then be reluctant to provide new money to debtors through the new institution meanwhile the official praised the philippine plan under which it would make interest payments on its debt in cash at no more than pct above libor the philippine proposal is very interesting it s quite unique and i don t think it s something that should be categorically rejected out of hand the official said banks which found this level unacceptably low would be offered an alternative of libor payments in cash and a margin above that of one pct in the form of philippine investment notes these tradeable dollar denominated notes would have a six year life and if banks swapped them for cash before maturity the country would guarantee a payment of point over libor until now bankers have criticised these spreads as far too low the talks now in their second week are aimed at stretching out repayments of billion dlrs of debt and granting easier terms on billion of already rescheduled debt the country which has enjoyed strong political support in washington since corazon aquino came to power early last year owes an overall billion dlrs of debt but the official denied the plan amounts to interest rate capitalisation a development until now unacceptable to the banks it s no more interest rate capitalisation than if you have a write down in the spread over libor from what existed before the official said in comments suggesting some ought to be granted the rate concessions they seek some people argue that cutting the spread is debt forgiveness what it really is is narrowing the spread on new money he added he said the u s debt strategy is sufficiently broad as an initiative to include plans like the philippines reuter'}) (input_keys={'text'})
设置 DSPy Signature 和 Module
最后,我们将定义我们的任务:文本分类。
您可以通过多种方式为 DSPy Signature 行为提供指导。目前,DSPy 允许用户指定
- 通过类文档字符串提供高层次目标。
- 一组输入字段,带有可选元数据。
- 一组输出字段,带有可选元数据。
DSPy 将利用这些信息来进行优化。
在下面的示例中,请注意我们只是简单地将预期标签提供给 TextClassificationSignature 类中的 output 字段。从这个初始状态,我们将寻求使用 DSPy 来学习提高分类器的准确性。
class TextClassificationSignature(dspy.Signature):
text = dspy.InputField()
label = dspy.OutputField(
desc=f"Label of predicted class. Possible labels are {unique_train_labels}"
)
class TextClassifier(dspy.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.generate_classification = dspy.Predict(TextClassificationSignature)
def forward(self, text: str):
return self.generate_classification(text=text)
运行!
Hello World
让我们通过 DSPy 模块和相关的 Signature 来演示预测。程序已从 Signature 的 desc 字段正确学习了我们的标签并生成了合理的预测。
from copy import copy
# Initilize our impact_improvement class
text_classifier = copy(TextClassifier())
message = "I am interested in space"
print(text_classifier(text=message))
message = "I enjoy ice skating"
print(text_classifier(text=message))
Prediction( label='interest' ) Prediction( label='interest' )
