模型签名和输入示例
模型签名和输入示例是定义模型使用方式的基础组件,可确保 MLflow 生态系统中的一致且可靠的交互。
什么是模型签名和输入示例?
模型签名 - 定义模型输入、输出和参数的预期格式。将其视为一个合同,精确指定模型期望什么数据以及将返回什么。
模型输入示例 - 提供有效模型输入的具体示例。这有助于开发人员理解所需的数据格式并验证模型是否正常工作。
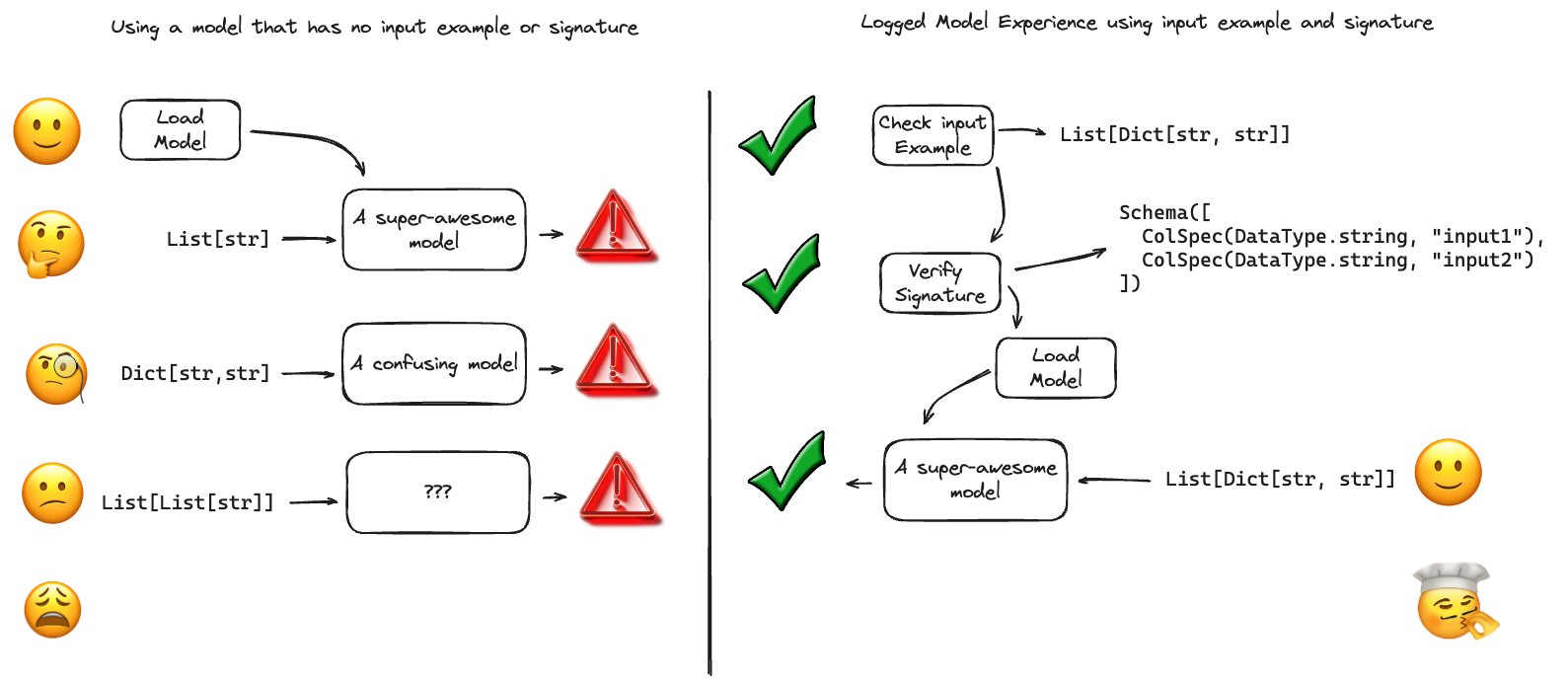
它们的重要性
模型签名和输入示例提供关键优势
- 一致性:确保所有模型交互都遵循相同的数据格式
- 验证:在数据格式错误到达模型之前捕获它们
- 文档:作为模型使用的实时文档
- 部署安全性:使 MLflow 部署工具能够自动验证请求
- UI 集成:允许 MLflow UI 显示清晰的模型要求
在 Databricks Unity Catalog 中注册模型需要模型签名。 Unity Catalog 会强制对所有注册模型执行具体的类型定义,并将拒绝没有适当签名的模型。在记录计划在 Databricks 环境中注册的模型时,请始终包含签名。
# ✅ Required for Databricks registration
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(
model,
name="my_model",
input_example=X_sample, # Generates required signature
signature=signature, # Or provide explicit signature
)
# ❌ Will fail in Databricks Unity Catalog
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(model, name="my_model") # No signature
快速入门:为模型添加签名
添加签名的最简单方法是在记录模型时提供输入示例
import mlflow
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
import pandas as pd
# Load data and train model
iris = load_iris(as_frame=True)
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
model = RandomForestClassifier().fit(X, y)
with mlflow.start_run():
# The input example automatically generates a signature
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(
model, name="iris_model", input_example=X.iloc[[0]] # First row as example
)
MLflow 自动
- 从输入示例推断签名
- 验证模型是否与示例一起正常工作
- 将签名和示例与模型一起存储
当您在模型记录过程中提供 input_example 时,MLflow 会自动生成模型签名。这适用于所有模型口味,并且是大多数用例的推荐方法。
理解模型签名
模型签名包含三个组成部分
- 输入模式
- 输出模式
- 参数模式
定义模型期望的数据结构和类型
# Column-based signature (DataFrames)
input_schema = Schema(
[
ColSpec("double", "sepal_length"),
ColSpec("double", "sepal_width"),
ColSpec("string", "species", required=False), # Optional field
]
)
# Tensor-based signature (NumPy arrays)
input_schema = Schema(
[TensorSpec(np.dtype(np.float32), (-1, 28, 28, 1))] # Batch of 28x28 images
)
主要特点:支持表格(DataFrame)和张量(NumPy)数据,通过 required=False 支持可选字段,以及丰富的(包括数组和对象)数据类型支持。
指定模型返回的内容
# Single prediction column
output_schema = Schema([ColSpec("long", "prediction")])
# Multiple outputs
output_schema = Schema(
[
ColSpec("double", "probability"),
ColSpec("string", "predicted_class"),
ColSpec("long", "confidence_score"),
]
)
# Tensor output
output_schema = Schema(
[TensorSpec(np.dtype(np.float32), (-1, 10))] # 10-class probabilities
)
定义可选的推理参数(如 temperature、max_length)
