使用模型记录 Prompt
Prompt 通常作为生成式AI应用程序的一部分使用。管理 Prompt 和模型之间的关联对于追踪模型的演变并确保不同环境之间的一致性至关重要。MLflow Prompt Registry 与 MLflow 的模型追踪功能集成,让您可以追踪模型和应用程序使用了哪些 Prompt(及版本)。
基本用法
要记录带有关联 Prompt 的模型,请在 log_model 方法中使用 prompts 参数。prompts 参数接受一个与模型关联的 Prompt URL 或 Prompt 对象列表。关联的 Prompt 会显示在模型运行的 MLflow UI 中。
import mlflow
with mlflow.start_run():
mlflow.<flavor>.log_model(
model,
...
# Specify a list of prompt URLs or prompt objects.
prompts=["prompts:/summarization-prompt/2"]
)
用于将 Prompt 与模型关联的 prompts 参数仅支持生成式AI风格,例如 OpenAI, LangChain, LlamaIndex, DSPy 等。有关支持风格的完整列表,请参阅生成式AI风格。
示例 1: 使用 LangChain 记录 Prompt
1. 创建 Prompt
如果您还没有创建 Prompt,请按照此步骤创建一个新的 Prompt。
2. 使用注册的 Prompt 定义一个 Chain
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
# Load registered prompt
prompt = mlflow.load_prompt("prompts:/summarization-prompt/2")
# Create LangChain prompt object
langchain_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
(
# IMPORTANT: Convert prompt template from double to single curly braces format
"system",
prompt.to_single_brace_format(),
),
("placeholder", "{messages}"),
]
)
# Define the LangChain chain
llm = ChatOpenAI()
chain = langchain_prompt | llm
# Invoke the chain
response = chain.invoke({"num_sentences": 1, "sentences": "This is a test sentence."})
print(response)
3. 将 Chain 记录到 MLflow
