使用 GEPA 对OpenAI Agent进行系统性 Prompt 优化
Prompt engineering 对于构建可靠的 AI 系统至关重要,但它充满了挑战。手动迭代耗时,缺乏系统性的改进保证,并且经常产生不一致的结果。如果您的系统有多个不同的 Prompt,这会更加困难。为了解决这个问题,已经开发了像 GEPA 和 MIPRO 这样的自动联合 Prompt 优化算法。虽然 DSPy 在其框架内提供了这些优化技术的访问,但将其应用于其他 Agent 框架(如 OpenAI Agents SDK、LangChain 或 Pydantic AI)在过去需要大量的集成工作。
MLflow 改变了这一现状。通过 mlflow.genai.optimize_prompts,您现在可以系统地优化 Prompt,无论您使用的是哪个 Agent 框架——前提是您在 MLflow Prompt 注册表中管理您的 Prompt。
在这篇博文中,我们将演示使用 OpenAI Agent 框架在 HotpotQA 数据集上的问答任务中的完整工作流。我们将展示 GEPA 算法的自动优化如何实现了 10% 的准确率提升,但这种方法广泛适用于您正在构建的任何 GenAI 应用。

挑战:复杂问答
问答系统经常在需要跨多个信息片段进行推理的复杂查询中遇到困难。考虑 HotpotQA 数据集中的这个例子
问题:“哪家出版公司出版了《Bizarre》以及一本致力于查尔斯·福特普及的异常现象的姐妹刊物?”
上下文(10 份文档)
- 文档 1:Fortean Times 是一份英国月刊,致力于查尔斯·福特普及的异常现象……现由 Dennis Publishing Ltd. 出版。
- 文档 2:查尔斯·福特 查尔斯·霍伊·福特(1874 年 8 月 6 日 - 1932 年 5 月 3 日)是一位美国作家和研究员,他专攻异常现象……
- 文档 3:Bob Rickard 罗伯特·“鲍勃”·J·M·里克ard 是英国杂志“Fortean Times: The Journal of Strange Phenomena”的创始人兼编辑……
- 文档 4:《Bizarre》是一本英国另类杂志,于 1997 年至 2015 年出版。它由 Dennis Publishing 出版,是《Fortean Times》的姐妹刊物……
预期答案:“Dennis Publishing”
这要求 Agent
- 识别“Fortean Times”致力于查尔斯·福特普及的现象(文档 1)
- 认识到“Bizarre”由 Dennis Publishing 出版(文档 4)
- 将 Bizarre 和 Fortean Times 连接起来,表明它们是姐妹刊物(文档 4)
- 综合信息回答“Dennis Publishing”
让模型持续提供正确的格式和推理来回答此类问题并非易事。
解决方案:自动 Prompt 优化
MLflow 的 optimize_prompts 提供了一种系统的方法,使用 GEPA 优化器来提高 Prompt 质量,而不是通过试错手动迭代 Prompt。
构建 OpenAI Agent QA 系统
让我们逐步构建一个完整的问答系统,使用 OpenAI Agent 框架并用 MLflow 进行优化。
1. 设置和依赖项
首先,安装所需的包
pip install openai-agents mlflow datasets openai gepa
设置您的环境
import asyncio
import os
from typing import Any
import mlflow
from agents import Agent, Runner
from datasets import load_dataset
from mlflow.entities import Feedback
from mlflow.genai import evaluate, scorer
from mlflow.genai.optimize import GepaPromptOptimizer
from mlflow.genai.judges import CategoricalRating
# Configure MLflow
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("https://:5000")
mlflow.set_experiment("HotpotQA Optimization")
mlflow.openai.autolog()
# Avoid hanging due to the conflict between async and threading (not necessary for sync agents)
os.environ["MLFLOW_GENAI_EVAL_MAX_WORKERS"] = "1"
# If running on notebooks
import nest_asyncio
nest_asyncio.apply()
启动您的 MLflow 跟踪服务器
mlflow ui --backend-store-uri sqlite:///mlruns.db
2. 创建和注册您的基础 Prompt
从一个简单、直接的 Prompt 模板开始
prompt_template = """You are a question answering assistant. Answer questions based ONLY on the provided context.
IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS:
- For yes/no questions, answer ONLY "yes" or "no"
- Do NOT include phrases like "based on the context" or "according to the documents"
Context:
{{context}}
Question: {{question}}
Answer:"""
# Register the prompt in MLflow
base_prompt = mlflow.genai.register_prompt(
name="hotpotqa-user-prompt",
template=prompt_template,
)
MLflow Prompt 注册表提供 Prompt 的版本控制,方便跟踪更改并在需要时回滚。
3. 初始化 OpenAI Agent
设置您的 Agent。
agent = Agent(
name="HotpotQA Question Answerer",
model="gpt-4o-mini",
)
4. 创建预测函数
预测函数使用 Prompt 模板格式化上下文和问题,然后运行 Agent。
# Create a wrapper for `predict_fn` to run the agent with different prompts
def create_predict_fn(prompt_uri: str):
prompt = mlflow.genai.load_prompt(prompt_uri)
@mlflow.trace
def predict_fn(context: str, question: str) -> str:
"""Predict function that uses the agent with the MLflow prompt."""
# Use prompt.format() with template variables
user_message = prompt.format(context=context, question=question)
# Run your agent
result = asyncio.run(Runner.run(agent, user_message))
return result.final_output
return predict_fn
5. 基线评估
在优化之前,通过在验证集上评估 Agent 来建立基线。在这里,我们定义了一个简单的自定义评分器,它将系统输出与预期输出进行相等比较,但您可以使用任何评分器对象。有关更多信息,请参阅 评分器概述。
def prepare_hotpotqa_data(num_samples: int, split: str = "validation") -> list[dict]:
"""Load and prepare HotpotQA data for MLflow GenAI (evaluate/optimize)."""
print(f"\nLoading HotpotQA dataset ({split} split)...")
dataset = load_dataset("hotpot_qa", "distractor", split=split)
dataset = dataset.select(range(0, min(num_samples, len(dataset))))
data = []
for example in dataset:
# Format context from HotpotQA
context_text = "\n\n".join([