# Define inference parameters
params_schema = ParamSchema(
[
ParamSpec("temperature", "double", 0.7), # Default temperature
ParamSpec("max_tokens", "long", 100), # Default max tokens
ParamSpec("stop_words", "string", [".", "!"], (-1,)), # List parameter
]
)
# Use in model signature
signature = ModelSignature(
inputs=input_schema, outputs=output_schema, params=params_schema
)
常用参数: temperature 控制生成时的随机性,max_length/max_tokens 限制输出长度,top_k 和 top_p 控制采样策略,repetition_penalty 减少重复输出。
签名类型概览
MLflow 支持两种主要签名类型
基于列的签名 - 适用于表格数据(DataFrames、字典)
# Perfect for traditional ML models
{"feature_1": 1.5, "feature_2": "category_a", "feature_3": [1, 2, 3]}
基于张量的签名 - 适用于数组数据(图像、音频、嵌入)
# Perfect for deep learning models
np.array([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], [[7, 8, 9], [1, 2, 3]]]) # Shape: (2, 2, 3)
模型签名的类型提示
类型提示支持是在 MLflow 2.20.0 中引入的。如果您使用的是早期版本的 MLflow,请参阅 “使用签名” 部分。
您可以使用 Python 类型提示自动定义模型签名并启用数据验证。这提供了一种更 Pythonic 的方式来指定模型的接口,同时获得自动验证和模式推断。
- 概览和优势
- 支持的类型提示
- Pydantic 模型
- 验证和转换
- 特殊类型提示
- 服务和部署
类型提示快速入门
import mlflow
from typing import List, Dict, Optional
import pydantic
class Message(pydantic.BaseModel):
role: str
content: str
metadata: Optional[Dict[str, str]] = None
class CustomModel(mlflow.pyfunc.PythonModel):
def predict(self, model_input: List[Message]) -> List[str]:
# Signature automatically inferred from type hints!
return [msg.content for msg in model_input]
# Log model - signature is auto-generated from type hints
with mlflow.start_run():
mlflow.pyfunc.log_model(
name="chat_model",
python_model=CustomModel(),
input_example=[
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello"}
], # Validates against type hints
)
主要优势
- 自动验证:输入数据在运行时会根据类型提示进行验证
- 模式推断:模型签名根据类型注解自动生成
- 类型安全:在类型不匹配到达模型之前捕获它们
- IDE 支持:开发过程中更好的自动补全和错误检测
- 文档:类型提示充当自文档化代码
- 一致性:PythonModel 实例和加载的 PyFunc 模型具有相同的验证
何时使用类型提示
✅ 推荐用于:复杂数据结构(聊天消息、工具定义、嵌套对象)、需要严格输入验证的模型、使用现代 Python 开发实践的团队,以及具有结构化输入的 GenAI 和 LLM 应用程序。
⚠️ 考虑其他选项用于:简单的表格数据(DataFrames 配合输入示例即可),不采用类型提示的旧代码库,以及输入结构高度动态的模型。
输入类型要求
输入签名必须是 List[...],因为 PythonModel 期望批量数据
# ✅ Correct - Always use List wrapper
def predict(self, model_input: List[str]) -> List[str]:
...
def predict(self, model_input: List[Message]) -> List[Dict]:
...
# ❌ Incorrect - Missing List wrapper
def predict(self, model_input: str) -> str:
...
def predict(self, model_input: Message) -> Dict:
...
