超越 Autolog:为新 LLM 提供商添加 MLflow 追踪
在本文中,我们将通过为 Ollama Python SDK 的 chat 方法添加跟踪支持,展示如何为新的 LLM 提供商添加 MLflow 跟踪。
MLflow 跟踪是 MLflow 中的一项可观察性工具,可以捕获 GenAI 应用程序和工作流的详细执行跟踪。除了单个调用的输入、输出和元数据外,MLflow 跟踪还可以捕获中间步骤,如工具调用、推理步骤、检索步骤或其他自定义步骤。
MLflow 为许多流行的 LLM 提供商和编排框架提供了内置跟踪支持。如果您使用的是这些提供商之一,只需一行代码即可启用跟踪:mlflow.<provider>.autolog()。虽然 MLflow 的自动日志记录功能涵盖了许多最广泛使用的 LLM 提供商和编排框架,但有时您可能需要为不受支持的提供商添加跟踪,或者进行自动日志记录无法提供的自定义跟踪。本文将通过以下方式演示 MLflow 跟踪的灵活性和可扩展性:
- 为不受支持的提供商(Ollama Python SDK)添加基本的跟踪支持
- 展示如何捕获简单的完成和更复杂的工具调用工作流
- 说明如何通过最小的代码更改来添加跟踪
我们将使用Ollama Python SDK,这是一个开源的 Python SDK,用于Ollama LLM 平台,作为我们的示例。我们将逐步完成整个过程,展示如何通过 MLflow 跟踪捕获关键信息,同时保持与提供商 SDK 的干净集成。请注意,MLflow 确实支持 Ollama 的自动日志记录,但目前仅通过 OpenAI 客户端使用,而不是直接使用 Ollama Python SDK。
为新提供商添加 MLflow 跟踪:通用原则
MLflow 文档有一个出色的指南,介绍如何为 MLflow 跟踪做出贡献。虽然在本示例中我们不直接为 MLflow 本身做出贡献,但我们将遵循相同的通用原则。
本文假设您对 MLflow 跟踪是什么以及它是如何工作的有基本了解。如果您只是在学习,或者需要复习,请查看跟踪概念指南。
为新提供商添加跟踪涉及几个关键考虑因素
-
了解提供商的关键功能:我们首先需要了解需要跟踪哪些 API 方法才能获得我们想要的跟踪信息。对于 LLM 推理提供商,这通常涉及诸如聊天完成、工具调用或嵌入生成等操作。在编排框架中,这可能涉及诸如检索、推理、路由或各种自定义步骤等操作。在我们的 Ollama 示例中,我们将重点关注聊天完成 API。此步骤因提供商而异。
-
将操作映射到 span:MLflow 跟踪使用不同的span 类型来表示不同类型的操作。您可以在此处找到内置 span 类型的描述。不同的 span 类型在 MLflow UI 中的显示方式不同,并且可以启用特定功能。在 span 中,我们还希望将提供商的输入和输出映射到 MLflow 期望的格式。MLflow 提供用于记录聊天和工具输入和输出的实用程序,这些内容随后将在 MLflow UI 中显示为格式化的消息。
在为新提供商添加跟踪时,我们的主要任务是将提供商的 API 方法映射到具有适当 span 类型的 MLflow 跟踪 span。
-
结构化和保留关键数据:对于我们想要跟踪的每个操作,我们需要确定我们想要保留的关键信息,并确保它以有用的方式被捕获和显示。例如,我们可能希望捕获控制操作行为的输入和配置数据,解释结果的输出和元数据,过早终止操作的错误等。查看类似提供商的跟踪和跟踪实现可以为如何结构化和保留这些数据提供一个良好的起点。
为 Ollama Python SDK 添加跟踪
现在我们对为新提供商添加跟踪的关键步骤有了高层次的了解,让我们逐步完成该过程,并为 Ollama Python SDK 添加跟踪。
步骤 1:安装和测试 Ollama Python SDK
首先,我们需要安装 Ollama Python SDK,并找出在添加跟踪支持时需要关注的方法。您可以使用 pip install ollama-python 安装 Ollama Python SDK。
如果您使用过 OpenAI Python SDK,Ollama Python SDK 将会非常熟悉。以下是它如何用于进行聊天完成调用
from ollama import chat
from rich import print
response = chat(model="llama3.2",
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": "Briefly describe the components of an MLflow model"}
]
)
print(response)
这将返回
ChatResponse(
model='llama3.2',
created_at='2025-01-30T15:57:39.097119Z',
done=True,
done_reason='stop',
total_duration=7687553708,
load_duration=823704250,
prompt_eval_count=35,
prompt_eval_duration=3414000000,
eval_count=215,
eval_duration=3447000000,
message=Message(
role='assistant',
content="In MLflow, a model consists of several key components:\n\n1. **Model Registry**: A centralized
storage for models, containing metadata such as the model's name, version, and description.\n2. **Model Version**:
A specific iteration of a model, represented by a unique version number. This can be thought of as a snapshot of
the model at a particular point in time.\n3. **Model Artifacts**: The actual model code, parameters, and data used
to train the model. These artifacts are stored in the Model Registry and can be easily deployed or reused.\n4.