f"Document {i+1}: {title}\n{' '.join(sentences)}"
for i, (title, sentences) in enumerate(zip(example["context"]["title"], example["context"]["sentences"]))
])
data.append({
"inputs": {
"context": context_text,
"question": example["question"],
},
"expectations": {
"expected_response": example["answer"],
}
})
print(f"Prepared {len(data)} samples")
return data
# Define a scorer for exact match
@scorer
def equivalence(outputs: str, expectations: dict[str, Any]) -> Feedback:
return Feedback(
name="equivalence",
value=CategoricalRating.YES if outputs == expectations["expected_response"] else CategoricalRating.NO,
)
def run_benchmark(
prompt_uri: str,
num_samples: int,
split: str = "validation",
) -> dict:
"""Run the agent on HotpotQA benchmark using mlflow.genai.evaluate()."""
# Prepare evaluation data
eval_data = prepare_hotpotqa_data(num_samples, split)
# Create prediction function
predict_fn = create_predict_fn(prompt_uri)
# Run evaluation
print(f"\nRunning evaluation on {len(eval_data)} samples...\n")
results = evaluate(
data=eval_data,
predict_fn=predict_fn,
scorers=[equivalence],
)
# Extract metrics
accuracy = results.metrics.get("equivalence/mean", 0.0) / 100.0
return {
"accuracy": accuracy,
"metrics": results.metrics,
"results": results,
}
# Run baseline evaluation
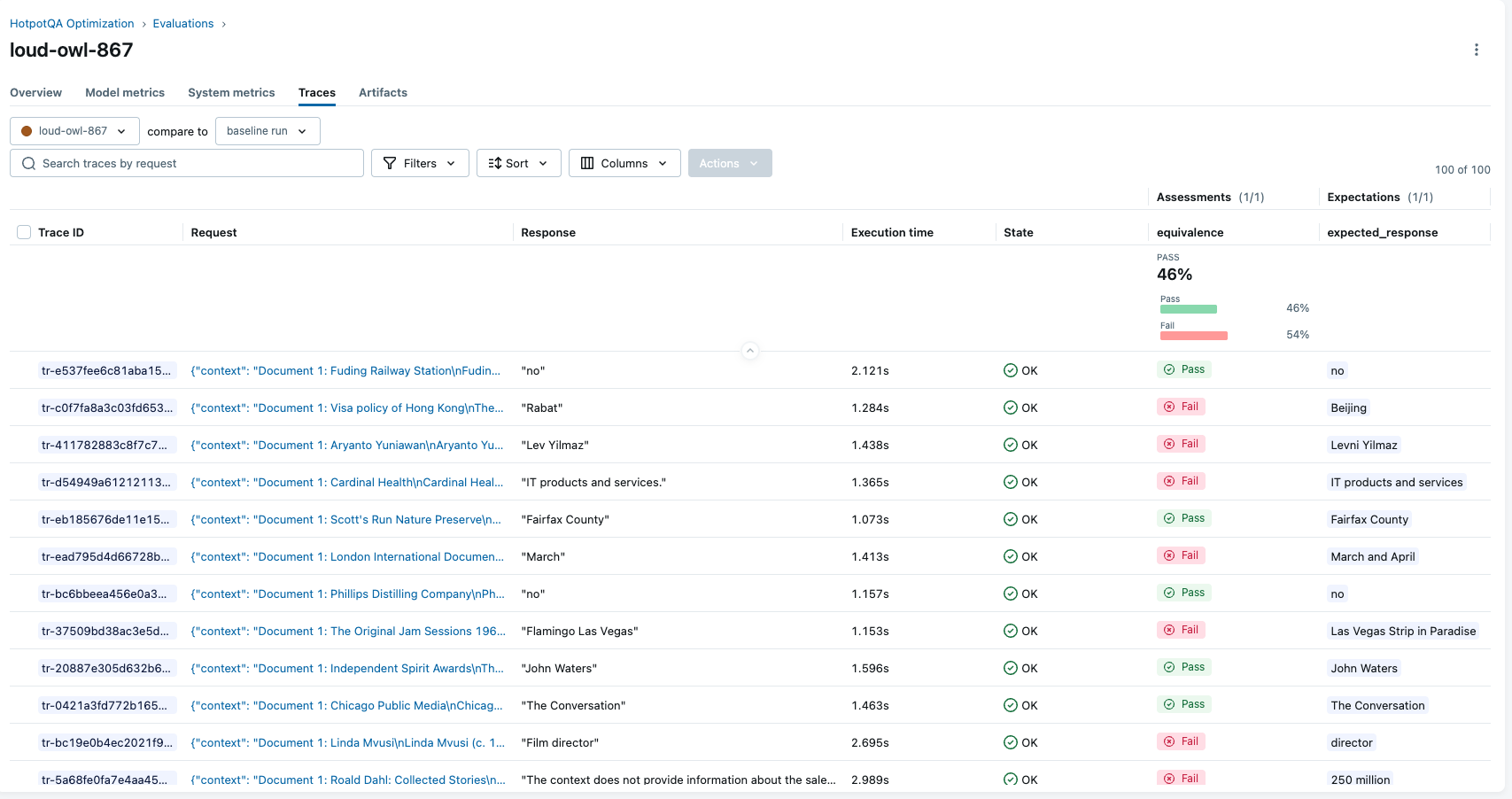
baseline_metrics = run_benchmark(base_prompt.uri, num_samples=100)
print(f"Baseline Accuracy: {baseline_metrics['accuracy']:.2%}")
# Output: Baseline Accuracy: 50.0%
6. 优化 Prompt
现在是激动人心的部分——使用 MLflow 自动改进 Prompt。
# Prepare training data using shared function
train_data = prepare_hotpotqa_data(num_samples=100, split="train")