原始类型
List[str] # String inputs
List[int] # Integer inputs
List[float] # Float inputs
List[bool] # Boolean inputs
List[bytes] # Binary data
List[datetime.datetime] # Timestamps
集合类型
List[List[str]] # Nested lists
List[Dict[str, int]] # Dictionaries
List[Dict[str, List[str]]] # Complex nested structures
联合和可选类型
List[Union[int, str]] # Multiple possible types (becomes AnyType)
List[Optional[str]] # Optional fields (in Pydantic models only)
List[Any] # Any type (no validation)
Pydantic 模型(推荐)
class UserData(pydantic.BaseModel):
name: str
age: int
email: Optional[str] = None # Optional with default
preferences: List[str] = [] # List with default
List[UserData] # Clean, validated structure
类型提示到模式映射
| 类型提示 | 生成的模式 |
|---|---|
List[str] | Schema([ColSpec(type=DataType.string)]) |
List[List[str]] | Schema([ColSpec(type=Array(DataType.string))]) |
List[Dict[str, str]] | Schema([ColSpec(type=Map(DataType.string))]) |
List[Union[int, str]] | Schema([ColSpec(type=AnyType())]) |
List[Message] | Schema([ColSpec(type=Object(...))]) |
基本 Pydantic 用法
import pydantic
from typing import Optional, List, Dict
class Message(pydantic.BaseModel):
role: str
content: str
timestamp: Optional[str] = None
class CustomModel(mlflow.pyfunc.PythonModel):
def predict(self, model_input: List[Message]) -> List[str]:
return [f"{msg.role}: {msg.content}" for msg in model_input]
# Both work - automatic conversion
model.predict([Message(role="user", content="Hi")]) # Pydantic object
model.predict([{"role": "user", "content": "Hi"}]) # Dict (auto-converted)
复杂的嵌套模型
class FunctionParams(pydantic.BaseModel):
properties: Dict[str, str]
type: str = "object"
required: Optional[List[str]] = None
class ToolDefinition(pydantic.BaseModel):
name: str
description: Optional[str] = None
parameters: Optional[FunctionParams] = None
class ChatRequest(pydantic.BaseModel):
messages: List[Message]
tools: Optional[List[ToolDefinition]] = None
temperature: float = 0.7
@mlflow.pyfunc.utils.pyfunc
def advanced_predict(model_input: List[ChatRequest]) -> List[Dict[str, str]]:
results = []
for request in model_input:
# Type validation ensures request.messages exists and is properly typed
response = {"response": f"Processed {len(request.messages)} messages"}
if request.tools:
response["tools_count"] = str(len(request.tools))
results.append(response)
return results
灵活的基类
class BaseMessage(pydantic.BaseModel):
model_config = pydantic.ConfigDict(extra="allow") # Allow extra fields
role: str
content: str
class SystemMessage(BaseMessage):
system_prompt: str
class UserMessage(BaseMessage):
user_id: str
@mlflow.pyfunc.utils.pyfunc
def flexible_predict(model_input: List[BaseMessage]) -> List[str]:
# Input automatically converted to BaseMessage objects
# Extra fields from subclasses preserved
results = []
for msg in model_input:
result = f"{msg.role}: {msg.content}"
if hasattr(msg, "system_prompt"):
result += f" (system: {msg.system_prompt})"
elif hasattr(msg, "user_id"):
result += f" (user: {msg.user_id})"
results.append(result)
return results
Pydantic 最佳实践
始终为可选字段提供默认值
# ✅ Good - Optional fields have defaults
class Message(pydantic.BaseModel):
role: str
content: str
metadata: Optional[Dict[str, str]] = None
timestamp: Optional[str] = None
# ❌ Bad - Optional field without default
class Message(pydantic.BaseModel):
role: str
content: str
metadata: Optional[Dict[str, str]] # Will cause validation errors
自动数据验证
类型提示为 PythonModel 实例和加载的 PyFunc 模型启用自动验证
model = CustomModel()
# ✅ Works: Pydantic objects
input_data = [Message(role="user", content="Hello")]
result = model.predict(input_data)
# ✅ Works: Dictionaries (auto-converted to Pydantic objects)
input_data = [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello"}]
result = model.predict(input_data)
# ❌ Fails: Missing required fields
input_data = [{"role": "user"}] # Missing 'content'
model.predict(input_data) # Raises validation error
# ❌ Fails: Wrong data type
input_data = ["hello"] # Expected dict/Pydantic object
model.predict(input_data) # Raises validation error
数据转换示例
# Input: Dictionary
input_dict = {"role": "system", "content": "Hello", "metadata": {"source": "api"}}
# Automatically converted to: Message object
# Message(role="system", content="Hello", metadata={"source": "api"})
# Works for nested structures too
complex_input = {
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hi"}],
"tools": [{"name": "search", "description": "Web search"}],
"temperature": 0.5,
}
# Automatically converted to: ChatRequest object with nested Message and ToolDefinition objects
验证错误示例
# Missing required field
try:
model.predict([{"role": "system"}]) # Missing 'content'
except Exception as e:
print(e)
# Output: 1 validation error for Message
# content
# Field required [type=missing, input_value={'role': 'system'}, input_type=dict]
# Wrong data type
try:
model.predict(["hello"]) # Expected dict/object
except Exception as e:
print(e)