然后将 Chain 记录到 MLflow,并在 prompts 参数中指定 Prompt URL
with mlflow.start_run(run_name="summarizer-model"):
mlflow.langchain.log_model(
chain, artifact_path="model", prompts=["prompts:/summarization-prompt/2"]
)
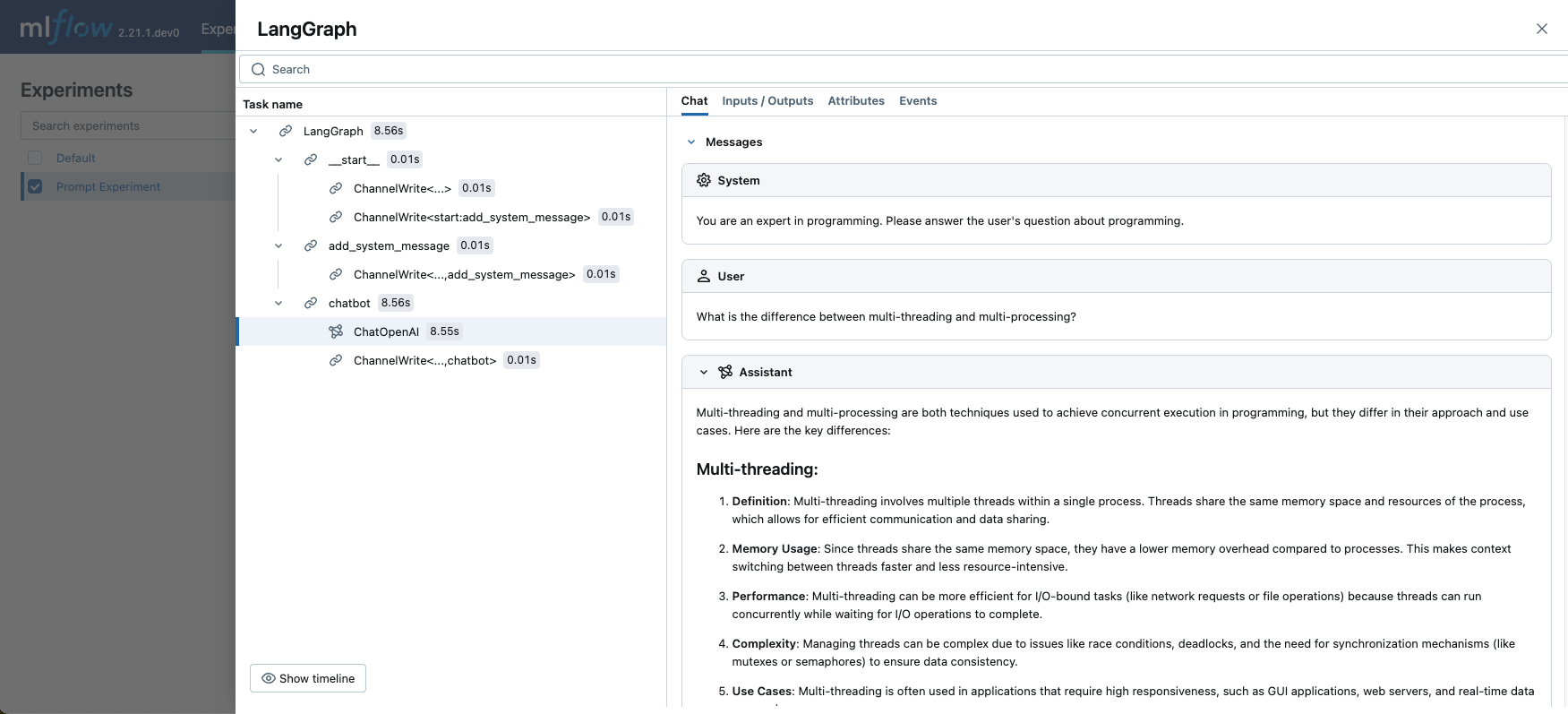
现在您可以在 MLflow UI 中查看与模型关联的 Prompt
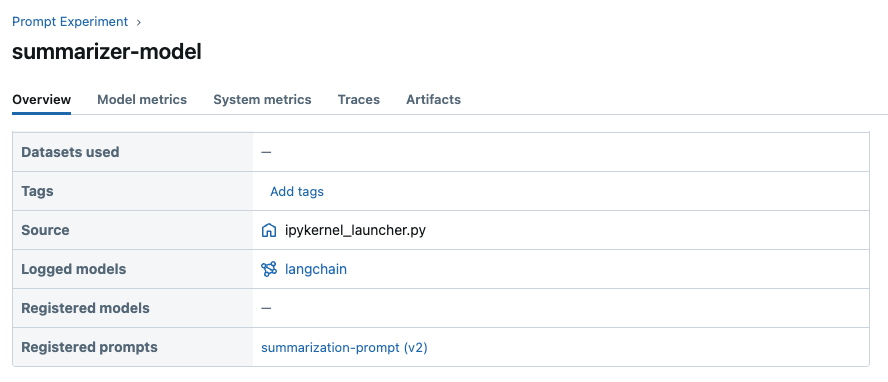
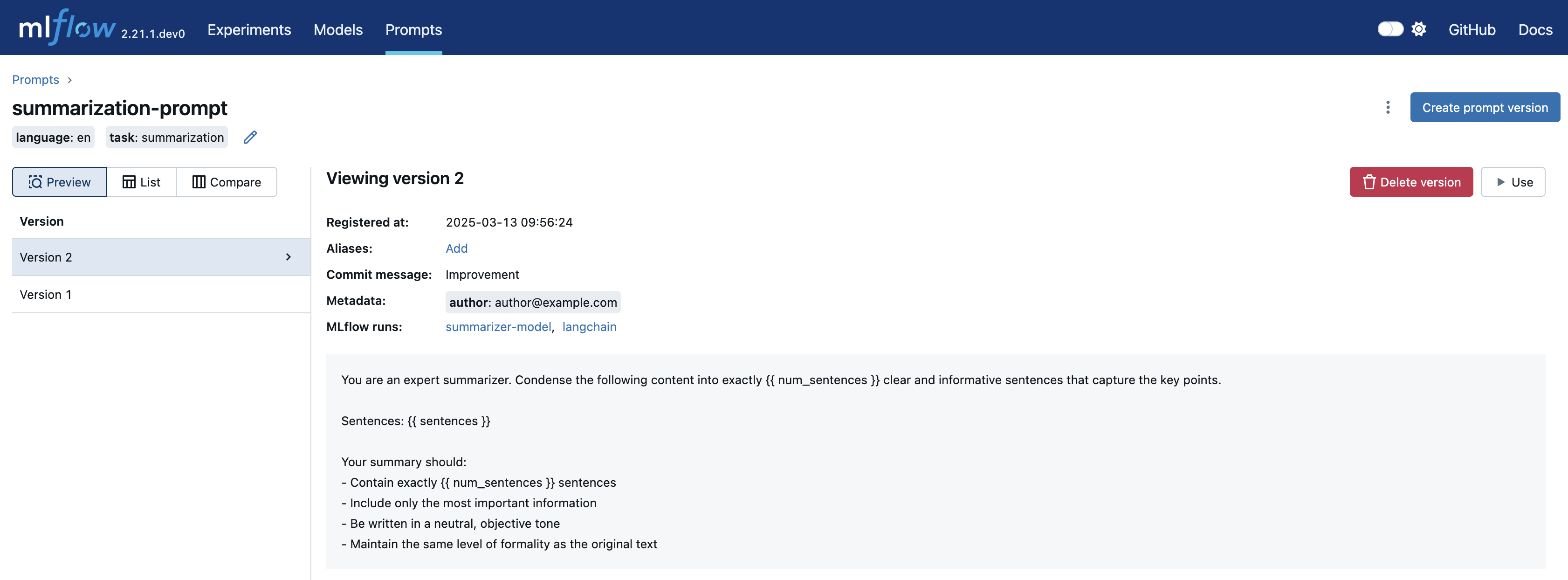
此外,您可以在 Prompt 详情页面查看使用特定 Prompt 的模型(运行)列表
示例 2: 使用 Models-from-Code 自动记录 Prompt
Models-from-Code 是一项允许您在代码中定义和记录模型的特性。使用代码记录模型带来了诸多好处,例如可移植性、可读性、避免序列化等。
结合 MLflow Prompt Registry,此特性解锁了管理 Prompt 版本的更多灵活性。值得注意的是,如果您的模型代码使用了 MLflow Prompt Registry 中的 Prompt,MLflow 会自动将其与模型一起记录。
在以下示例中,我们使用 LangGraph 定义了一个使用注册 Prompt 的非常简单的聊天机器人。
1. 创建 Prompt
import mlflow
# Register a new prompt
prompt = mlflow.register_prompt(
name="chat-prompt",
template="You are an expert in programming. Please answer the user's question about programming.",
)
2. 使用注册的 Prompt 定义一个 Graph
创建一个名为 chatbot.py 的 Python 脚本,内容如下。
如果您使用 Jupyter notebook,可以取消注释 %writefile magic 命令并在单元格中运行以下代码以生成脚本。
# %%writefile chatbot.py
import mlflow
from typing import Annotated
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
class State(TypedDict):
messages: list
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0.1)
system_prompt = mlflow.load_prompt("prompts:/chat-prompt/1")
