使用 MLflow 3.0 的 GenAI Agent
前提条件:运行以下命令安装 MLflow 3.0 和 OpenAI 包。
pip install --upgrade mlflow>=3.0.0rc0 --pre
pip install openai
本示例演示了如何使用 MLflow 追踪和评估使用提示工程的 OpenAI 请求。它展示了如何注册提示、生成追踪以及使用评估数据集评估响应性能。该示例还强调了追踪交互式追踪并将它们链接到已记录模型以实现更好的可观测性的能力。
初始化 OpenAI 客户端
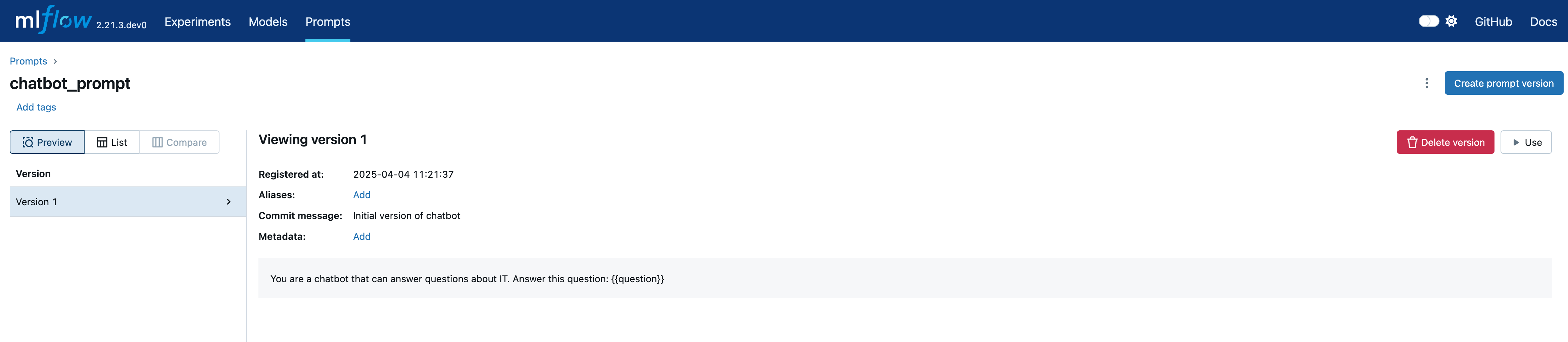
首先,我们初始化一个 OpenAI 客户端,使用其聊天完成 API 回答问题,并利用 MLflow 的提示注册功能有效管理和链接提示。
from openai import OpenAI
import mlflow
mlflow.set_experiment("genai_example")
client = OpenAI()
question = "What is MLflow?"
# register a prompt so we can link it when logging the model
system_prompt = mlflow.register_prompt(
name="chatbot_prompt",
template="You are a chatbot that can answer questions about IT. Answer this question: {{question}}",
commit_message="Initial version of chatbot",
)
print(
client.completions.create(
prompt=system_prompt.format(question=question),
model="gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct",
temperature=0.1,
max_tokens=2000,
)
.choices[0]
.text
)
切换到提示 (Prompts) 选项卡查看注册的提示及其详细信息
通过追踪可观测性测试模型
在本节中,我们手动使用示例查询测试模型,并利用 MLflow Tracing 分析输出和调试潜在问题。启用自动日志记录后,MLflow 会自动创建一个 LoggedModel 并将生成的追踪链接到它,确保无缝的可观测性。
# Enable autologging so that interactive traces from the client are automatically linked to a LoggedModel
mlflow.openai.autolog()
questions = [
"What is MLflow Tracking and how does it work?",
"What is Unity Catalog?",
"What are user-defined functions (UDFs)?",
]
outputs = []
for question in questions:
outputs.append(
client.completions.create(
prompt=system_prompt.format(question=question),
model="gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct",
temperature=0.1,
max_tokens=2000,
)
.choices[0]
.text
)
logged_model = mlflow.last_logged_model()
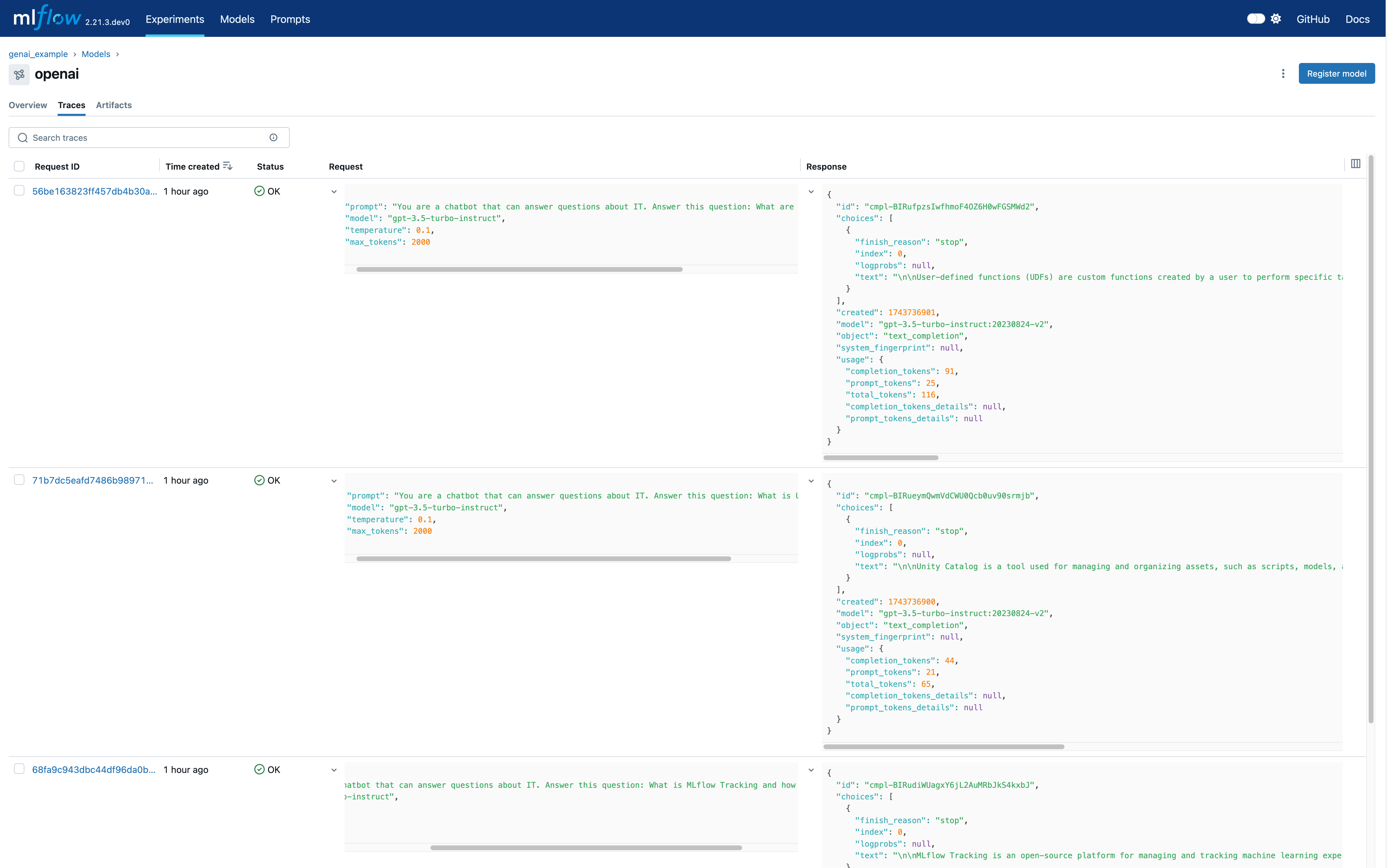
traces = mlflow.search_traces(model_id=logged_model.model_id)