# Run optimization
result = mlflow.genai.optimize_prompts(
predict_fn=create_predict_fn(base_prompt.uri),
train_data=train_data,
prompt_uris=[base_prompt.uri],
optimizer=GepaPromptOptimizer(
reflection_model="openai:/gpt-4o",
max_metric_calls=500,
),
scorers=[equivalence],
enable_tracking=True,
)
# Get the optimized prompt URI
optimized_prompt_uri = result.optimized_prompts[0].uri
print(f" Base prompt: {base_prompt.uri}")
print(f" Optimized prompt: {optimized_prompt_uri}")
优化过程
- 评估训练样本上的当前 Prompt
- 分析失败模式和常见问题
- 生成改进的 Prompt 变体
- 测试这些变体以找到表现最佳的
- 迭代直到达到最大指标调用次数或收敛
7. 评估优化后的 Prompt
让我们看看我们进步了多少。
# Evaluate optimized prompt on the same validation set
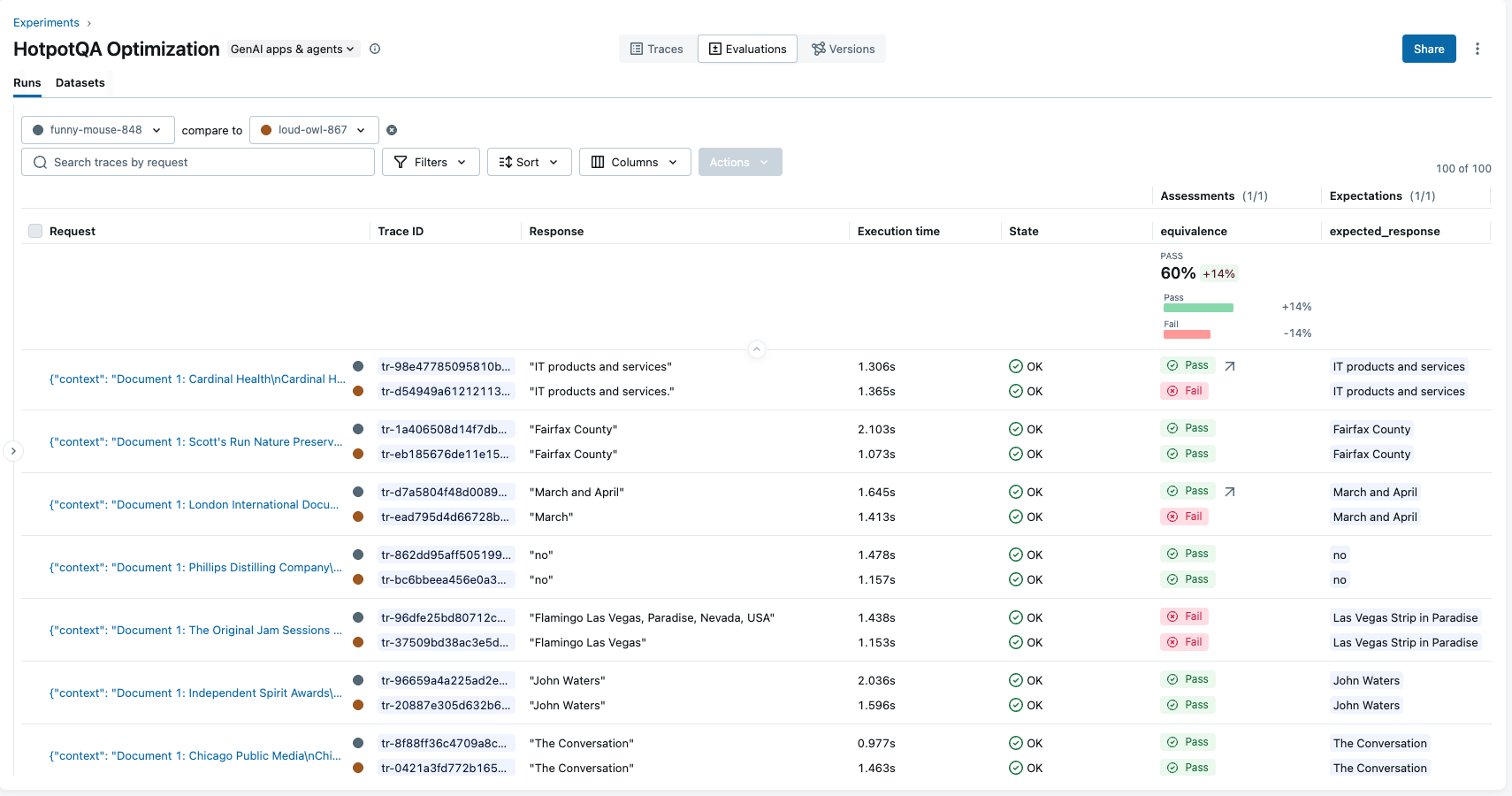
optimized_metrics = run_benchmark(optimized_prompt_uri, num_samples=100)
print(f"Optimized Accuracy: {optimized_metrics['accuracy']:.2%}")
# Output: Optimized Accuracy: 60.0%
improvement = optimized_metrics['accuracy'] - baseline_metrics['accuracy']
print(f"Improvement: {improvement:+.2%}")
# Output: Improvement: +14.0%
理解优化后的 Prompt
让我们比较一下原始 Prompt 和优化后的 Prompt。
原始 Prompt:
You are a question answering assistant. Answer questions based ONLY on the provided context.
IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS:
- For yes/no questions, answer ONLY "yes" or "no"
- Do NOT include phrases like "based on the context" or "according to the documents"
Context:
{{context}}
Question: {{question}}
Answer:
优化后的 Prompt:
You are a question answering assistant. Your job is to answer questions using ONLY the information given in the provided Context block of documents. Do not use outside knowledge.