# Output: Failed to validate data against type hint `list[Message]`, invalid elements:
# [('hello', "Expecting example to be a dictionary or pydantic model instance...")]
验证范围
MLflow 会根据类型提示验证输入数据,但不验证模型输出。输出类型提示仅用于模型签名推断。
TypeFromExample
当您希望从输入示例自动推断类型时
from mlflow.types.type_hints import TypeFromExample
class FlexibleModel(mlflow.pyfunc.PythonModel):
def predict(self, model_input: TypeFromExample):
# Type determined by input_example at logging time
return [
item.upper() if isinstance(item, str) else str(item) for item in model_input
]
# Input example determines the expected type
with mlflow.start_run():
mlflow.pyfunc.log_model(
name="flexible_model",
python_model=FlexibleModel(),
input_example=["sample", "data"], # Expects List[str]
)
# At inference, validates against List[str] type
loaded_model = mlflow.pyfunc.load_model(model_uri)
result = loaded_model.predict(["hello", "world"]) # ✅ Works
旧版类型提示(无验证)
这些类型提示有效,但不能提供验证或模式推断
# Supported but no validation
def predict(self, model_input: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
...
def predict(self, model_input: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
...
def predict(self, model_input: scipy.sparse.csr_matrix):
...
# You must provide explicit signature or input_example
with mlflow.start_run():
mlflow.pyfunc.log_model(
name="legacy_model",
python_model=model,
input_example=sample_dataframe, # Required for legacy types
)
使用 @pyfunc 装饰器
适用于可调用函数(非类)
from mlflow.pyfunc.utils import pyfunc
@pyfunc
def predict(model_input: List[Message]) -> List[str]:
return [msg.content for msg in model_input]
# Same validation works as with PythonModel
predict([{"role": "user", "content": "Hi"}]) # ✅ Auto-converts dict to Message
predict(["hello"]) # ❌ Validation error
联合类型行为
# Union types become AnyType (no validation)
def predict(self, model_input: List[Union[str, int]]) -> List[str]:
# MLflow infers this as List[AnyType] - no validation performed
return [str(item) for item in model_input]
# Better approach: Use Pydantic discriminated unions for validation
from typing import Literal
class TextInput(pydantic.BaseModel):
type: Literal["text"] = "text"
content: str
class NumberInput(pydantic.BaseModel):
type: Literal["number"] = "number"
value: int
# Discriminated union with validation
def predict(self, model_input: List[Union[TextInput, NumberInput]]) -> List[str]:
...
使用类型提示服务模型
在服务带有类型提示的模型时,请始终在 JSON 请求中使用 inputs 键
# Start local server
mlflow models serve -m runs/<run_id>/model --env-manager local
# Correct request format
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:5000/invocations \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"inputs": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello"}]}'
# ❌ Incorrect - missing inputs wrapper
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:5000/invocations \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '[{"role": "user", "content": "Hello"}]'
部署最佳实践
输入示例验证
# Always provide input examples that match your type hints
with mlflow.start_run():
model_info = mlflow.pyfunc.log_model(
name="chat_model",
python_model=CustomModel(),
input_example=[{"role": "user", "content": "test"}], # Matches List[Message]
)
# MLflow validates the input_example against type hints at logging time
部署前测试
# Test locally first
model = CustomModel()
test_input = [{"role": "user", "content": "test"}]
# Verify validation works
try:
result = model.predict(test_input)
print("✅ Validation passed")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Validation failed: {e}")
# Test loaded model
loaded_model = mlflow.pyfunc.load_model(model_info.model_uri)
result = loaded_model.predict(test_input)
生产考量
错误处理
class RobustModel(mlflow.pyfunc.PythonModel):
def predict(self, model_input: List[Message]) -> List[str]:
try:
return [msg.content for msg in model_input]
except Exception as e:
# Log validation errors for monitoring
logger.error(f"Prediction failed: {e}")
raise
性能:类型验证开销极小,Pydantic 验证经过高度优化,您应该考虑对相似结构进行重复验证的缓存。
类型提示最佳实践
开发工作流
# ✅ Recommended pattern
class MyModel(mlflow.pyfunc.PythonModel):
def predict(self, model_input: List[MyPydanticModel]) -> List[str]:
# Clear type annotations
# Automatic validation
# Good IDE support
return [process(item) for item in model_input]
关键指南
- 为复杂数据结构使用 Pydantic 模型
- 在 Pydantic 模型中为可选字段设置默认值
- 使用类型提示时不要传递显式的
signature参数 - 始终提供与您的类型提示匹配的输入示例
- 当您需要灵活性而无需显式类型时,请使用
TypeFromExample - 在部署前进行本地验证测试
- 使用类型提示时切勿传递显式的
signature参数 - MLflow 将使用推断的签名,并在不匹配时发出警告 - 联合类型将变为 AnyType - 使用 Pydantic 鉴别联合以进行正确验证
TypeFromExample和旧版类型提示需要输入示例
数据类型和示例
- 基于列的数据类型
- 基于张量的数据类型
- 推理参数
原始类型
Python 到 MLflow 的类型映射
这些类型的用法仅支持标量定义或一维数组。不允许混合类型。
| Python 类型 | MLflow 类型 | 示例 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
str | 字符串 | "hello world" | |
int | long | 42 | 64 位整数 |
np.int32 | integer | np.int32(42) | 32 位整数 |
浮点数 | double | 3.14159 | 64 位浮点数 |
np.float32 | 浮点数 | np.float32(3.14) | 32 位浮点数 |
bool | boolean | True | |
np.bool_ | boolean | np.bool_(True) | NumPy 布尔值 |
datetime | datetime | pd.Timestamp("2023-01-01") | |
bytes | binary | b"binary data" | |
bytearray | binary | bytearray(b"data") | |
np.bytes_ | binary | np.bytes_(b"data") | NumPy 字节 |
复合类型
数组(列表/NumPy 数组)
{
"simple_list": ["a", "b", "c"],
"nested_array": [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]],
"numpy_array": np.array([1.1, 2.2, 3.3]),
}
对象(字典)
{"user_profile": {"name": "Alice", "age": 30, "preferences": ["sports", "music"]}}
可选字段
# Include None values to make fields optional
pd.DataFrame(
{
"required_field": [1, 2, 3],
"optional_field": [1.0, None, 3.0], # This becomes optional
}
)
兼容性说明
版本要求
- 数组和对象类型:要求 MLflow ≥ 2.10.0
- Spark ML 向量:要求 MLflow ≥ 2.15.0
- AnyType:要求 MLflow ≥ 2.19.0
NumPy 数据类型
张量签名支持所有 NumPy 数据类型
np.float32 # 32-bit float
np.float64 # 64-bit float (double)
np.int8 # 8-bit integer
np.int32 # 32-bit integer
np.uint8 # Unsigned 8-bit (common for images)
np.bool_ # Boolean
形状规格
使用 -1 表示可以变化的维度(通常是批量大小)
# Image batch: variable batch size, 28x28 pixels, 1 channel
TensorSpec(np.dtype(np.uint8), (-1, 28, 28, 1))
# Text embeddings: variable batch size, 768-dimensional vectors
TensorSpec(np.dtype(np.float32), (-1, 768))
# Fixed shape: exactly 10 classes
TensorSpec(np.dtype(np.float32), (10,))
常用模式
计算机视觉
# Grayscale images
TensorSpec(np.dtype(np.uint8), (-1, 28, 28, 1))
# RGB images
TensorSpec(np.dtype(np.uint8), (-1, 224, 224, 3))
# Feature maps
TensorSpec(np.dtype(np.float32), (-1, 512, 7, 7))
自然语言处理
# Token IDs
TensorSpec(np.dtype(np.int64), (-1, 512))
# Embeddings
TensorSpec(np.dtype(np.float32), (-1, 768))
# Attention masks
TensorSpec(np.dtype(np.bool_), (-1, 512))
参数规格
参数允许对模型行为进行运行时自定义
ParamSpec(
name="temperature", # Parameter name
dtype="double", # Data type
default=0.7, # Default value
shape=None, # Shape (None for scalars, (-1,) for lists)
)
支持的参数类型
参数仅限于标量或一维数组。不支持多维数组作为推理参数。
| MLflow 类型 | Python 类型 | 标量示例 | 一维数组示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
字符串 | str | "gpt-4" | ["stop1", "stop2"] |
long | int (64 位) | 100 | [100, 200, 300] |
integer | int (32 位) | 50 | [10, 20, 30] |
double | float (64 位) | 0.7 | [0.1, 0.5, 0.9] |
浮点数 | float (32 位) | 0.5 | [0.1, 0.2, 0.3] |
boolean | bool | True | [True, False, True] |
datetime | datetime | datetime.now() | [datetime1, datetime2] |
binary | bytes | b"data" | [b"data1", b"data2"] |
常用参数模式
文本生成
params_schema = ParamSchema(
[
ParamSpec("temperature", "double", 0.7),
ParamSpec("max_tokens", "long", 100),
ParamSpec("top_p", "double", 0.9),
ParamSpec("frequency_penalty", "double", 0.0),
ParamSpec("stop_sequences", "string", [], (-1,)), # List of strings
]
)
模型选择
params_schema = ParamSchema(
[
ParamSpec("model_name", "string", "default"),
ParamSpec("use_cache", "boolean", True),
ParamSpec("timeout", "long", 30),
]
)
推理时使用参数
# Model with parameters
loaded_model = mlflow.pyfunc.load_model(model_uri)
# Use default parameters
result = loaded_model.predict(input_data)
# Override specific parameters
result = loaded_model.predict(input_data, params={"temperature": 0.1, "max_tokens": 50})
签名强制执行和验证

MLflow 会在以下情况下自动根据模型签名验证输入:
- 加载为 PyFunc 模型(
mlflow.pyfunc.load_model) - 使用 MLflow 部署工具
- 通过 MLflow 的 REST API 服务模型
验证规则
输入验证
- 必需字段:必须存在,否则验证失败
- 可选字段:可以缺失而不会出错
- 额外字段:将被忽略(不传递给模型)
- 类型转换:在可能的情况下应用安全转换
参数验证
- 类型检查:参数必须与指定的类型匹配
- 形状验证:列表参数会根据正确形状进行验证
- 默认值:在未提供参数时应用
- 未知参数:会生成警告但不会失败
处理常见问题
包含缺失值的整数列