**Experiment**: A collection of runs that use the same hyperparameters and model version to train and evaluate a
model. Experiments help track progress, provide reproducibility, and facilitate collaboration.\n5. **Run**: An
individual instance of training or testing a model using a specific experiment. Runs capture the output of each
run, including metrics such as accuracy, loss, and more.\n\nThese components work together to enable efficient
model management, version control, and reproducibility in machine learning workflows.",
images=None,
tool_calls=None
)
)
我们已验证 Ollama Python SDK 已设置并正常工作。我们也知道在添加跟踪支持时需要关注的方法:ollama.chat。
步骤 2:编写跟踪装饰器
我们可以通过几种方式为 Ollama 的 SDK 添加跟踪——我们可以直接修改 SDK 代码,创建一个包装器类,或者使用 Python 的方法修补功能。在本例中,我们将使用装饰器来修补 SDK 的 chat 方法。这种方法使我们能够在不修改 SDK 代码或创建其他包装器类的情况下添加跟踪,尽管它确实需要理解 Python 的装饰器模式和 MLflow 跟踪的工作原理。
import mlflow
from mlflow.entities import SpanType
from mlflow.tracing.utils import set_span_chat_messages
from functools import wraps
from ollama import chat as ollama_chat
def _get_span_type(task_name: str) -> str:
span_type_mapping = {
"chat": SpanType.CHAT_MODEL,
}
return span_type_mapping.get(task_name, SpanType.UNKNOWN)
def trace_ollama_chat(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
with mlflow.start_span(
name="ollama.chat",
span_type=_get_span_type("chat"),
) as span:
# Set model name as a span attribute
model_name = kwargs.get("model", "")
span.set_attribute("model_name", model_name)
# Log the inputs
input_messages = kwargs.get("messages", [])
span.set_inputs({
"messages": input_messages,
"model": model_name,
})
# Set input messages
set_span_chat_messages(span, input_messages)
# Make the API call
response = func(*args, **kwargs)
# Log the outputs
if hasattr(response, 'to_dict'):
output = response.to_dict()
else:
output = response
span.set_outputs(output)
output_message = response.message
# Append the output message
set_span_chat_messages(span, [{"role": output_message.role, "content": output_message.content}], append=True)
return response
return wrapper
让我们分解代码并看看它是如何工作的。
-
我们首先定义一个名为
_get_span_type的辅助函数,它将 Ollama 方法映射到 MLflow span 类型。这并非严格必要,因为我们目前只跟踪chat函数,但它展示了一个可以应用于其他方法的模式。这遵循了Anthropic 提供商的参考实现,如跟踪贡献指南中所建议的。 -
我们使用
functools.wraps定义了一个名为trace_ollama_chat的装饰器,该装饰器修补了chat函数。这里有几个关键步骤:-
我们使用
mlflow.start_span启动一个新 span。span 名称设置为 "ollama.chat",span 类型设置为_get_span_type返回的值。 -
我们使用
span.set_attribute将model_name设置为 span 的属性。这并非严格必要,因为模型名称将在输入中捕获,但它说明了如何设置 span 的任意属性。 -
我们使用
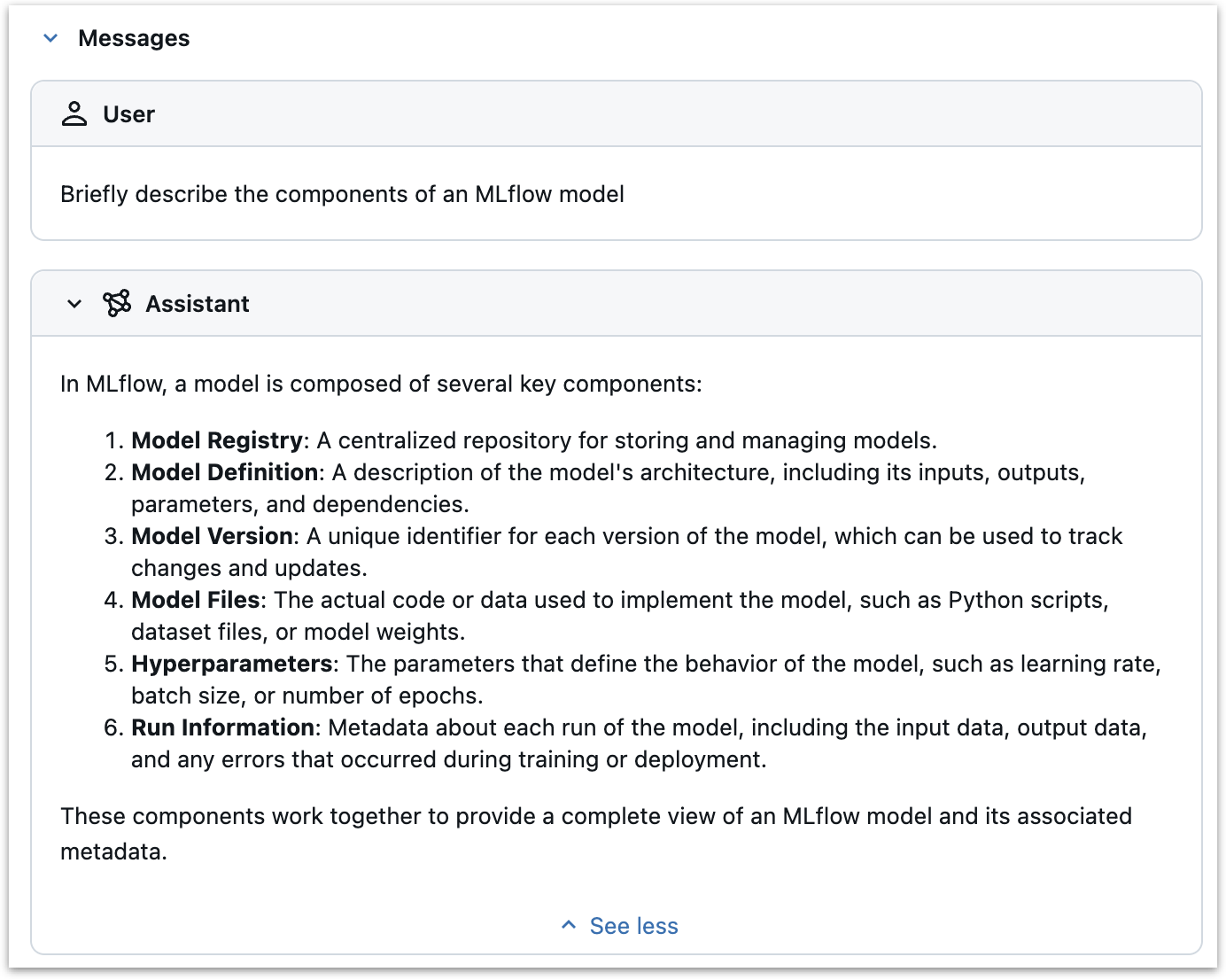
span.set_inputs将消息作为 span 的输入进行记录。我们通过访问kwargs字典从messages参数中获取这些信息。这些消息将被记录到 MLflow UI 中 span 的“inputs”部分。我们还将模型名称作为输入进行记录,再次说明如何记录任意输入。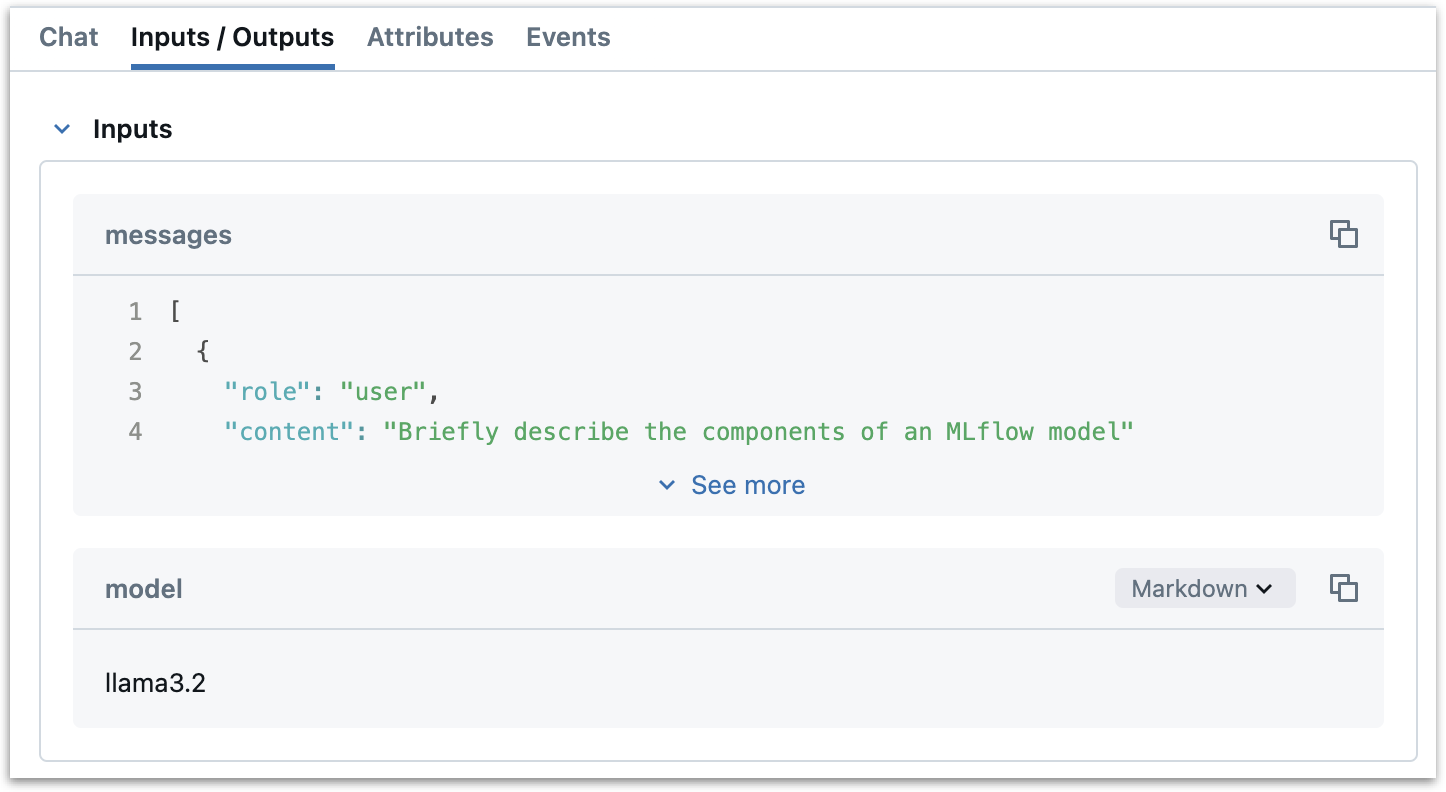