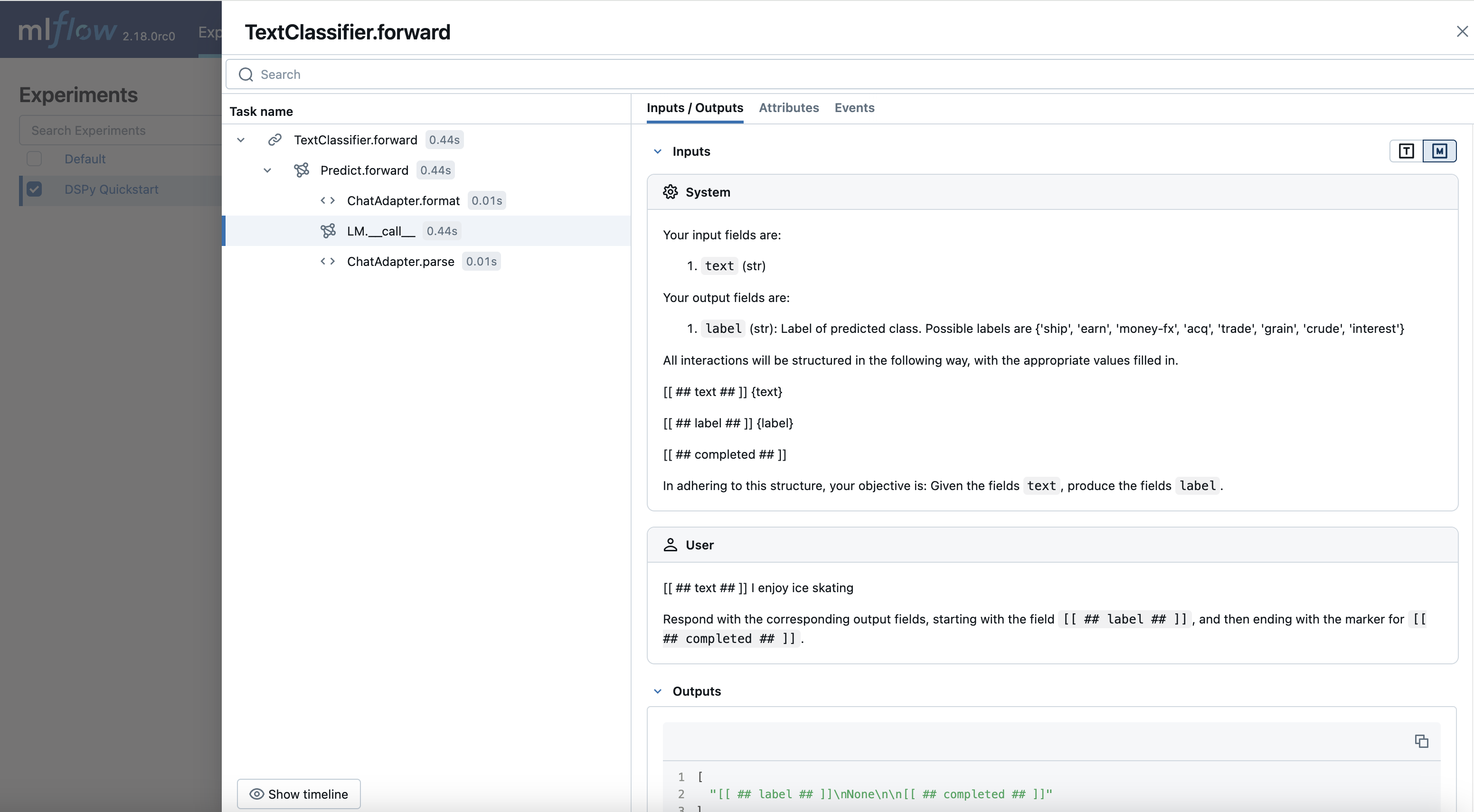
查看跟踪
- 打开 MLflow UI 并选择
"DSPy Quickstart"实验。 - 转到
"Traces"标签页查看生成的跟踪信息。
现在,您可以观察 DSPy 如何转换您的查询并与 LLM 交互。此功能对于调试、迭代改进系统中的组件以及监控生产环境中的模型非常宝贵。虽然本教程中的模块相对简单,但随着模型复杂度的增加,跟踪功能将变得更加强大。
编译
训练
为了进行训练,我们将利用 BootstrapFewShotWithRandomSearch,这是一个优化器,它将从我们的训练集中获取 Bootstrap 样本,并利用随机搜索策略来优化我们的预测准确性。
请注意,在下面的示例中,我们利用了在 validate_classification 中定义的简单精确匹配指标,但是 dspy.Metrics 可以包含复杂的基于 LM 的逻辑来正确评估我们的准确性。
from dspy.teleprompt import BootstrapFewShotWithRandomSearch
def validate_classification(example, prediction, trace=None) -> bool:
return example.label == prediction.label
optimizer = BootstrapFewShotWithRandomSearch(
metric=validate_classification,
num_candidate_programs=5,
max_bootstrapped_demos=2,
num_threads=1,
)
compiled_pe = optimizer.compile(copy(TextClassifier()), trainset=train_dataset)
Going to sample between 1 and 2 traces per predictor. Will attempt to bootstrap 5 candidate sets. Average Metric: 19 / 24 (79.2): 100%|██████████| 24/24 [00:19<00:00, 1.26it/s] New best score: 79.17 for seed -3 Scores so far: [79.17] Best score so far: 79.17 Average Metric: 22 / 24 (91.7): 100%|██████████| 24/24 [00:20<00:00, 1.17it/s] New best score: 91.67 for seed -2 Scores so far: [79.17, 91.67] Best score so far: 91.67
17%|█▋ | 4/24 [00:02<00:13, 1.50it/s]
Bootstrapped 2 full traces after 5 examples in round 0. Average Metric: 21 / 24 (87.5): 100%|██████████| 24/24 [00:19<00:00, 1.21it/s] Scores so far: [79.17, 91.67, 87.5] Best score so far: 91.67
12%|█▎ | 3/24 [00:02<00:18, 1.13it/s]
Bootstrapped 2 full traces after 4 examples in round 0. Average Metric: 22 / 24 (91.7): 100%|██████████| 24/24 [00:29<00:00, 1.23s/it] Scores so far: [79.17, 91.67, 87.5, 91.67] Best score so far: 91.67
4%|▍ | 1/24 [00:00<00:18, 1.27it/s]
Bootstrapped 1 full traces after 2 examples in round 0. Average Metric: 22 / 24 (91.7): 100%|██████████| 24/24 [00:20<00:00, 1.18it/s] Scores so far: [79.17, 91.67, 87.5, 91.67, 91.67] Best score so far: 91.67
8%|▊ | 2/24 [00:01<00:20, 1.10it/s]
Bootstrapped 1 full traces after 3 examples in round 0. Average Metric: 22 / 24 (91.7): 100%|██████████| 24/24 [00:22<00:00, 1.06it/s] Scores so far: [79.17, 91.67, 87.5, 91.67, 91.67, 91.67] Best score so far: 91.67
4%|▍ | 1/24 [00:01<00:30, 1.31s/it]
Bootstrapped 1 full traces after 2 examples in round 0. Average Metric: 23 / 24 (95.8): 100%|██████████| 24/24 [00:25<00:00, 1.04s/it] New best score: 95.83 for seed 3 Scores so far: [79.17, 91.67, 87.5, 91.67, 91.67, 91.67, 95.83] Best score so far: 95.83
4%|▍ | 1/24 [00:00<00:20, 1.12it/s]
Bootstrapped 1 full traces after 2 examples in round 0. Average Metric: 22 / 24 (91.7): 100%|██████████| 24/24 [00:24<00:00, 1.03s/it] Scores so far: [79.17, 91.67, 87.5, 91.67, 91.67, 91.67, 95.83, 91.67] Best score so far: 95.83 8 candidate programs found.