# ❌ Problem: Integer column with NaN becomes float, causing type mismatch
df = pd.DataFrame({"int_col": [1, 2, None]}) # Becomes float64
# ✅ Solution: Define as double from the start
df = pd.DataFrame({"int_col": [1.0, 2.0, None]}) # Stays float64
类型转换示例
# ✅ Safe conversions (allowed)
int → long # 32-bit to 64-bit integer
int → double # Integer to float
float → double # 32-bit to 64-bit float
# ❌ Unsafe conversions (rejected)
long → double # Potential precision loss
string → int # No automatic parsing
处理签名
- 记录带签名的模型
- 更新现有模型
- 高级签名模式
自动签名推断
最简单的方法 - 提供输入示例
import mlflow
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
# Train your model
model = RandomForestClassifier().fit(X_train, y_train)
with mlflow.start_run():
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(
model,
name="my_model",
input_example=X_train.iloc[[0]], # Signature inferred automatically
)
手动创建签名
为了获得更多控制,请显式创建签名
from mlflow.models import ModelSignature
from mlflow.types.schema import Schema, ColSpec
# Define input schema
input_schema = Schema(
[
ColSpec("double", "feature_1"),
ColSpec("string", "feature_2"),
ColSpec("long", "feature_3", required=False), # Optional
]
)
# Define output schema
output_schema = Schema([ColSpec("double", "prediction")])
# Create signature
signature = ModelSignature(inputs=input_schema, outputs=output_schema)
# Log with explicit signature
with mlflow.start_run():
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(model, name="my_model", signature=signature)
签名推断助手
在自定义工作流中使用 infer_signature
from mlflow.models import infer_signature
# Generate predictions for signature inference
predictions = model.predict(X_test)
# Infer signature from data
signature = infer_signature(X_test, predictions)
# Log with inferred signature
with mlflow.start_run():
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(model, name="my_model", signature=signature)
为已记录的模型添加签名
使用 set_signature 为现有模型添加或更新签名
from mlflow.models import set_signature, infer_signature
# Load existing model (without signature)
model_uri = "models:/<model_id>"
model = mlflow.pyfunc.load_model(model_uri)
# Create signature from test data
signature = infer_signature(X_test, model.predict(X_test))
# Apply signature to existing model
set_signature(model_uri, signature)
# Verify signature was set
from mlflow.models.model import get_model_info
assert get_model_info(model_uri).signature == signature
为注册的模型版本添加签名
对于注册的模型版本,底层工件是不可变的,因此我们需要加载模型工件并创建一个带有签名的新版本
from mlflow.client import MlflowClient
client = MlflowClient()
model_name = "my_registered_model"
model_version = 1
# Get existing model version
mv = client.get_model_version(name=model_name, version=model_version)
# Load the model, be sure to match the flavor of the original model.
# Can use a snippet like this to get the original flavor:
"""
model_info = mlflow.models.get_model_info(mv.source)
print(f"Original flavor: {list(model_info.flavors.keys())}")
"""
loaded_model = mlflow.sklearn.load_model(mv.source)
# Provide signature, e.g. via infer_signature on dataset
signature = infer_signature(X_test, predictions)
with mlflow.start_run():
model_info = mlflow.sklearn.log_model(
loaded_model,
name="my_model",
signature=signature,
)
# Create new model version with updated signature
client.create_model_version(name=model_name, source=model_info.model_uri)
注意:对于 pyfunc 模型,您需要按如下方式解包模型:
with mlflow.start_run():
model_info = mlflow.pyfunc.log_model(
python_model=loaded.unwrap_python_model(),
name="my_model",
signature=signature,
)
# Create new model version with updated signature
client.create_model_version(name=model_name, source=model_info.model_uri)
GenAI 模型签名
对于 LangChain、OpenAI 和类似模型,当您提供输入示例时,签名会自动推断
# Input example for chat model
input_example = {"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "What is machine learning?"}]}
# Optional fields example
input_example = [
{"name": "Alice", "message": "Hello"}, # name is present
{"message": "Hi there"}, # name is missing (becomes optional)
]
# Log model - signature auto-generated from input_example
with mlflow.start_run():
mlflow.langchain.log_model(
chain,
name="chat_model",
input_example=input_example, # Signature automatically inferred!