-
我们使用 MLflow 的
set_span_chat_messages实用函数来格式化输入消息,以便在 MLflow UI 的聊天面板中显示。此帮助程序确保消息得到正确格式化,并为每个消息角色显示适当的样式。 -
我们使用
func(*args, **kwargs)调用原始函数。这是 Ollamachat函数。 -
我们使用
span.set_outputs将函数的输出记录为 span 属性。这会获取 Ollama API 的响应并将其设置为 span 的属性。这些输出将被记录到 MLflow UI 中 span 的“outputs”部分。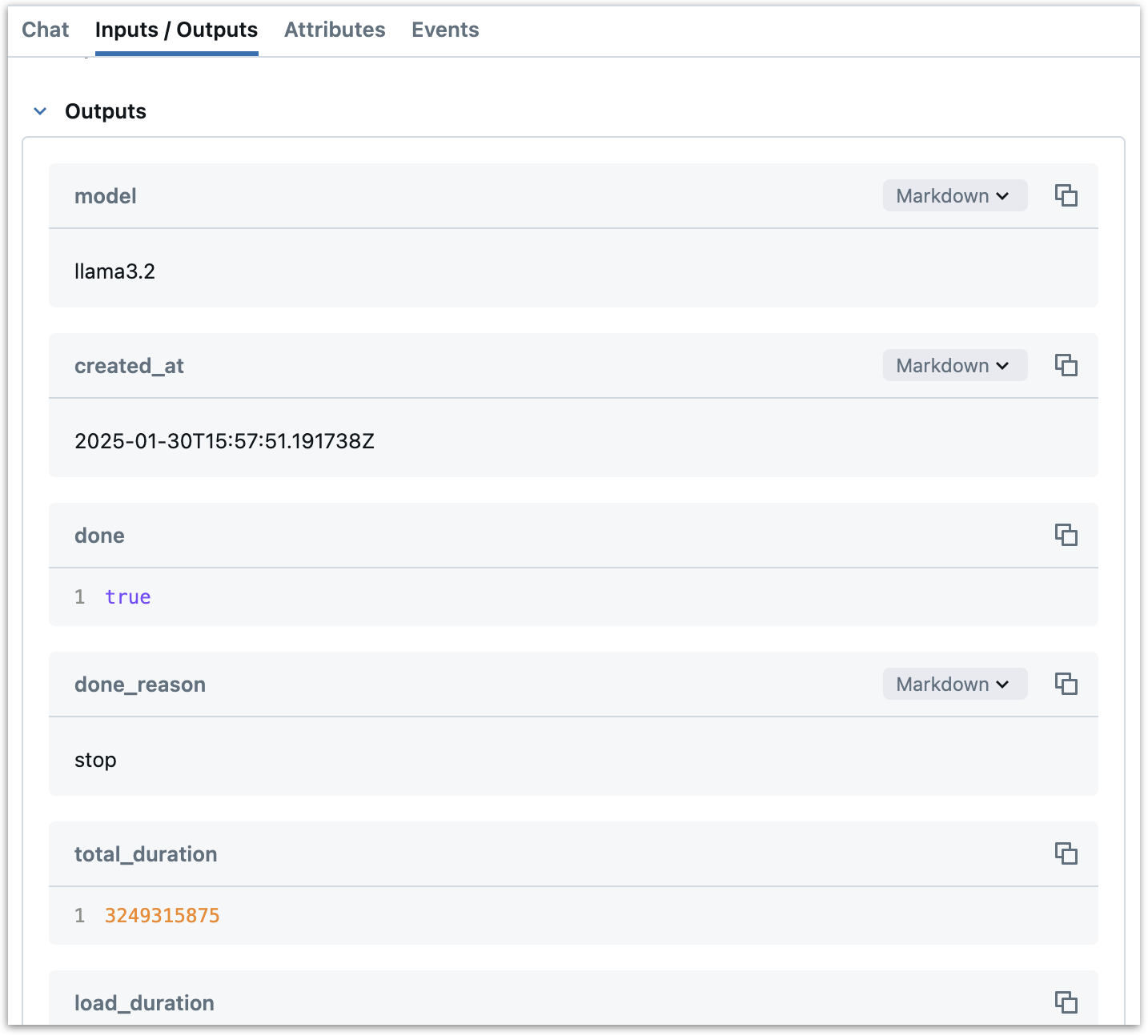
-
我们从响应中提取输出消息,并再次使用
set_span_chat_messages将其追加到聊天历史记录中,确保它出现在 MLflow UI 的聊天面板中。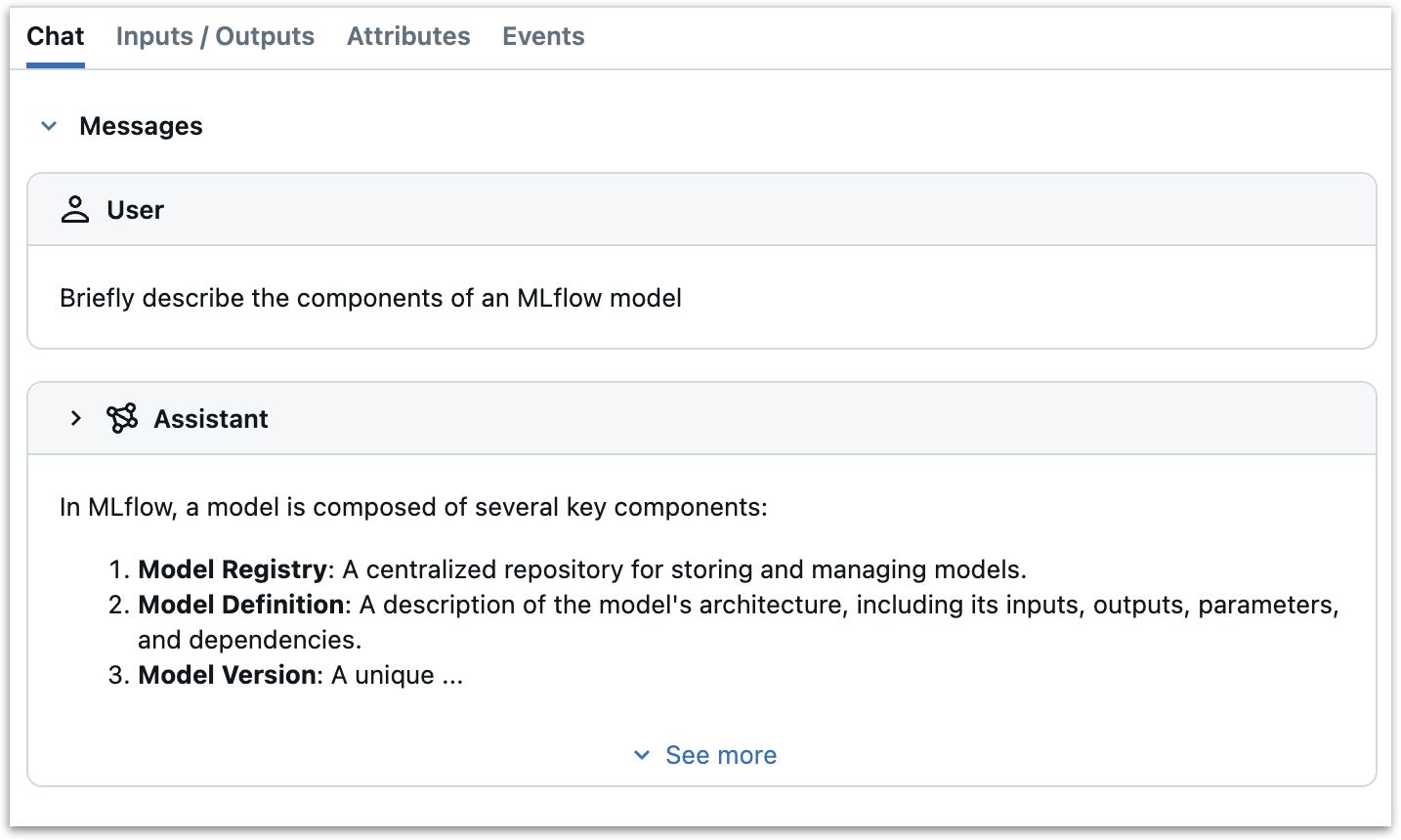
-
最后,我们返回 API 调用的响应,不做任何更改。现在,当我们使用
trace_ollama_chat修补 chat 函数时,该函数将被跟踪,但否则将正常运行。
-
有几点需要注意
- 此实现使用简单的装饰器模式,在不修改底层 Ollama SDK 代码的情况下添加跟踪。这使其成为一种轻量级且可维护的方法。
- 使用
set_span_chat_messages可确保输入和输出消息在 MLflow UI 的聊天面板中以用户友好的方式显示,从而轻松跟踪对话流程。 - 我们可以通过其他几种方式实现此跟踪行为。我们可以编写一个包装器类,或者使用一个简单的包装器函数,该函数使用
@mlflow.trace来装饰chat函数。某些编排框架可能需要更复杂的方法,例如回调或 API 钩子。有关更多详细信息,请参阅MLflow 跟踪贡献指南。
步骤 3:修补 chat 方法并进行测试
现在我们有了跟踪装饰器,我们可以修补 Ollama 的 chat 方法并进行测试。
original_chat = ollama_chat
chat = trace_ollama_chat(ollama_chat)
此代码有效地在当前范围内修补了 ollama.chat 函数。我们首先将原始函数存储在 original_chat 中以妥善保管,然后将 chat 重新分配给装饰后的版本。这意味着我们代码中任何后续对 chat() 的调用都将使用跟踪后的版本,同时保留原始功能。
现在,当我们调用 chat() 时,该方法将被跟踪,并且结果将被记录到 MLflow UI 中
mlflow.set_experiment("ollama-tracing")
response = chat(model="llama3.2",
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": "Briefly describe the components of an MLflow model"}
]
)

跟踪工具和工具调用