Task and approach:
- You may need to use multi-hop reasoning across documents. Find the entity or event mentioned in one document, then retrieve the requested attribute from the relevant document, making sure all constraints in the question are satisfied.
- Always extract the minimal answer string directly from the context, preserving the original wording and formatting where applicable.
Answer type decision:
- If and only if the question is a yes/no question (starts with Is/Are/Was/Were/Do/Does/Did/Can/Could/Will/Would or is clearly answerable by yes/no), answer with exactly one word: yes or no.
- For all other questions (what/who/which/where/when/why/how/how many, etc.), provide the specific answer phrase (entity, number, date, place, etc.) from the context.
Extraction and disambiguation rules:
- Use multi-hop reasoning across documents when needed. Cross-reference facts across different documents to satisfy all constraints in the question.
- Disambiguate carefully. Pay attention to qualifiers such as nationality, profession, location, time period, roles, and other descriptors. Choose the answer that satisfies ALL constraints.
- Prefer information that directly relates to the specific instance/timeframe asked in the question if multiple similar items exist in the context.
Strict output format:
- Provide only the minimal answer string. No explanations or extra words.
- Do NOT include phrases like “based on the context” or “according to the documents”.
- Do NOT add quotes, punctuation, or extra sentences.
- Preserve capitalization and surface form exactly as it appears in the context when returning names, titles, and labeled entities.
- For measurement questions (length/width/height/distance/area/duration, etc.), return the full measurement expression exactly as it appears in the context, including units and any descriptive words such as long, wide, tall, hours, minutes (e.g., 6.213 km long).
- For dates and times, return the date/time in the exact format used in the context.
- For location-specific questions:
- If asked “which city”, return only the city name.
- If asked “which US state/country”, return only the state or country name.
- For list questions, return a concise, comma-separated list in the order supported by the context (only if the question explicitly asks for multiple items).
- If the context does not contain enough information to answer, reply with unknown (do not guess).
Guidance for multi-hop and pattern matching (use only if supported by the given context):
- Track/event length: If asked “What is the length of the track where [event] was staged?”, find the document about the event to identify the track name, then retrieve the track’s length from the track’s document, and return the exact measurement phrase (e.g., 6.213 km long).
- Film identification with constraints: If asked to identify a film by director and starring actors (e.g., “South Korean actor X starred in what 2016 movie directed by Yeon Sang-ho and starring Gong Yoo, Jung Yu-mi, and Ma Dong-seok?”), locate the film document that matches those constraints and return the exact film title as it appears.
- Geographic containment: If asked about a base located in an area of a county “in which US state?”, locate the base’s document that states the state and return only the state name.
Template:
Context:
{{context}}
Question: {{question}}
Answer:
GEPA 确定的关键改进:
GEPA 实现的改进包括:明确输出格式,使 Prompt 精确定义什么是有效答案;通过提供指示性问题词的示例来增强是/否问题的检测;通过指定信息可以跨文档组合来允许多文档推理;指示模型通过使用带头衔的全规范名称来处理名称;直接针对优化过程中发现的特定失败模式来解决显著的边缘情况;以及强制执行严格的格式保留,要求答案在拼写、大小写和格式上与上下文中的一致。
在 MLflow 中跟踪一切
在整个工作流中,MLflow 会自动跟踪
- Prompt:所有版本及其时间戳和元数据
- 运行:每次优化运行及其配置
- 指标:基线和优化后的准确率得分
- 跟踪:Agent 的详细执行跟踪
性能考量
训练时间:使用 100 个训练样本和 500 次最大指标调用进行优化大约需要 30 分钟。
可扩展性:对于生产系统,建议从较小的样本量(50-100)开始,以加快迭代速度。使用验证集来验证改进是否超出了训练数据的范围。为了提高效率和降低成本,请考虑缓存预测结果,以避免重复的 API 调用。
结论
手动 Prompt engineering 耗时且结果往往不理想。MLflow 的 optimize_prompts 提供了一种系统、数据驱动的方法来自动改进 Prompt 质量。
在我们 HotpotQA 的实验中,我们观察到优化后准确率绝对提高了 14%(从 46% 提高到 60%)。此工作流实现了系统性优化,而不是依赖于试错,并为可重现性提供了完整的实验跟踪。
OpenAI 的 Agent 框架的执行能力与 MLflow 的优化能力相结合,为构建生产级 AI 系统创造了一个强大的工作流。
进一步阅读
有疑问或遇到问题?请在 MLflow 的 GitHub Issues 上提交报告。