print(traces)
# request_id trace ... tags assessments
# 0 56be163823ff457db4b30a97e704c709 Trace(request_id=56be163823ff457db4b30a97e704c... ... {'mlflow.artifactLocation': 'file:///Users/ser... []
# 1 71b7dc5eafd7486b989712e428a96522 Trace(request_id=71b7dc5eafd7486b989712e428a96... ... {'mlflow.artifactLocation': 'file:///Users/ser... []
# 2 68fa9c943dbc44df96da0b89611ed643 Trace(request_id=68fa9c943dbc44df96da0b89611ed... ... {'mlflow.artifactLocation': 'file:///Users/ser... []
查看实验中的模型 (Models) 选项卡以查看新记录的模型。
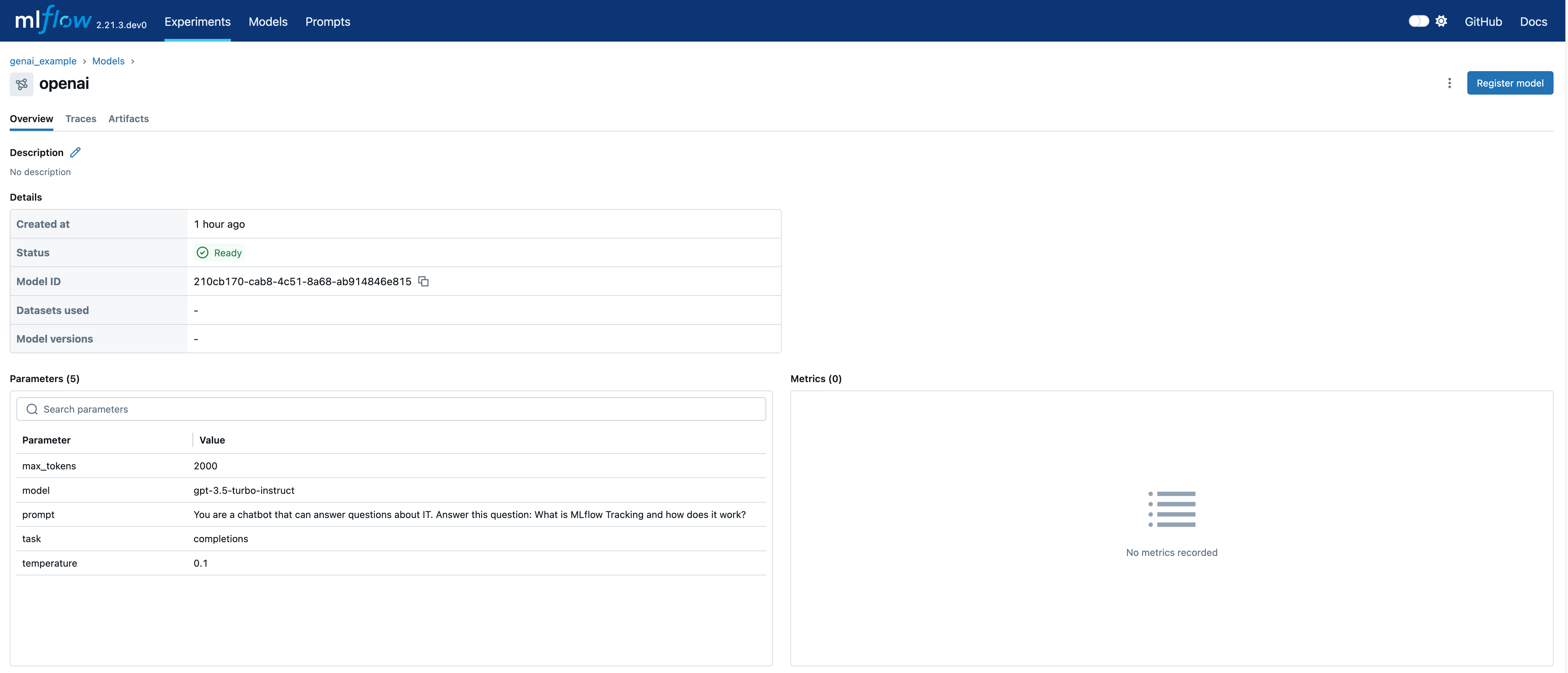
在已记录的模型 (Logged Model) 页面上,您可以查看详细信息,包括 model_id。
导航到模型页面的追踪 (Traces) 选项卡,您可以查看刚刚生成的追踪。
评估 Agent 的性能
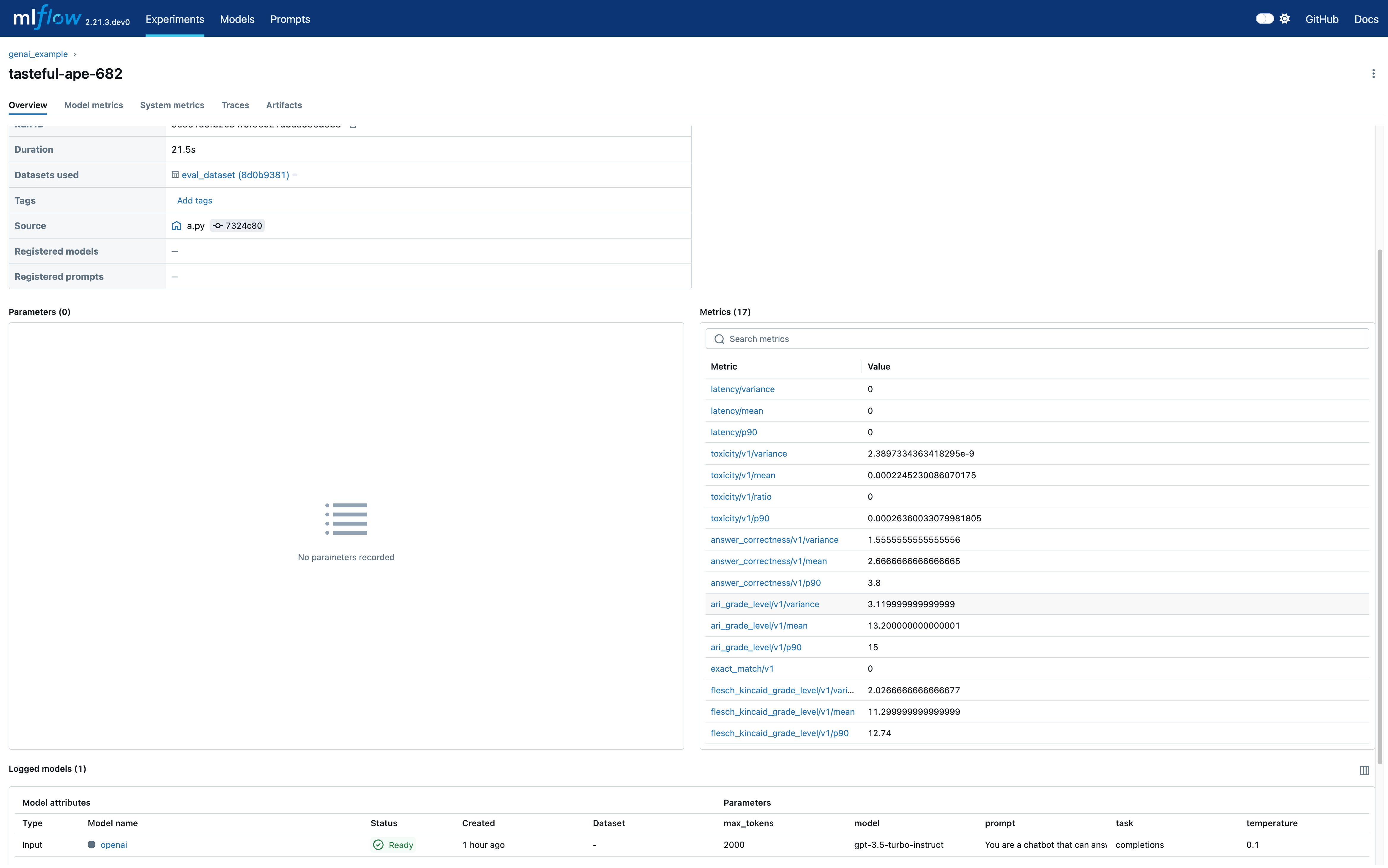
最后,我们使用mlflow.evaluate() 在评估数据集上评估已记录模型的性能。此步骤涉及计算额外指标,例如延迟和答案正确性,以更深入地了解模型的行为和准确性。
# Prepare the eval dataset in a pandas DataFrame
import pandas as pd
from mlflow.entities import LoggedModelInput
eval_df = pd.DataFrame(
{
"messages": questions,
"expected_response": [
"""MLflow Tracking is a key component of the MLflow platform designed to record and manage machine learning experiments. It enables data scientists and engineers to log parameters, code versions, metrics, and artifacts in a systematic way, facilitating experiment tracking and reproducibility.\n\nHow It Works:\n\nAt the heart of MLflow Tracking is the concept of a run, which is an execution of a machine learning code. Each run can log the following:\n\nParameters: Input variables or hyperparameters used in the model (e.g., learning rate, number of trees). Metrics: Quantitative measures to evaluate the model's performance (e.g., accuracy, loss). Artifacts: Output files like models, datasets, or images generated during the run. Source Code: The version of the code or Git commit hash used. These logs are stored in a tracking server, which can be set up locally or on a remote server. The tracking server uses a backend storage (like a database or file system) to keep a record of all runs and their associated data.