Ollama Python SDK 支持工具调用。我们要记录两件事:
- 可供 LLM 使用的工具
- 实际的工具调用,包括具体的工具及其传递的参数。
请注意,“工具调用”是指 LLM 指定使用哪个工具以及传递什么参数——而不是实际执行该工具。当 LLM 进行工具调用时,它实际上是在说“应使用这些参数运行此工具”,而不是自己运行该工具。工具的实际执行是单独进行的,通常在应用程序代码中。
这是跟踪代码的更新版本,修补了 Ollama 聊天方法,该版本记录了可用工具并捕获了工具调用
from mlflow.entities import SpanType
from mlflow.tracing.utils import set_span_chat_messages, set_span_chat_tools
from functools import wraps
from ollama import chat as ollama_chat
import json
from uuid import uuid4
def _get_span_type(task_name: str) -> str:
span_type_mapping = {
"chat": SpanType.CHAT_MODEL,
}
return span_type_mapping.get(task_name, SpanType.UNKNOWN)
def trace_ollama_chat(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
with mlflow.start_span(
name="ollama.chat",
span_type=_get_span_type("chat"),
) as span:
# Set model name as a span attribute
model_name = kwargs.get("model", "")
span.set_attribute("model_name", model_name)
# Log the inputs
input_messages = kwargs.get("messages", [])
tools = kwargs.get("tools", [])
span.set_inputs({
"messages": input_messages,
"model": model_name,
"tools": tools,
})
# Set input messages and tools
set_span_chat_messages(span, input_messages)
if tools:
set_span_chat_tools(span, tools)
# Make the API call
response = func(*args, **kwargs)
# Log the outputs
if hasattr(response, "to_dict"):
output = response.to_dict()
else:
output = response
span.set_outputs(output)
output_message = response.message
# Prepare the output message for span
output_span_message = {
"role": output_message.role,
"content": output_message.content,
}
# Handle tool calls if present
if output_message.tool_calls:
tool_calls = []
for tool_call in output_message.tool_calls:
tool_calls.append({
"id": str(uuid4()),
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": tool_call.function.name,
"arguments": json.dumps(tool_call.function.arguments),
}
})
output_span_message["tool_calls"] = tool_calls
# Append the output message
set_span_chat_messages(span, [output_span_message], append=True)
return response
return wrapper
这里的关键更改是:
- 我们使用
tools = kwargs.get("tools", [])从tools参数中提取了可用工具列表,将它们记录为输入,并使用set_span_chat_tools来捕获它们以包含在聊天面板中。 - 我们添加了对输出消息中工具调用的特定处理,确保按照ToolCall规范对其进行格式化。
现在让我们用一个简单的提示计算工具来测试这一点。工具是根据OpenAI 规范定义的,用于工具调用。
chat = trace_ollama_chat(ollama_chat)
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "calculate_tip",
"description": "Calculate the tip amount based on the bill amount and tip percentage",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"bill_amount": {
"type": "number",
"description": "The total bill amount"
},
"tip_percentage": {
"type": "number",
"description": "The percentage of the bill to be given as a tip, given as a whole number."