def add_system_message(state: State):
return {
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": system_prompt.to_single_brace_format(),
},
*state["messages"],
]
}
def chatbot(state: State):
return {"messages": [llm.invoke(state["messages"])]}
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
graph_builder.add_node("add_system_message", add_system_message)
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)
graph_builder.add_edge(START, "add_system_message")
graph_builder.add_edge("add_system_message", "chatbot")
graph_builder.add_edge("chatbot", END)
graph = graph_builder.compile()
mlflow.models.set_model(graph)
3. 将 Graph 记录到 MLflow
在 model 参数中指定脚本的文件路径
with mlflow.start_run():
model_info = mlflow.langchain.log_model(
lc_model="./chatbot.py",
artifact_path="graph",
)
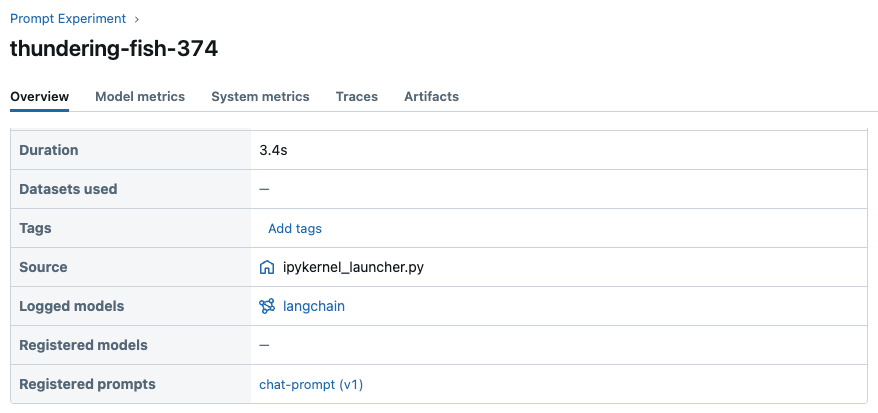
这次我们没有指定 prompts 参数,但 MLflow 会自动将脚本中加载的 Prompt 记录到日志模型中。现在您可以在 MLflow UI 中查看关联的 Prompt
4. 加载 Graph 并调用
最后,让我们将 Graph 加载回来并调用它,看看聊天机器人的实际运行效果。
# Enable MLflow tracing for LangChain to view the prompt passed to LLM.
mlflow.langchain.autolog()
# Load the graph
graph = mlflow.langchain.load_model(model_info.model_uri)
graph.invoke(
{
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is the difference between multi-threading and multi-processing?",
}
]
}
)