\n\n Users interact with MLflow Tracking through its APIs available in multiple languages (Python, R, Java, etc.). By invoking these APIs in the code, you can start and end runs, and log data as the experiment progresses. Additionally, MLflow offers autologging capabilities for popular machine learning libraries, automatically capturing relevant parameters and metrics without manual code changes.\n\nThe logged data can be visualized using the MLflow UI, a web-based interface that displays all experiments and runs. This UI allows you to compare runs side-by-side, filter results, and analyze performance metrics over time. It aids in identifying the best models and understanding the impact of different parameters.\n\nBy providing a structured way to record experiments, MLflow Tracking enhances collaboration among team members, ensures transparency, and makes it easier to reproduce results. It integrates seamlessly with other MLflow components like Projects and Model Registry, offering a comprehensive solution for managing the machine learning lifecycle.""",
"""Unity Catalog is a feature in Databricks that allows you to create a centralized inventory of your data assets, such as tables, views, and functions, and share them across different teams and projects. It enables easy discovery, collaboration, and reuse of data assets within your organization.\n\nWith Unity Catalog, you can:\n\n1. Create a single source of truth for your data assets: Unity Catalog acts as a central repository of all your data assets, making it easier to find and access the data you need.\n2. Improve collaboration: By providing a shared inventory of data assets, Unity Catalog enables data scientists, engineers, and other stakeholders to collaborate more effectively.\n3. Foster reuse of data assets: Unity Catalog encourages the reuse of existing data assets, reducing the need to create new assets from scratch and improving overall efficiency.\n4. Enhance data governance: Unity Catalog provides a clear view of data assets, enabling better data governance and compliance.\n\nUnity Catalog is particularly useful in large organizations where data is scattered across different teams, projects, and environments. It helps create a unified view of data assets, making it easier to work with data across different teams and projects.""",
"""User-defined functions (UDFs) in the context of Databricks and Apache Spark are custom functions that you can create to perform specific tasks on your data. These functions are written in a programming language such as Python, Java, Scala, or SQL, and can be used to extend the built-in functionality of Spark.\n\nUDFs can be used to perform complex data transformations, data cleaning, or to apply custom business logic to your data. Once defined, UDFs can be invoked in SQL queries or in DataFrame transformations, allowing you to reuse your custom logic across multiple queries and applications.\n\nTo use UDFs in Databricks, you first need to define them in a supported programming language, and then register them with the SparkSession. Once registered, UDFs can be used in SQL queries or DataFrame transformations like any other built-in function.