}
},
"required": ["bill_amount", "tip_percentage"]
}
}
}
]
response = chat(
model="llama3.2",
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "What is the tip for a $187.32 bill with a 22% tip?"}
],
tools=tools,
)
我们可以检查 MLflow UI 中的跟踪,现在显示了可用工具和工具调用的结果
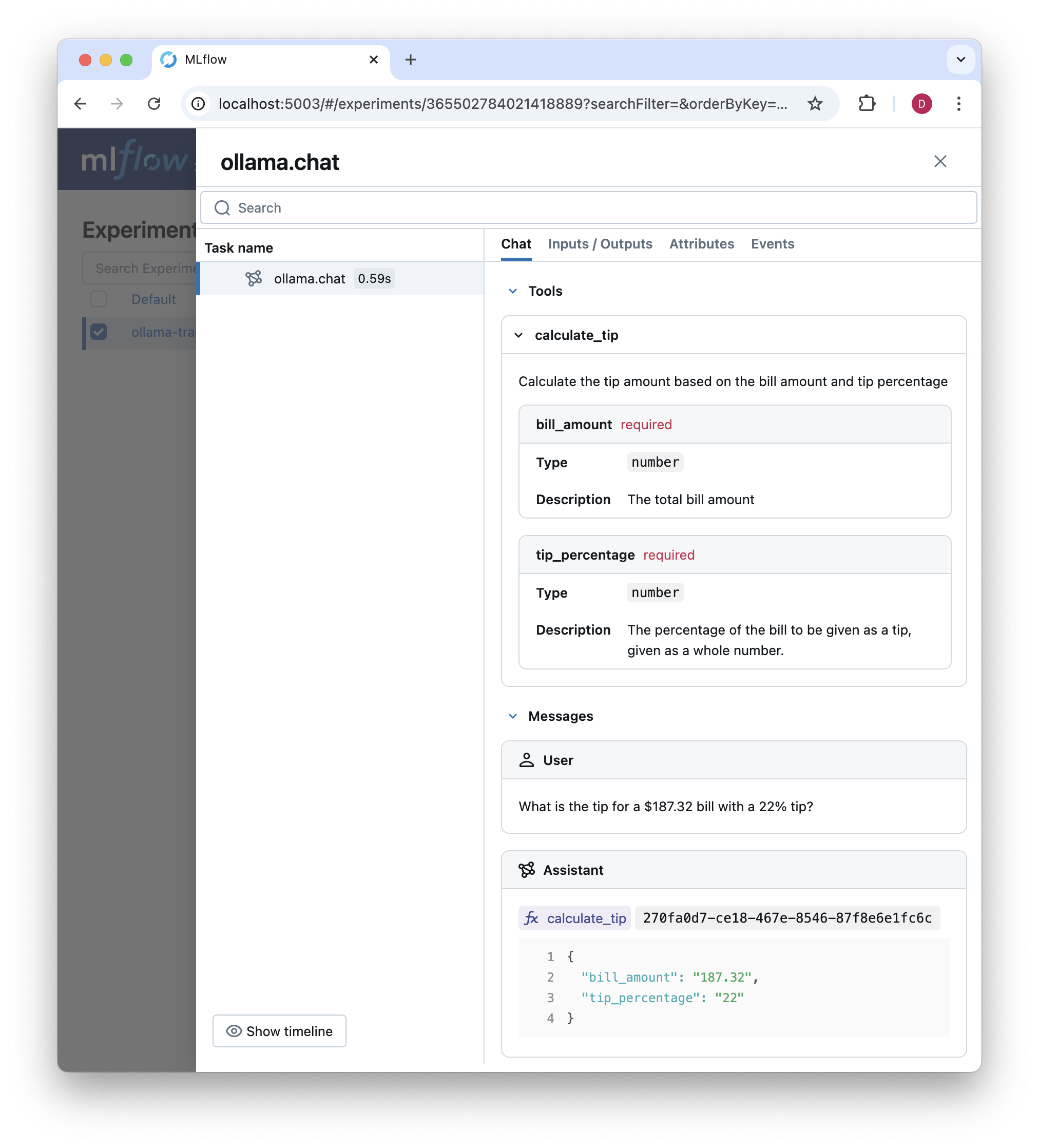
编排:构建工具调用循环
到目前为止,Ollama 示例在每次进行聊天完成时只会生成一个 span。但许多 GenAI 应用程序包含多个 LLM 调用、检索步骤、工具执行和其他自定义步骤。虽然我们在这里不会详细介绍如何为编排框架添加跟踪,但我们将通过定义一个基于我们之前定义的工具的工具调用循环来阐明一些关键概念。
工具调用循环将遵循以下模式:
- 将用户提示作为输入
- 响应工具调用或多个工具调用
- 对于每个工具调用,执行该工具并存储结果
- 将工具调用结果追加到具有
tool角色的消息历史记录中 - 使用工具调用结果再次调用 LLM,提示它为用户的提示提供最终答案
这是实现了一个工具调用的版本。
class ToolExecutor:
def __init__(self):
self.tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "calculate_tip",
"description": "Calculate the tip amount based on the bill amount and tip percentage",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"bill_amount": {
"type": "number",
"description": "The total bill amount"
},
"tip_percentage": {
"type": "number",
"description": "The percentage of the bill to be given as a tip, represented as a whole number."