)
带参数的模型
在签名中包含推理参数 - 当同时提供输入和参数时,签名会自动推断
# Input data and parameters
input_data = "Translate to French: Hello world"
params = {"temperature": 0.3, "max_tokens": 50, "stop_sequences": [".", "!"]}
# Create signature with parameters - automatically inferred
signature = infer_signature(
input_data, model.predict(input_data), params # Include parameters in signature
)
with mlflow.start_run():
mlflow.transformers.log_model(model, name="translation_model", signature=signature)
复杂数据结构
处理嵌套对象和数组 - 签名会根据复杂的输入示例自动推断
# Complex input structure
input_example = {
"user_data": {
"id": 12345,
"preferences": ["action", "comedy"],
"metadata": {"created_date": "2023-01-01", "is_premium": True},
},
"context": {"device": "mobile", "location": None}, # Optional field
}
# Signature automatically handles nested structure when provided as input_example
with mlflow.start_run():
mlflow.pyfunc.log_model(
python_model=custom_model,
name="complex_model",
input_example=input_example, # Auto-infers complex nested schema
)
输入示例详解
输入示例除了签名推断之外,还有其他多个重要作用
输入示例的优势
- 签名推断:自动生成模型签名
- 模型验证:在记录期间验证模型是否正常工作
- 依赖项检测:帮助识别必需的包
- 文档:向开发人员展示正确的输入格式
- 部署测试:验证 REST 端点负载格式
输入示例格式
- DataFrame 示例
- 张量示例
- JSON 示例
- 带参数的示例
import pandas as pd
# Single record example
single_record = pd.DataFrame(
[{"sepal_length": 5.1, "sepal_width": 3.5, "petal_length": 1.4, "petal_width": 0.2}]
)
# Multiple records example
batch_example = pd.DataFrame(
[
{"feature_1": 1.0, "feature_2": "A"},
{"feature_1": 2.0, "feature_2": "B"},
{"feature_1": 3.0, "feature_2": "C"},
]
)
# Log model with DataFrame example
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(model, name="model", input_example=single_record)
import numpy as np
# Image batch example (MNIST-style)
image_batch = np.random.randint(0, 255, size=(3, 28, 28, 1), dtype=np.uint8)
# Multi-input dictionary
multi_input = {
"image": np.random.random((2, 224, 224, 3)),
"metadata": np.array([[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0]]),
}
# Sparse matrix example
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
sparse_example = csr_matrix([[1, 0, 2], [0, 0, 3]])
# Log model with tensor example
mlflow.tensorflow.log_model(model, name="model", input_example=image_batch)
# Dictionary example
dict_example = {
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant"},
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"},
],
"temperature": 0.7,
}
# List example
list_example = [
{"text": "First document", "category": "news"},
{"text": "Second document", "category": "sports"},
]
# Simple scalar
scalar_example = "What is the capital of France?"
# Log model with JSON example
mlflow.langchain.log_model(model, name="model", input_example=dict_example)
# Combine input data with parameters using tuple
input_data = "Translate to Spanish: Good morning"
params = {"temperature": 0.2, "max_length": 50, "do_sample": True}
# Create tuple for logging
input_example = (input_data, params)
# Log model with parameters
mlflow.transformers.log_model(
model, name="translation_model", input_example=input_example
)
# At inference time
loaded_model = mlflow.pyfunc.load_model(model_uri)
# Use default parameters
result1 = loaded_model.predict(input_data)
# Override parameters
result2 = loaded_model.predict(input_data, params={"temperature": 0.1})
模型服务和部署
服务输入示例
MLflow 会自动生成兼容服务的示例
# When you log a model with input_example
input_example = {"question": "What is MLflow?"}
with mlflow.start_run():
model_info = mlflow.pyfunc.log_model(
python_model=MyModel(), name="model", input_example=input_example
)
# MLflow creates two files:
# 1. input_example.json - Original format
# 2. serving_input_example.json - REST API format
生成的文件
| 文件 | 内容 | 目的 |
|---|---|---|
input_example.json | {"question": "What is MLflow?"} | 原始输入格式 |
serving_input_example.json | {"inputs": {"question": "What is MLflow?"}} | REST 端点格式 |
验证服务示例
在部署前测试模型
from mlflow.models.utils import load_serving_example
from mlflow.models import validate_serving_input
# Load serving example
serving_example = load_serving_example(model_info.model_uri)
# Validate it works
result = validate_serving_input(model_info.model_uri, serving_example)
print(f"Validation result: {result}")
# Test with local server
# mlflow models serve --model-uri <model_uri>
# curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
# -d '<serving_example>' https://:5000/invocations
签名沙盒和示例
通过我们的交互式示例探索签名行为
下载签名示例笔记本或直接查看示例:签名示例笔记本
快速参考示例
- 基本示例
- DataFrame 示例
- 张量示例
from mlflow.models import infer_signature
# Simple dictionary
simple_dict = {"name": "Alice", "age": 30, "active": True}
print(infer_signature(simple_dict))
# → Schema: [name: string, age: long, active: boolean]
# With optional fields
optional_fields = [
{"name": "Alice", "email": "alice@example.com"},
{"name": "Bob", "email": None}, # email becomes optional