\n\nHere\'s an example of how to define and register a UDF in Python:\n\n```python\nfrom pyspark.sql.functions import udf\nfrom pyspark.sql.types import IntegerType\n\n# Define the UDF function\ndef multiply_by_two(value):\n return value * 2\n\n# Register the UDF with the SparkSession\nmultiply_udf = udf(multiply_by_two, IntegerType())\n\n# Use the UDF in a DataFrame transformation\ndata = spark.range(10)\nresult = data.withColumn("multiplied", multiply_udf(data.id))\nresult.show()\n```\n\nIn this example, we define a UDF called `multiply_by_two` that multiplies a given value by two. We then register this UDF with the SparkSession using the `udf` function, and use it in a DataFrame transformation to multiply the `id` column of a DataFrame by two.""",
],
"predictions": outputs,
}
)
# Start a run to represent the evaluation job
with mlflow.start_run() as evaluation_run:
eval_dataset = mlflow.data.from_pandas(
df=eval_df,
name="eval_dataset",
targets="expected_response",
predictions="predictions",
)
mlflow.log_input(
dataset=eval_dataset, model=LoggedModelInput(logged_model.model_id)
)
# Run the evaluation based on extra metrics
result = mlflow.evaluate(
data=eval_dataset,
model_type="question-answering",
extra_metrics=[
mlflow.metrics.latency(),
mlflow.metrics.genai.answer_correctness("openai:/gpt-4o"),
],
# This is needed since answer_correctness looks for 'inputs' field
evaluator_config={"col_mapping": {"inputs": "messages"}},
)
print(result.tables["eval_results_table"])
# messages ... answer_correctness/v1/justification
# 0 What is MLflow Tracking and how does it work? ... The output is mostly correct, providing accura...
# 1 What is Unity Catalog? ... The output is completely incorrect as it descr...
# 2 What are user-defined functions (UDFs)? ... The output provides a general definition of us...
导航到评估运行,您可以在 MLflow UI 中查看显示的指标及其详细信息。这包括延迟和答案正确性等指标,提供了对模型性能的深入了解。