}
},
"required": ["bill_amount", "tip_percentage"]
}
}
}
]
# Map tool names to their Python implementations
self.tool_implementations = {
"calculate_tip": self._calculate_tip
}
def _calculate_tip(self, bill_amount: float, tip_percentage: float) -> float:
"""Calculate the tip amount based on the bill amount and tip percentage."""
bill_amount = float(bill_amount)
tip_percentage = float(tip_percentage)
return round(bill_amount * (tip_percentage / 100), 2)
def execute_tool_calling_loop(self, messages):
"""Execute a complete tool calling loop with tracing."""
with mlflow.start_span(
name="ToolCallingLoop",
span_type="CHAIN",
) as parent_span:
# Set initial inputs
parent_span.set_inputs({
"initial_messages": messages,
"available_tools": self.tools
})
# Set input messages
set_span_chat_messages(parent_span, messages)
# First LLM call (already traced by our chat method patch)
response = chat(
messages=messages,
model="llama3.2",
tools=self.tools,
)
messages.append(response.message)
tool_calls = response.message.tool_calls
tool_results = []
# Execute tool calls
for tool_call in tool_calls:
with mlflow.start_span(
name=f"ToolExecution_{tool_call.function.name}",
span_type="TOOL",
) as tool_span:
# Parse tool inputs
tool_inputs = tool_call.function.arguments
tool_span.set_inputs(tool_inputs)
# Execute tool
func = self.tool_implementations.get(tool_call.function.name)
if func is None:
raise ValueError(f"No implementation for tool: {tool_call.function.name}")
result = func(**tool_inputs)
tool_span.set_outputs({"result": result})
tool_results.append({
"tool_call_id": str(uuid4()),
"output": str(result)
})
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": str(uuid4()),
"content": str(result)
})
# Prepare messages for final response
messages.append({
"role": "user",
"content": "Answer the initial question based on the tool call results. Do not refer to the tool call results in your response. Just give a direct answer."
})
# Final LLM call (already traced by our chat method patch)
final_response = chat(
messages=messages,
model="llama3.2"
)
# Set the final output for the parent span
parent_span.set_outputs({
"final_response": final_response.message.content,
"tool_results": tool_results
})
print(final_response)
# set output messages
set_span_chat_messages(parent_span, [final_response.message.model_dump()], append=True)
return final_response
这是我们在此工具调用循环中处理跟踪的方式:
- 我们首先使用
mlflow.start_span为工具调用循环设置一个父 span。我们将 span 名称设置为 "ToolCallingLoop",span 类型设置为 "CHAIN",表示一系列操作。 - 我们将初始消息和可用工具作为输入记录到 span 中。这有助于将来的调试,使我们能够验证工具是否可用并正确配置。
- 我们使用经过修补的
chat函数进行第一次 LLM 调用。此调用已通过我们的装饰器进行跟踪,因此我们无需执行任何特殊操作即可跟踪它。 - 我们遍历工具调用,执行每个工具并存储结果。每个工具执行都通过一个名为工具函数名称的新 span 进行跟踪。输入和输出作为 span 的属性进行记录。
- 我们将工具调用结果追加到具有
tool角色的消息历史记录中。这使得 LLM 能够在后续请求中看到工具调用的结果。它还使我们能够在 MLflow UI 中看到工具调用的结果。 - 我们为最终响应准备消息,包括一个提示,要求根据工具调用结果回答初始问题。
- 我们使用经过修补的
chat函数进行最终 LLM 调用。同样,因为我们使用的是经过修补的函数,所以此调用已经被跟踪。 - 我们为父 span 设置最终输出,包括 LLM 的最终响应和工具结果。
- 最后,我们使用
set_span_chat_messages将最终响应追加到 MLflow UI 的聊天历史记录中。请注意,为了保持简洁,我们仅使用set_span_chat_messages将用户的初始查询和最终响应记录到父 span。我们可以单击嵌套 span 来查看工具调用结果和其他详细信息。
此过程创建了整个工具调用循环的全面跟踪,从初始请求到工具执行和最终响应。
我们可以如下执行此操作。但是,请注意,您不应该在完全了解 LLM 生成或调用的任意代码在您的系统上会做什么之前运行它。
executor = ToolExecutor()
response = executor.execute_tool_calling_loop(
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "What is the tip for a $235.32 bill with a 22% tip?"}
]
)
结果是以下跟踪

结论
本文展示了如何将 MLflow 跟踪扩展到其内置提供商支持之外。我们从一个简单的示例开始——为 Ollama Python SDK 的 chat 方法添加跟踪——并看到了如何通过轻量级的修补,我们可以捕获有关每次聊天完成的详细信息。然后,我们在该基础上构建,以跟踪更复杂的工具执行循环。
主要收获是:
- MLflow 跟踪高度可定制,可以适应没有自动日志记录的提供商。
- 添加基本的跟踪支持通常只需进行最少的代码更改。在本例中,我们修补了 Ollama Python SDK 的
chat方法,并编写了几行代码来添加跟踪支持。 - 用于简单 API 调用的相同原则可以扩展到具有多个步骤的复杂工作流。在本例中,我们跟踪了一个包含多个步骤和工具调用的工具调用循环。