比较编译前/后的准确率
最后,让我们看看我们训练好的模型在未见过测试数据上的预测效果如何。
def check_accuracy(classifier, test_data: pd.DataFrame = test_dataset) -> float:
residuals = []
predictions = []
for example in test_data:
prediction = classifier(text=example["text"])
residuals.append(int(validate_classification(example, prediction)))
predictions.append(prediction)
return residuals, predictions
uncompiled_residuals, uncompiled_predictions = check_accuracy(copy(TextClassifier()))
print(f"Uncompiled accuracy: {np.mean(uncompiled_residuals)}")
compiled_residuals, compiled_predictions = check_accuracy(compiled_pe)
print(f"Compiled accuracy: {np.mean(compiled_residuals)}")
Uncompiled accuracy: 0.625 Compiled accuracy: 0.875
如上所示,我们编译后的准确率是非零的——我们的基础 LLM 仅通过我们的初始 Prompt 推断了分类标签的含义。然而,通过 DSPy 训练,Prompt、演示和输入/输出 Signature 已更新,使我们的模型在未见过的数据上达到了 88% 的准确率。这提升了 25 个百分点!
让我们看看测试集中的每个预测结果。
for uncompiled_residual, uncompiled_prediction in zip(uncompiled_residuals, uncompiled_predictions):
is_correct = "Correct" if bool(uncompiled_residual) else "Incorrect"
prediction = uncompiled_prediction.label
print(f"{is_correct} prediction: {' ' * (12 - len(is_correct))}{prediction}")
Incorrect prediction: money-fx Correct prediction: crude Correct prediction: money-fx Correct prediction: earn Incorrect prediction: interest Correct prediction: grain Correct prediction: trade Incorrect prediction: trade
for compiled_residual, compiled_prediction in zip(compiled_residuals, compiled_predictions):
is_correct = "Correct" if bool(compiled_residual) else "Incorrect"
prediction = compiled_prediction.label
print(f"{is_correct} prediction: {' ' * (12 - len(is_correct))}{prediction}")
Correct prediction: interest Correct prediction: crude Correct prediction: money-fx Correct prediction: earn Correct prediction: acq Correct prediction: grain Correct prediction: trade Incorrect prediction: crude
使用 MLflow 记录和加载模型
现在我们有了一个具有更高分类准确率的编译模型,让我们利用 MLflow 记录此模型并加载它以进行推理。
import mlflow
with mlflow.start_run():
model_info = mlflow.dspy.log_model(
compiled_pe,
"model",
input_example="what is 2 + 2?",
)
Downloading artifacts: 0%| | 0/7 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
再次打开 MLflow UI,检查已编译模型是否记录到了一个新的 MLflow Run 中。现在您可以使用 mlflow.dspy.load_model 或 mlflow.pyfunc.load_model 加载模型进行推理。
💡 MLflow 会记住存储在 dspy.settings 中的环境配置,例如实验期间使用的语言模型(LM)。这确保了您的实验具有出色的可重现性。
# Define input text
print("
==============Input Text============")
text = test_dataset[0]["text"]
print(f"Text: {text}")
# Inference with original DSPy object
print("
--------------Original DSPy Prediction------------")
print(compiled_pe(text=text).label)
# Inference with loaded DSPy object
print("
--------------Loaded DSPy Prediction------------")
loaded_model_dspy = mlflow.dspy.load_model(model_info.model_uri)
print(loaded_model_dspy(text=text).label)
# Inference with MLflow PyFunc API
loaded_model_pyfunc = mlflow.pyfunc.load_model(model_info.model_uri)
print("
--------------PyFunc Prediction------------")
print(loaded_model_pyfunc.predict(text)["label"])
==============Input Text============ Text: top discount rate at u k bill tender rises to pct --------------Original DSPy Prediction------------ interest --------------Loaded DSPy Prediction------------ interest --------------PyFunc Prediction------------ interest
后续步骤
本示例演示了 DSPy 的工作原理。以下是使用 DSPy 和 MLflow 改进此项目的一些潜在扩展。
DSPy
MLflow
- 使用 MLflow serving 部署模型。
- 使用 MLflow 尝试各种优化策略。
祝您编码愉快!