]
print(infer_signature(optional_fields))
# → Schema: [name: string, email: string (optional)]
# Arrays and nested objects
complex_data = {
"user": {"id": 123, "tags": ["premium", "beta"]},
"scores": [0.8, 0.9, 0.7],
}
print(infer_signature(complex_data))
# → Nested schema with arrays and objects
import pandas as pd
# Basic DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(
{
"feature_1": [1.0, 2.0, 3.0],
"feature_2": ["A", "B", "C"],
"feature_3": [True, False, True],
}
)
print(infer_signature(df))
# → Column-based schema
# With missing values (creates optional columns)
df_optional = pd.DataFrame(
{"required_col": [1, 2, 3], "optional_col": [1.0, None, 3.0]} # Contains None
)
print(infer_signature(df_optional))
# → optional_col marked as optional
# Mixed data types
df_mixed = pd.DataFrame(
{
"numbers": [1, 2, 3],
"arrays": [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]], # Lists in DataFrame
"objects": [{"a": 1}, {"b": 2}, {"c": 3}], # Dicts in DataFrame
}
)
print(infer_signature(df_mixed))
# → Complex schema with Array and Object types
import numpy as np
# Simple tensor
tensor_2d = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(infer_signature(tensor_2d))
# → Tensor(int64, (-1, 3))
# Image-like tensor
image_batch = np.random.randint(0, 255, (10, 28, 28, 1), dtype=np.uint8)
print(infer_signature(image_batch))
# → Tensor(uint8, (-1, 28, 28, 1))
# Multiple tensors
multi_tensor = {
"image": np.random.random((5, 224, 224, 3)),
"mask": np.random.randint(0, 2, (5, 224, 224, 1)),
}
print(infer_signature(multi_tensor))
# → Schema with multiple tensor specs
最佳实践和提示
开发工作流
始终包含输入示例
# ✅ Good: Always provide examples
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(model, name="model", input_example=X_sample)
# ❌ Avoid: Logging without examples
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(model, name="model") # No signature or validation
测试您的签名
# Validate signature works as expected
signature = infer_signature(X_test, y_pred)
loaded_model = mlflow.pyfunc.load_model(model_uri)
# Test with your signature
try:
result = loaded_model.predict(X_test)
print("✅ Signature validation passed")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Signature issue: {e}")
性能考量
对于大型 DataFrame
# Use a representative sample for input_example
large_df = pd.DataFrame(...) # 1M+ rows
sample_df = large_df.sample(n=100, random_state=42) # Representative sample
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(model, name="model", input_example=sample_df)
对于复杂对象
# Provide minimal but representative examples
minimal_example = {
"required_field": "example_value",
"optional_field": None, # Shows field is optional
"array_field": ["sample"], # Shows it's an array
}
常见陷阱
整数处理
# ❌ Problem: Integers with NaN become floats
df = pd.DataFrame({"int_col": [1, 2, None]}) # Type becomes float64
# ✅ Solution: Use consistent types
df = pd.DataFrame({"int_col": [1.0, 2.0, None]}) # Explicit float64
嵌套结构一致性
# ❌ Problem: Inconsistent nesting
inconsistent = [
{"level1": {"level2": "value"}},
{"level1": "direct_value"}, # Different structure
]
# ✅ Solution: Consistent structure
consistent = [
{"level1": {"level2": "value1"}},
{"level1": {"level2": "value2"}}, # Same structure
]
PythonModel 的类型提示(MLflow 2.20.0+)
from typing import Dict, List
class TypedModel(mlflow.pyfunc.PythonModel):
def predict(self, context, model_input: List[Dict[str, str]]) -> List[str]:
# Signature automatically inferred from type hints!
return [item["text"].upper() for item in model_input]
故障排除
常见错误消息
"缺少必需的输入字段"
当模型需要一个输入数据中不存在的必需字段时,会发生此错误。
# Example: Model expects field "age" but input only has "name"
input_data = {"name": "Alice"} # Missing required "age" field
解决方案: 在输入数据中包含所有必需字段,或通过在输入示例中包含 None 值将字段标记为可选。
"无法将类型 X 转换为类型 Y"
当您尝试传递一种类型的数据,而签名期望另一种类型时,会发生这种情况。
# Example: Trying to pass string where integer expected
input_data = {"score": "85"} # String value
# But signature expects: {"score": 85} # Integer value
解决方案: 将输入数据类型修复为与签名匹配,或者在类型更改是故意的情况下更新签名。
"张量形状不匹配"
当张量输入与签名中定义的预期形状不匹配时,会发生此错误。
# Example: Model expects shape (None, 784) but got (None, 28, 28)
input_tensor = np.random.random((10, 28, 28)) # Wrong shape
# But signature expects: (10, 784) # Flattened shape
解决方案: 将输入数据重塑为匹配预期的维度,或者在形状要求已更改的情况下更新签名。
调试签名
使用这些技术诊断与签名相关的问题
# Inspect existing model signature
from mlflow.models.model import get_model_info
model_info = get_model_info(model_uri)
print("Current signature:")
print(model_info.signature)
# Compare with inferred signature
inferred = infer_signature(your_input_data)
print("Inferred signature:")
print(inferred)
# Check compatibility
if model_info.signature != inferred:
print("⚠️ Signatures don't match - consider updating")
其他资源
- 签名示例笔记本 - 交互式示例
- 模型 API 文档 - 完整的 API 参考
- 部署指南 - 在生产环境中使用签名
- MLflow 模型格式 - 技术规范